+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | catalytic core of human telomerase holoenzyme | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Telomerase / REPLICATION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of hair cycle / template-free RNA nucleotidyltransferase / positive regulation of transdifferentiation / TERT-RMRP complex / DNA strand elongation / RNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / siRNA transcription / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleolus / telomerase catalytic core complex / RNA-templated DNA biosynthetic process ...positive regulation of hair cycle / template-free RNA nucleotidyltransferase / positive regulation of transdifferentiation / TERT-RMRP complex / DNA strand elongation / RNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / siRNA transcription / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleolus / telomerase catalytic core complex / RNA-templated DNA biosynthetic process / establishment of protein localization to telomere / telomerase activity / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in DNA replication, damage repair and senescence / nuclear telomere cap complex / siRNA processing / telomere maintenance via recombination / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / telomerase holoenzyme complex / telomerase RNA binding / DNA biosynthetic process / RNA-templated transcription / telomeric DNA binding / positive regulation of stem cell proliferation / mitochondrial nucleoid / negative regulation of cellular senescence / replicative senescence / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / positive regulation of protein binding / response to cadmium ion / telomere maintenance via telomerase / negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / telomere maintenance / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Meiotic synapsis / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / innate immune response in mucosa / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / positive regulation of D-glucose import / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / mitochondrion organization / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / PML body / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / regulation of protein stability / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / positive regulation of miRNA transcription / Meiotic recombination / RNA-directed DNA polymerase / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / transcription coactivator binding / Metalloprotease DUBs / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / positive regulation of angiogenesis / protein import into nucleus / HCMV Early Events / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / nucleosome / heterochromatin formation / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / protein-folding chaperone binding / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.54 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wan F / Ding Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2021Title: Zipper head mechanism of telomere synthesis by human telomerase. Authors: Futang Wan / Yongbo Ding / Yuebin Zhang / Zhenfang Wu / Shaobai Li / Lin Yang / Xiangyu Yan / Pengfei Lan / Guohui Li / Jian Wu / Ming Lei /  Abstract: Telomerase, a multi-subunit ribonucleoprotein complex, is a unique reverse transcriptase that catalyzes the processive addition of a repeat sequence to extend the telomere end using a short fragment ...Telomerase, a multi-subunit ribonucleoprotein complex, is a unique reverse transcriptase that catalyzes the processive addition of a repeat sequence to extend the telomere end using a short fragment of its own RNA component as the template. Despite recent structural characterizations of human and Tetrahymena telomerase, it is still a mystery how telomerase repeatedly uses its RNA template to synthesize telomeric DNA. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of human telomerase holoenzyme bound with telomeric DNA at resolutions of 3.5 Å and 3.9 Å for the catalytic core and biogenesis module, respectively. The structure reveals that a leucine residue Leu980 in telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) catalytic subunit functions as a zipper head to limit the length of the short primer-template duplex in the active center. Moreover, our structural and computational analyses suggest that TERT and telomerase RNA (hTR) are organized to harbor a preformed active site that can accommodate short primer-template duplex substrates for catalysis. Furthermore, our findings unveil a double-fingers architecture in TERT that ensures nucleotide addition processivity of human telomerase. We propose that the zipper head Leu980 is a structural determinant for the sequence-based pausing signal of DNA synthesis that coincides with the RNA element-based physical template boundary. Functional analyses unveil that the non-glycine zipper head plays an essential role in both telomerase repeat addition processivity and telomere length homeostasis. In addition, we also demonstrate that this zipper head mechanism is conserved in all eukaryotic telomerases. Together, our study provides an integrated model for telomerase-mediated telomere synthesis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_31811.map.gz emd_31811.map.gz | 255.