+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
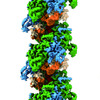
| Title | Structure of UmuD in complex with RecA filament | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SOS response / RecA / UmuD / Filament / DNA repair / Helical Reconstruction / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA COMPLEX | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationrepressor LexA / SOS response / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Serine endopeptidases / single-stranded DNA binding / DNA recombination / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / damaged DNA binding / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / hydrolase activity ...repressor LexA / SOS response / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Serine endopeptidases / single-stranded DNA binding / DNA recombination / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / damaged DNA binding / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / hydrolase activity / DNA repair / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA binding / ATP binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.31 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gao B / Feng Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis for regulation of SOS response in bacteria. Authors: Bo Gao / Liang Liang / Lu Su / Aijia Wen / Chun Zhou / Yu Feng /  Abstract: In response to DNA damage, bacterial RecA protein forms filaments with the assistance of DinI protein. The RecA filaments stimulate the autocleavage of LexA, the repressor of more than 50 SOS genes, ...In response to DNA damage, bacterial RecA protein forms filaments with the assistance of DinI protein. The RecA filaments stimulate the autocleavage of LexA, the repressor of more than 50 SOS genes, and activate the SOS response. During the late phase of SOS response, the RecA filaments stimulate the autocleavage of UmuD and λ repressor CI, leading to mutagenic repair and lytic cycle, respectively. Here, we determined the cryo-electron microscopy structures of RecA filaments in complex with DinI, LexA, UmuD, and λCI by helical reconstruction. The structures reveal that LexA and UmuD dimers bind in the filament groove and cleave in an intramolecular and an intermolecular manner, respectively, while λCI binds deeply in the filament groove as a monomer. Despite their distinct folds and oligomeric states, all RecA filament binders recognize the same conserved protein features in the filament groove. The SOS response in bacteria can lead to mutagenesis and antimicrobial resistance, and our study paves the way for rational drug design targeting the bacterial SOS response. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_34153.map.gz emd_34153.map.gz | 37.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-34153-v30.xml emd-34153-v30.xml emd-34153.xml emd-34153.xml | 16.2 KB 16.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_34153.png emd_34153.png | 537.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_34153_msk_1.map emd_34153_msk_1.map | 40.6 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-34153.cif.gz emd-34153.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_34153_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34153_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34153_half_map_2.map.gz emd_34153_half_map_2.map.gz | 31.3 MB 31.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34153 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34153 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34153 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34153 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_34153_validation.pdf.gz emd_34153_validation.pdf.gz | 957.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_34153_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_34153_full_validation.pdf.gz | 956.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_34153_validation.xml.gz emd_34153_validation.xml.gz | 11.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_34153_validation.cif.gz emd_34153_validation.cif.gz | 13 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34153 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34153 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34153 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34153 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8gmtMC  7ywaC  8gmsC  8gmuC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_34153.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 40.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_34153.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 40.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.19 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
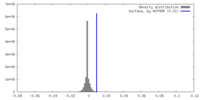
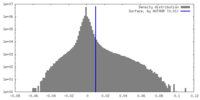
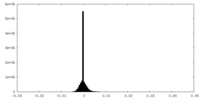
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_34153_msk_1.map emd_34153_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
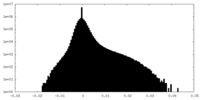
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_34153_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_34153_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RecA-UmuD complex
| Entire | Name: RecA-UmuD complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RecA-UmuD complex
| Supramolecule | Name: RecA-UmuD complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA polymerase V subunit UmuD
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA polymerase V subunit UmuD / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: repressor LexA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.017207 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MLFIKPADLR EIVTFPLFSD LVQCGFPSPA ADYVEQRIDL NQLLIQHPSA TYFVKASGDS MIDGGISDGD LLIVDSAITA SHGDIVIAA VDGEFTVAKL QLRPTVQLIP MNSAYSPITI SSEDTLDVFG VVIHVVKAMR UniProtKB: DNA polymerase V subunit UmuD |
-Macromolecule #3: Protein RecA
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein RecA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 38.016277 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAIDENKQKA LAAALGQIEK QFGKGSIMRL GEDRSMDVET ISTGSLSLDI ALGAGGLPMG RIVEIYGPES SGKTTLTLQV IAAAQREGK TCAFIDAEHA LDPIYARKLG VDIDNLLCSQ PDTGEQALEI CDALARSGAV DVIVVDSVAA LTPKAEIEGE I GDSHMGLA ...String: MAIDENKQKA LAAALGQIEK QFGKGSIMRL GEDRSMDVET ISTGSLSLDI ALGAGGLPMG RIVEIYGPES SGKTTLTLQV IAAAQREGK TCAFIDAEHA LDPIYARKLG VDIDNLLCSQ PDTGEQALEI CDALARSGAV DVIVVDSVAA LTPKAEIEGE I GDSHMGLA ARMMSQAMRK LAGNLKQSNT LLIFINQIRM KIGVMFGNPE TTTGGNALKF YASVRLDIRR IGAVKEGENV VG SETRVKV VKNKIAAPFK QAEFQILYGE GINFYGELVD LGVKEKLIEK AGAWYSYKGE KIGQGKANAT AWLKDNPETA KEI EKKVRE LLLSNPNSTP DFSVDDSEGV AETNEDF UniProtKB: Protein RecA |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA (5'-D(P*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*T)-3')
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (5'-D(P*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*T)-3') / type: dna / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.780199 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: AGS |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.247 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-AGS: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | helical array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 31.6 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 118.3 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.31 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 137040 |
|---|---|
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)