[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-32373: Cryo-EM structure of nucleosome in complex with p300 acetyltransf... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 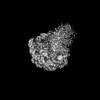 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
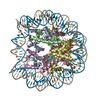
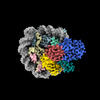
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of nucleosome in complex with p300 acetyltransferase catalytic core (complex I) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
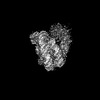
 Map data Map data | The cryo-EM map of p300-NCP complex I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | p300 / nucleosome / acetyltransferase / GENE REGULATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbehavioral defense response / negative regulation of protein oligomerization / peptidyl-lysine propionylation / histone lactyltransferase (CoA-dependent) activity / peptidyl-lysine crotonylation / peptidyl-lysine butyrylation / histone butyryltransferase activity / swimming / histone H3K122 acetyltransferase activity / peptide butyryltransferase activity ...behavioral defense response / negative regulation of protein oligomerization / peptidyl-lysine propionylation / histone lactyltransferase (CoA-dependent) activity / peptidyl-lysine crotonylation / peptidyl-lysine butyrylation / histone butyryltransferase activity / swimming / histone H3K122 acetyltransferase activity / peptide butyryltransferase activity / regulation of tubulin deacetylation / histone H2B acetyltransferase activity / internal protein amino acid acetylation / peptide 2-hydroxyisobutyryltransferase activity / histone crotonyltransferase activity / protein propionyltransferase activity / NOTCH2 intracellular domain regulates transcription / thigmotaxis / L-lysine N-acetyltransferase activity, acting on acetyl phosphate as donor / positive regulation of TORC2 signaling / internal peptidyl-lysine acetylation / histone H4 acetyltransferase activity / cellular response to L-leucine / histone H3 acetyltransferase activity / NFE2L2 regulating ER-stress associated genes / acetylation-dependent protein binding / NFE2L2 regulating inflammation associated genes / Activation of the TFAP2 (AP-2) family of transcription factors / NGF-stimulated transcription / histone H3K18 acetyltransferase activity / N-terminal peptidyl-lysine acetylation / LRR FLII-interacting protein 1 (LRRFIP1) activates type I IFN production / histone H3K27 acetyltransferase activity / NFE2L2 regulates pentose phosphate pathway genes / STAT3 nuclear events downstream of ALK signaling / NFE2L2 regulating MDR associated enzymes / Polo-like kinase mediated events / host-mediated activation of viral transcription / TGFBR3 expression / regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / regulation of mitochondrion organization / Regulation of gene expression in late stage (branching morphogenesis) pancreatic bud precursor cells / Regulation of FOXO transcriptional activity by acetylation / RUNX3 regulates NOTCH signaling / NOTCH4 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Regulation of NFE2L2 gene expression / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / Regulation of gene expression by Hypoxia-inducible Factor / face morphogenesis / platelet formation / NOTCH3 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / regulation of glycolytic process / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation / NFE2L2 regulating tumorigenic genes / NFE2L2 regulating anti-oxidant/detoxification enzymes / protein-lysine-acetyltransferase activity / megakaryocyte development / nuclear androgen receptor binding / protein acetylation / STAT family protein binding / Formation of paraxial mesoderm / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / acetyltransferase activity / acyltransferase activity / FOXO-mediated transcription of cell death genes / stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway / fat cell differentiation / Zygotic genome activation (ZGA) / PI5P Regulates TP53 Acetylation / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / histone acetyltransferase complex / RUNX3 regulates p14-ARF / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / pre-mRNA intronic binding / NF-kappaB binding / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / Attenuation phase / somitogenesis / positive regulation of T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment / cellular response to nutrient levels / histone acetyltransferase activity / skeletal muscle tissue development / : / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / histone acetyltransferase / regulation of cellular response to heat / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / NR1H3 & NR1H2 regulate gene expression linked to cholesterol transport and efflux / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / SARS-CoV-1 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Acetylation / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / : / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
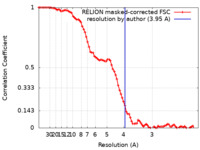
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.95 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hatazawa S / Liu J / Takizawa Y / Zandian M / Negishi L / Kutateladze TG / Kurumizaka H | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, Japan,  United States, 12 items United States, 12 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: iScience / Year: 2022 Journal: iScience / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for binding diversity of acetyltransferase p300 to the nucleosome. Authors: Suguru Hatazawa / Jiuyang Liu / Yoshimasa Takizawa / Mohamad Zandian / Lumi Negishi / Tatiana G Kutateladze / Hitoshi Kurumizaka /   Abstract: p300 is a human acetyltransferase that associates with chromatin and mediates vital cellular processes. We now report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of the p300 catalytic core in complex ...p300 is a human acetyltransferase that associates with chromatin and mediates vital cellular processes. We now report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of the p300 catalytic core in complex with the nucleosome core particle (NCP). In the most resolved structure, the HAT domain and bromodomain of p300 contact nucleosomal DNA at superhelical locations 2 and 3, and the catalytic site of the HAT domain are positioned near the N-terminal tail of histone H4. Mutations of the p300-DNA interfacial residues of p300 substantially decrease binding to NCP. Three additional classes of p300-NCP complexes show different modes of the p300-NCP complex formation. Our data provide structural details critical to our understanding of the mechanism by which p300 acetylates multiple sites on the nucleosome. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_32373.map.gz emd_32373.map.gz | 5.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-32373-v30.xml emd-32373-v30.xml emd-32373.xml emd-32373.xml | 19.5 KB 19.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_32373_fsc.xml emd_32373_fsc.xml | 8.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_32373.png emd_32373.png | 83.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-32373.cif.gz emd-32373.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32373 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32373 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32373 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32373 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 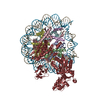 7w9vMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_32373.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_32373.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | The cryo-EM map of p300-NCP complex I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Nucleosome in complex with p300 acetyltransferase catalytic core ...
