+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
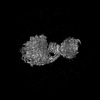
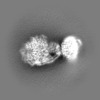
| Title | Human ATP synthase state 2 (combined) | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of cell adhesion involved in substrate-bound cell migration / Formation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / estradiol binding / angiostatin binding / ATP biosynthetic process / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / Mitochondrial protein import / cellular response to interleukin-7 / proton channel activity ...negative regulation of cell adhesion involved in substrate-bound cell migration / Formation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / estradiol binding / angiostatin binding / ATP biosynthetic process / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / Mitochondrial protein import / cellular response to interleukin-7 / proton channel activity / oxidative phosphorylation / response to copper ion / response to muscle activity / negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / proton transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to cytokine stimulus / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / MHC class I protein binding / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / mitochondrial nucleoid / positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / response to hyperoxia / cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / cellular response to nitric oxide / proton transmembrane transport / substantia nigra development / Mitochondrial protein degradation / cellular response to cAMP / aerobic respiration / regulation of intracellular pH / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / lipid metabolic process / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / ADP binding / mitochondrial membrane / fibrillar center / osteoblast differentiation / protease binding / angiogenesis / nuclear membrane / response to ethanol / mitochondrial inner membrane / membrane raft / mitochondrial matrix / hydrolase activity / lipid binding / protein-containing complex binding / structural molecule activity / cell surface / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / ATP binding / membrane / nucleus / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.77 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lai Y / Zhang Y / Liu F / Gao Y / Gong H / Rao Z | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 4 items China, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023Title: Structure of the human ATP synthase. Authors: Yuezheng Lai / Yuying Zhang / Shan Zhou / Jinxu Xu / Zhanqiang Du / Ziyan Feng / Long Yu / Ziqing Zhao / Weiwei Wang / Yanting Tang / Xiuna Yang / Luke W Guddat / Fengjiang Liu / Yan Gao / ...Authors: Yuezheng Lai / Yuying Zhang / Shan Zhou / Jinxu Xu / Zhanqiang Du / Ziyan Feng / Long Yu / Ziqing Zhao / Weiwei Wang / Yanting Tang / Xiuna Yang / Luke W Guddat / Fengjiang Liu / Yan Gao / Zihe Rao / Hongri Gong /   Abstract: Biological energy currency ATP is produced by FF-ATP synthase. However, the molecular mechanism for human ATP synthase action remains unknown. Here, we present snapshot images for three main ...Biological energy currency ATP is produced by FF-ATP synthase. However, the molecular mechanism for human ATP synthase action remains unknown. Here, we present snapshot images for three main rotational states and one substate of human ATP synthase using cryoelectron microscopy. These structures reveal that the release of ADP occurs when the β subunit of FF-ATP synthase is in the open conformation, showing how ADP binding is coordinated during synthesis. The accommodation of the symmetry mismatch between F and F motors is resolved by the torsional flexing of the entire complex, especially the γ subunit, and the rotational substep of the c subunit. Water molecules are identified in the inlet and outlet half-channels, suggesting that the proton transfer in these two half-channels proceed via a Grotthus mechanism. Clinically relevant mutations are mapped to the structure, showing that they are mainly located at the subunit-subunit interfaces, thus causing instability of the complex. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_34581.map.gz emd_34581.map.gz | 473.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-34581-v30.xml emd-34581-v30.xml emd-34581.xml emd-34581.xml | 30.7 KB 30.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_34581.png emd_34581.png | 130.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-34581.cif.gz emd-34581.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34581 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34581 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34581 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34581 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8h9tMC  8h9eC  8h9fC  8h9gC  8h9iC  8h9jC  8h9kC  8h9lC  8h9mC  8h9nC  8h9pC  8h9qC  8h9rC  8h9sC  8h9uC  8h9vC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_34581.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_34581.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.73 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
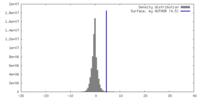
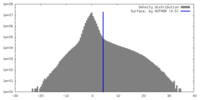
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Human ATP synthase
+Supramolecule #1: Human ATP synthase
+Macromolecule #1: ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit B1, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #2: ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #3: ATP synthase subunit d, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #4: ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C1, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #5: ATP synthase subunit delta, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #6: ATP synthase subunit epsilon, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #7: ATP synthase subunit a
+Macromolecule #8: ATP synthase subunit ATP5MJ, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #9: ATP synthase subunit f, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #10: ATP synthase subunit g, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #11: ATP synthase subunit e, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #12: ATP synthase protein 8
+Macromolecule #13: ATP synthase subunit alpha, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #14: ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #15: ATP synthase subunit gamma, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #16: ATP synthase subunit O, mitochondrial
+Macromolecule #17: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #18: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #19: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: TFS Selectris X / Energy filter - Slit width: 10 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












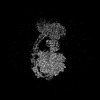


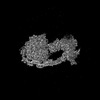

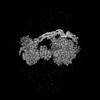





 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)