+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human Nav1.7 in complex with vixotrigine | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Inhibitor complex. / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationresponse to pyrethroid / corticospinal neuron axon guidance / positive regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity / action potential propagation / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception / voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / membrane depolarization during Purkinje myocyte cell action potential / cardiac conduction ...response to pyrethroid / corticospinal neuron axon guidance / positive regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity / action potential propagation / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception / voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / membrane depolarization during Purkinje myocyte cell action potential / cardiac conduction / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane depolarization during action potential / positive regulation of sodium ion transport / regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport / axon initial segment / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / node of Ranvier / voltage-gated sodium channel complex / sodium channel inhibitor activity / neuronal action potential propagation / locomotion / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / behavioral response to pain / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / intercalated disc / sodium channel regulator activity / membrane depolarization / neuronal action potential / cardiac muscle contraction / T-tubule / sensory perception of pain / axon terminus / axon guidance / sodium ion transmembrane transport / post-embryonic development / circadian rhythm / positive regulation of neuron projection development / response to toxic substance / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / nervous system development / response to heat / gene expression / chemical synaptic transmission / perikaryon / transmembrane transporter binding / cell adhesion / inflammatory response / axon / synapse / extracellular region / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wu QR / Yan N | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, China,  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Structural mapping of Na1.7 antagonists. Authors: Qiurong Wu / Jian Huang / Xiao Fan / Kan Wang / Xueqin Jin / Gaoxingyu Huang / Jiaao Li / Xiaojing Pan / Nieng Yan /   Abstract: Voltage-gated sodium (Na) channels are targeted by a number of widely used and investigational drugs for the treatment of epilepsy, arrhythmia, pain, and other disorders. Despite recent advances in ...Voltage-gated sodium (Na) channels are targeted by a number of widely used and investigational drugs for the treatment of epilepsy, arrhythmia, pain, and other disorders. Despite recent advances in structural elucidation of Na channels, the binding mode of most Na-targeting drugs remains unknown. Here we report high-resolution cryo-EM structures of human Na1.7 treated with drugs and lead compounds with representative chemical backbones at resolutions of 2.6-3.2 Å. A binding site beneath the intracellular gate (site BIG) accommodates carbamazepine, bupivacaine, and lacosamide. Unexpectedly, a second molecule of lacosamide plugs into the selectivity filter from the central cavity. Fenestrations are popular sites for various state-dependent drugs. We show that vinpocetine, a synthetic derivative of a vinca alkaloid, and hardwickiic acid, a natural product with antinociceptive effect, bind to the III-IV fenestration, while vixotrigine, an analgesic candidate, penetrates the IV-I fenestration of the pore domain. Our results permit building a 3D structural map for known drug-binding sites on Na channels summarized from the present and previous structures. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
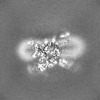
| Map data |  emd_35198.map.gz emd_35198.map.gz | 59.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-35198-v30.xml emd-35198-v30.xml emd-35198.xml emd-35198.xml | 21.1 KB 21.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_35198.png emd_35198.png | 73.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-35198.cif.gz emd-35198.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_35198_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35198_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35198_half_map_2.map.gz emd_35198_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.3 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35198 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35198 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35198 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35198 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8i5yMC  8i5bC  8i5gC  8i5xC  8j4fC  8s9bC  8s9cC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_35198.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_35198.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0825 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
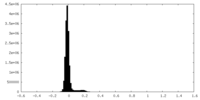
| File | emd_35198_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
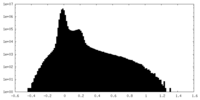
| File | emd_35198_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : human Nav1.7 in complex with vixotrigine
+Supramolecule #1: human Nav1.7 in complex with vixotrigine
+Macromolecule #1: Sodium channel protein type 9 subunit alpha
+Macromolecule #2: Sodium channel subunit beta-1
+Macromolecule #3: Sodium channel subunit beta-2
+Macromolecule #5: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #6: O-[(R)-{[(2R)-2,3-bis(octadecanoyloxy)propyl]oxy}(hydroxy)phospho...
+Macromolecule #7: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
+Macromolecule #8: (3beta,14beta,17beta,25R)-3-[4-methoxy-3-(methoxymethyl)butoxy]sp...
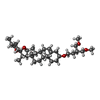
+Macromolecule #9: Vixotrigine
+Macromolecule #10: SODIUM ION
+Macromolecule #11: 1-O-OCTADECYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE
+Macromolecule #12: (2S,3R,4E)-2-(acetylamino)-3-hydroxyoctadec-4-en-1-yl dihydrogen ...
+Macromolecule #13: 1,2-DIOLEOYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE
+Macromolecule #14: water
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 535763 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)