| Entire | Name: Nucleosome in complex with p300 acetyltransferase catalytic core (complex I) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Nucleosome in complex with p300 acetyltransferase catalytic core ...
| Supramolecule | Name: Nucleosome in complex with p300 acetyltransferase catalytic core (complex I) type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.305969 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: ARTKQTARKS TGGKAPRKQL ATKAARKSAP ATGGVKKPHR YRPGTVALRE IRRYQKSTEL LIRKLPFQRL VREIAQDFKT DLRFQSSAV MALQEACEAY LVGLFEDTNL CAIHAKRVTI MPKDIQLARR IRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.676703 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMSGRGKG GKGLGKGGAK RHRKVLRDNI QGITKPAIRR LARRGGVKRI SGLIYEETRG VLKVFLENVI RDAVTYTEHA KRKTVTAMD VVYALKRQGR TLYGFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1-B/E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.447825 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMSGRGKQ GGKARAKAKT RSSRAGLQFP VGRVHRLLRK GNYSERVGAG APVYLAAVLE YLTAEILELA GNAARDNKKT RIIPRHLQL AIRNDEELNK LLGRVTIAQG GVLPNIQAVL LPKKTESHHK AKGK UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1-B/E |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-J
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-J / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.217516 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMPEPAKS APAPKKGSKK AVTKAQKKDG KKRKRSRKES YSIYVYKVLK QVHPDTGISS KAMGIMNSFV NDIFERIAGE ASRLAHYNK RSTITSREIQ TAVRLLLPGE LAKHAVSEGT KAVTKYTSAK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-J |
-Macromolecule #7: Histone acetyltransferase p300
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone acetyltransferase p300 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: histone acetyltransferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 74.42657 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: TQSSPAPGQS KKKIFKPEEL RQALMPTLEA LYRQDPESLP FRQPVDPQLL GIPDYFDIVK SPMDLSTIKR KLDTGQYQEP WQYVDDIWL MFNNAWLYNR KTSRVYKYCS KLSEVFEQEI DPVMQSLGYC CGRKLEFSPQ TLCCYGKQLC TIPRDATYYS Y QNRYHFCE ...String: TQSSPAPGQS KKKIFKPEEL RQALMPTLEA LYRQDPESLP FRQPVDPQLL GIPDYFDIVK SPMDLSTIKR KLDTGQYQEP WQYVDDIWL MFNNAWLYNR KTSRVYKYCS KLSEVFEQEI DPVMQSLGYC CGRKLEFSPQ TLCCYGKQLC TIPRDATYYS Y QNRYHFCE KCFNEIQGES VSLGDDPSQP QTTINKEQFS KRKNDTLDPE LFVECTECGR KMHQICVLHH EIIWPAGFVC DG CLKKSAR TRKENKFSAK RLPSTRLGTF LENRVNDFLR RQNHPESGEV TVRVVHASDK TVEVKPGMKA RFVDSGEMAE SFP YRTKAL FAFEEIDGVD LCFFGMHVQE YGSDCPPPNQ RRVYISYLDS VHFFRPKCLR TAVYHEILIG YLEYVKKLGY TTGH IWACP PSEGDDYIFH CHPPDQKIPK PKRLQEWFKK MLDKAVSERI VHDYKDIFKQ ATEDRLTSAK ELPYFEGDFW PNVLE ESIK ESGGSGSQKL YATMEKHKEV FFVIRLIAGP AANSLPPIVD PDPLIPCDLM DGRDAFLTLA RDKHLEFSSL RRAQWS TMC MLVELHTQSQ DRFVYTCNEC KHHVETRWHC TVCEDYDLCI TCYNTKNHDH KMEKLGLGLD DESNNQQHHH HHHHH UniProtKB: Histone acetyltransferase p300, Histone acetyltransferase p300 |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (145-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (145-MER) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.520383 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DC)(DG) (DA)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA (145-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (145-MER) / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.99166 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DG) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DG) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DT) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 56.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.3000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)