[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
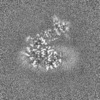
Yorodumi- EMDB-35576: Cryo-EM structure of GPI-T (inactive mutant) with GPI and proULBP... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
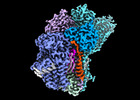
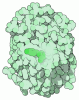
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of GPI-T (inactive mutant) with GPI and proULBP2, a proprotein substrate | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | cryo-EM / glycosylphosphatidylinositol / GPI / GPI anchored protein / GPI-AP / membrane protein complex / proprotein / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationGPI-anchor transamidase activity / attachment of GPI anchor to protein / GPI-anchor transamidase complex / GPI anchored protein biosynthesis / GPI anchor biosynthetic process / GPI anchor binding / Attachment of GPI anchor to uPAR / protein retention in ER lumen / natural killer cell lectin-like receptor binding / Transferases; Transferring nitrogenous groups; Transaminases ...GPI-anchor transamidase activity / attachment of GPI anchor to protein / GPI-anchor transamidase complex / GPI anchored protein biosynthesis / GPI anchor biosynthetic process / GPI anchor binding / Attachment of GPI anchor to uPAR / protein retention in ER lumen / natural killer cell lectin-like receptor binding / Transferases; Transferring nitrogenous groups; Transaminases / Post-translational modification: synthesis of GPI-anchored proteins / natural killer cell activation / regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-independent / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class Ib / bioluminescence / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity / neuron differentiation / neuron apoptotic process / cytoplasmic vesicle / immune response / receptor ligand activity / external side of plasma membrane / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / centrosome / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / cell surface / endoplasmic reticulum / mitochondrion / proteolysis / extracellular space / extracellular region / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Clavularia sp. (invertebrata) Clavularia sp. (invertebrata) | |||||||||
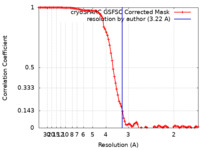
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.22 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li T / Xu Y / Qu Q / Li D | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Structures of liganded glycosylphosphatidylinositol transamidase illuminate GPI-AP biogenesis. Authors: Yidan Xu / Tingting Li / Zixuan Zhou / Jingjing Hong / Yulin Chao / Zhini Zhu / Ying Zhang / Qianhui Qu / Dianfan Li /  Abstract: Many eukaryotic receptors and enzymes rely on glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors for membrane localization and function. The transmembrane complex GPI-T recognizes diverse proproteins at a ...Many eukaryotic receptors and enzymes rely on glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors for membrane localization and function. The transmembrane complex GPI-T recognizes diverse proproteins at a signal peptide region that lacks consensus sequence and replaces it with GPI via a transamidation reaction. How GPI-T maintains broad specificity while preventing unintentional cleavage is unclear. Here, substrates- and products-bound human GPI-T structures identify subsite features that enable broad proprotein specificity, inform catalytic mechanism, and reveal a multilevel safeguard mechanism against its promiscuity. In the absence of proproteins, the catalytic site is invaded by a locally stabilized loop. Activation requires energetically unfavorable rearrangements that transform the autoinhibitory loop into crucial catalytic cleft elements. Enzyme-proprotein binding in the transmembrane and luminal domains respectively powers the conformational rearrangement and induces a competent cleft. GPI-T thus integrates various weak specificity regions to form strong selectivity and prevent accidental activation. These findings provide important mechanistic insights into GPI-anchored protein biogenesis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_35576.map.gz emd_35576.map.gz | 78.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-35576-v30.xml emd-35576-v30.xml emd-35576.xml emd-35576.xml | 38.3 KB 38.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_35576_fsc.xml emd_35576_fsc.xml | 9.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_35576.png emd_35576.png | 95.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-35576.cif.gz emd-35576.cif.gz | 10.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_35576_additional_1.map.gz emd_35576_additional_1.map.gz emd_35576_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35576_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35576_half_map_2.map.gz emd_35576_half_map_2.map.gz | 41.9 MB 77.7 MB 77.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35576 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35576 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35576 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35576 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_35576_validation.pdf.gz emd_35576_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_35576_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_35576_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_35576_validation.xml.gz emd_35576_validation.xml.gz | 17.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_35576_validation.cif.gz emd_35576_validation.cif.gz | 22.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35576 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35576 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35576 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35576 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8imyMC  8imxC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_35576.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_35576.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
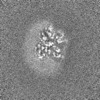
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.832 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
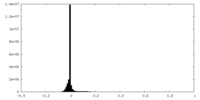
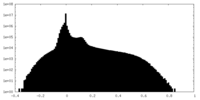
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_35576_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
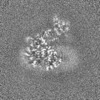
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
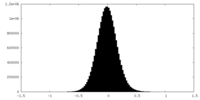
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_35576_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
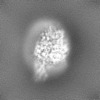
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_35576_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Complex of GPI-T (inactive mutant) with GPI and proULBP2
+Supramolecule #1: Complex of GPI-T (inactive mutant) with GPI and proULBP2
+Macromolecule #1: Glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor attachment 1 protein,GFP-like...
+Macromolecule #2: GPI-anchor transamidase,GFP-like fluorescent chromoprotein cFP484
+Macromolecule #3: Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class U protein,G...
+Macromolecule #4: GPI transamidase component PIG-T,GFP-like fluorescent chromoprote...
+Macromolecule #5: GPI transamidase component PIG-S,GFP-like fluorescent chromoprote...
+Macromolecule #6: UL16-binding protein 2
+Macromolecule #8: Digitonin
+Macromolecule #9: [(2~{R})-1-[2-azanylethoxy(oxidanyl)phosphoryl]oxy-3-hexadecanoyl...
+Macromolecule #10: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
+Macromolecule #11: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #12: 2-azanylethyl [(2~{S},3~{S},4~{S},5~{S},6~{R})-6-(hydroxymethyl)-...
+Macromolecule #13: 2-azanylethyl [(2R,3S,4S,5S,6S)-3,4,5,6-tetrakis(oxidanyl)oxan-2-...
+Macromolecule #14: CALCIUM ION
+Macromolecule #15: 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
+Macromolecule #16: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #17: [(2R)-1-[[(1S,2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-hexadecanoyloxy-3,4,5,6-tetrakis(...
+Macromolecule #18: 2-amino-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #19: [(2R)-1-hexadecanoyloxy-3-[[3-[[(2R)-3-hexadecanoyloxy-2-[(Z)-oct...
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 25 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
Details: 0.1 % Digitonin, 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0 | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 35 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.026000000000000002 kPa | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: SerialEM (ver. 3.8.0) |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 4555 / Average exposure time: 2.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 53648 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)