+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Lodoxamide-bound GPR35 in complex with G13 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPR35 / G13 / Lodoxamide / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationD5 dopamine receptor binding / regulation of fibroblast migration / Rho-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity / C-X-C chemokine receptor activity / chemokine-mediated signaling pathway / Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) / regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / NRAGE signals death through JNK / branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis ...D5 dopamine receptor binding / regulation of fibroblast migration / Rho-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity / C-X-C chemokine receptor activity / chemokine-mediated signaling pathway / Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) / regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / NRAGE signals death through JNK / branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis / CDC42 GTPase cycle / regulation of postsynapse assembly / Rho protein signal transduction / RAC1 GTPase cycle / cytoskeleton organization / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / brush border membrane / G protein-coupled receptor activity / platelet activation / regulation of blood pressure / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G-protein activation / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / photoreceptor disc membrane / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / G alpha (z) signalling events / melanosome / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / GPER1 signaling / G-protein beta-subunit binding / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / regulation of cell shape / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / extracellular vesicle / sensory perception of taste / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / G protein activity / retina development in camera-type eye / GTPase binding / Ca2+ pathway / fibroblast proliferation / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / G alpha (i) signalling events / G alpha (s) signalling events / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G alpha (q) signalling events / in utero embryonic development / Ras protein signal transduction / cell differentiation / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / cell population proliferation / postsynapse / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / lysosomal membrane / focal adhesion / GTPase activity / synapse / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / signal transduction / extracellular exosome / metal ion binding / nucleus / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yuan Q / Duan J / Liu Q / Xu HE / Jiang Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2022 Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2022Title: Insights into divalent cation regulation and G-coupling of orphan receptor GPR35. Authors: Jia Duan / Qiufeng Liu / Qingning Yuan / Yujie Ji / Shengnan Zhu / Yangxia Tan / Xinheng He / Youwei Xu / Jingjing Shi / Xi Cheng / Hualiang Jiang / H Eric Xu / Yi Jiang /  Abstract: Endogenous ions play important roles in the function and pharmacology of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) with limited atomic evidence. In addition, compared with G protein subtypes G, G, and G, ...Endogenous ions play important roles in the function and pharmacology of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) with limited atomic evidence. In addition, compared with G protein subtypes G, G, and G, insufficient structural evidence is accessible to understand the coupling mechanism of G protein by GPCRs. Orphan receptor GPR35, which is predominantly expressed in the gastrointestinal tract and is closely related to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), stands out as a prototypical receptor for investigating ionic modulation and G coupling. Here we report a cryo-electron microscopy structure of G-coupled GPR35 bound to an anti-allergic drug, lodoxamide. This structure reveals a novel divalent cation coordination site and a unique ionic regulatory mode of GPR35 and also presents a highly positively charged binding pocket and the complementary electrostatic ligand recognition mode, which explain the promiscuity of acidic ligand binding by GPR35. Structural comparison of the GPR35-G complex with other G protein subtypes-coupled GPCRs reveals a notable movement of the C-terminus of α5 helix of the Gα subunit towards the receptor core and the least outward displacement of the cytoplasmic end of GPR35 TM6. A featured 'methionine pocket' contributes to the G coupling by GPR35. Together, our findings provide a structural basis for divalent cation modulation, ligand recognition, and subsequent G protein coupling of GPR35 and offer a new opportunity for designing GPR35-targeted drugs for the treatment of IBDs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_34549.map.gz emd_34549.map.gz | 56.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-34549-v30.xml emd-34549-v30.xml emd-34549.xml emd-34549.xml | 19.7 KB 19.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_34549.png emd_34549.png | 38.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-34549.cif.gz emd-34549.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_34549_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34549_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34549_half_map_2.map.gz emd_34549_half_map_2.map.gz | 49.8 MB 49.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34549 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34549 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34549 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34549 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8h8jMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_34549.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_34549.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
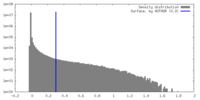
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_34549_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
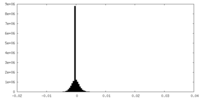
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_34549_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Lodoxamide-GPR35-G13 complex
| Entire | Name: Lodoxamide-GPR35-G13 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Lodoxamide-GPR35-G13 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Lodoxamide-GPR35-G13 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 42.423633 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGCTLSAEDK AAVERSKMID KCLSREKTYV KRLVKILLLG AGESGKSTFL KQMRIIHGQD FDQRAREEFR PTIYSNVIKG MRVLVDARE KLHIPWGDNS NQQHGDKMMS FDTRAPMAAQ GMVETRVFLQ YLPAIRALWA DSGIQNAYDR RREFQLGESV K YFLDNLDK ...String: MGCTLSAEDK AAVERSKMID KCLSREKTYV KRLVKILLLG AGESGKSTFL KQMRIIHGQD FDQRAREEFR PTIYSNVIKG MRVLVDARE KLHIPWGDNS NQQHGDKMMS FDTRAPMAAQ GMVETRVFLQ YLPAIRALWA DSGIQNAYDR RREFQLGESV K YFLDNLDK LGEPDYIPSQ QDILLARRPT KGIHEYDFEI KNVPFKMVDV GGQRSERKRW FECFDSVTSI LFLVSSSEFD QV LMEDRLT NRLTESLNIF ETIVNNRVFS NVSIILFLNK TDLLEEKVQI VSIKDYFLEF EGDPHCLRDV QKFLVECFRN KRR DQQQKP LYHHFTTAIN TENIRLVFRD VKDTILHDNL KQLMLQ UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 |
-Macromolecule #2: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.226992 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSLLQSELD QLRQEAEQLK NQIRDARKAC ADATLSQITN NIDPVGRIQM RTRRTLRGHL AKIYAMHWGT DSRLLVSASQ DGKLIIWDS YTTNKVHAIP LRSSWVMTCA YAPSGNYVAC GGLDNICSIY NLKTREGNVR VSRELAGHTG YLSCCRFLDD N QIVTSSGD ...String: MGSLLQSELD QLRQEAEQLK NQIRDARKAC ADATLSQITN NIDPVGRIQM RTRRTLRGHL AKIYAMHWGT DSRLLVSASQ DGKLIIWDS YTTNKVHAIP LRSSWVMTCA YAPSGNYVAC GGLDNICSIY NLKTREGNVR VSRELAGHTG YLSCCRFLDD N QIVTSSGD TTCALWDIET GQQTTTFTGH TGDVMSLSLA PDTRLFVSGA CDASAKLWDV REGMCRQTFT GHESDINAIC FF PNGNAFA TGSDDATCRL FDLRADQELM TYSHDNIICG ITSVSFSKSG RLLLAGYDDF NCNVWDALKA DRAGVLAGHD NRV SCLGVT DDGMAVATGS WDSFLKIWNG SSGGGGSGGG GSSGVSGWRL FKKIS UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: G-protein coupled receptor 35
| Macromolecule | Name: G-protein coupled receptor 35 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.972047 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: NGTYNTCGSS DLTWPPAIKL GFYAYLGVLL VLGLLLNSLA LWVFCCRMQQ WTETRIYMTN LAVADLCLLC TLPFVLHSLR DTSDTPLCQ LSQGIYLTNR YMSISLVTAI AVDRYVAVRH PLRARGLRSP RQAAAVCAVL WVLVIGSLVA RWLLGIQEGG F CFRSTRHN ...String: NGTYNTCGSS DLTWPPAIKL GFYAYLGVLL VLGLLLNSLA LWVFCCRMQQ WTETRIYMTN LAVADLCLLC TLPFVLHSLR DTSDTPLCQ LSQGIYLTNR YMSISLVTAI AVDRYVAVRH PLRARGLRSP RQAAAVCAVL WVLVIGSLVA RWLLGIQEGG F CFRSTRHN FNSMAFPLLG FYLPLAVVVF CSLKVVTALA QRPPTDVGQA EATRKAARMV WANLLVFVVC FLPLHVGLTV RL AVGWNAC ALLETIRRAL YITSKLSDAN CCLDAICYYY MAKEFQEASA LAVAPSAKAH KSQDSLCVTL A UniProtKB: G-protein coupled receptor 35 |
-Macromolecule #4: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 7.861143 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MASNNTASIA QARKLVEQLK MEANIDRIKV SKAAADLMAY CEAHAKEDPL LTPVPASENP FREKKFFCAI L UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 |
-Macromolecule #5: scFv16
| Macromolecule | Name: scFv16 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 26.277299 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: VQLVESGGGL VQPGGSRKLS CSASGFAFSS FGMHWVRQAP EKGLEWVAYI SSGSGTIYYA DTVKGRFTIS RDDPKNTLFL QMTSLRSED TAMYYCVRSI YYYGSSPFDF WGQGTTLTVS AGGGGSGGGG SGGGGSADIV MTQATSSVPV TPGESVSISC R SSKSLLHS ...String: VQLVESGGGL VQPGGSRKLS CSASGFAFSS FGMHWVRQAP EKGLEWVAYI SSGSGTIYYA DTVKGRFTIS RDDPKNTLFL QMTSLRSED TAMYYCVRSI YYYGSSPFDF WGQGTTLTVS AGGGGSGGGG SGGGGSADIV MTQATSSVPV TPGESVSISC R SSKSLLHS NGNTYLYWFL QRPGQSPQLL IYRMSNLASG VPDRFSGSGS GTAFTLTISR LEAEDVGVYY CMQHLEYPLT FG AGTKLEL |
-Macromolecule #6: 2,2'-[(2-chloro-5-cyano-1,3-phenylene)bis(azanediyl)]bis(oxoaceti...
| Macromolecule | Name: 2,2'-[(2-chloro-5-cyano-1,3-phenylene)bis(azanediyl)]bis(oxoacetic acid) type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: WYB |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 311.635 Da |
| Chemical component information | 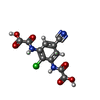 ChemComp-WYB: |
-Macromolecule #7: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #8: CHOLESTEROL
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: CLR |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 386.654 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CLR: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.04 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 591246 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)