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-31811-v30.xml emd-31811-v30.xml emd-31811.xml emd-31811.xml | 13.5 KB 13.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_31811.png emd_31811.png | 97 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-31811.cif.gz emd-31811.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31811 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31811 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31811 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31811 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_31811_validation.pdf.gz emd_31811_validation.pdf.gz | 446.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_31811_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_31811_full_validation.pdf.gz | 446.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_31811_validation.xml.gz emd_31811_validation.xml.gz | 7.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_31811_validation.cif.gz emd_31811_validation.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31811 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31811 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31811 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-31811 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7v99MC 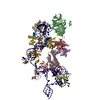 7v9aC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_31811.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 274.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_31811.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 274.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Catalytic core
| Entire | Name: Catalytic core |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Catalytic core
| Supramolecule | Name: Catalytic core / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Telomerase reverse transcriptase
| Macromolecule | Name: Telomerase reverse transcriptase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RNA-directed DNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 127.195812 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MPRAPRCRAV RSLLRSHYRE VLPLATFVRR LGPQGWRLVQ RGDPAAFRAL VAQCLVCVPW DARPPPAAPS FRQVSCLKEL VARVLQRLC ERGAKNVLAF GFALLDGARG GPPEAFTTSV RSYLPNTVTD ALRGSGAWGL LLRRVGDDVL VHLLARCALF V LVAPSCAY ...String: MPRAPRCRAV RSLLRSHYRE VLPLATFVRR LGPQGWRLVQ RGDPAAFRAL VAQCLVCVPW DARPPPAAPS FRQVSCLKEL VARVLQRLC ERGAKNVLAF GFALLDGARG GPPEAFTTSV RSYLPNTVTD ALRGSGAWGL LLRRVGDDVL VHLLARCALF V LVAPSCAY QVCGPPLYQL GAATQARPPP HASGPRRRLG CERAWNHSVR EAGVPLGLPA PGARRRGGSA SRSLPLPKRP RR GAAPEPE RTPVGQGSWA HPGRTRGPSD RGFCVVSPAR PAEEATSLEG ALSGTRHSHP SVGRQHHAGP PSTSRPPRPW DTP CPPVYA ETKHFLYSSG DKEQLRPSFL LSSLRPSLTG ARRLVETIFL GSRPWMPGTP RRLPRLPQRY WQMRPLFLEL LGNH AQCPY GVLLKTHCPL RAAVTPAAGV CAREKPQGSV AAPEEEDTDP RRLVQLLRQH SSPWQVYGFV RACLRRLVPP GLWGS RHNE RRFLRNTKKF ISLGKHAKLS LQELTWKMSV RDCAWLRRSP GVGCVPAAEH RLREEILAKF LHWLMSVYVV ELLRSF FYV TETTFQKNRL FFYRKSVWSK LQSIGIRQHL KRVQLRELSE AEVRQHREAR PALLTSRLRF IPKPDGLRPI VNMDYVV GA RTFRREKRAE RLTSRVKALF SVLNYERARR PGLLGASVLG LDDIHRAWRT FVLRVRAQDP PPELYFVKVD VTGAYDTI P QDRLTEVIAS IIKPQNTYCV RRYAVVQKAA HGHVRKAFKS HVSTLTDLQP YMRQFVAHLQ ETSPLRDAVV IEQSSSLNE ASSGLFDVFL RFMCHHAVRI RGKSYVQCQG IPQGSILSTL LCSLCYGDME NKLFAGIRRD GLLLRLVDDF LLVTPHLTHA KTFLRTLVR GVPEYGCVVN LRKTVVNFPV EDEALGGTAF VQMPAHGLFP WCGLLLDTRT LEVQSDYSSY ARTSIRASLT F NRGFKAGR NMRRKLFGVL RLKCHSLFLD LQVNSLQTVC TNIYKILLLQ AYRFHACVLQ LPFHQQVWKN PTFFLRVISD TA SLCYSIL KAKNAGMSLG AKGAAGPLPS EAVQWLCHQA FLLKLTRHRV TYVPLLGSLR TAQTQLSRKL PGTTLTALEA AAN PALPSD FKTILD UniProtKB: Telomerase reverse transcriptase |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1-B/E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.034355 KDa |
| Sequence | String: SGRGKQGGKA RAKAKTRSSR AGLQFPVGRV HRLLRKGNYS ERVGAGAPVY LAAVLEYLTA EILELAGNAA RDNKKTRIIP RHLQLAIRN DEELNKLLGR VTIAQGGVLP NIQAVLLPKK TESHHKAKGK UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1-B/E |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2B type 1-K
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-K / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.790018 KDa |
| Sequence | String: PEPAKSAPAP KKGSKKAVTK AQKKDGKKRK RSRKESYSVY VYKVLKQVHP DTGISSKAMG IMNSFVNDIF ERIAGEASRL AHYNKRSTI TSREIQTAVR LLLPGELAKH AVSEGTKAVT KYTSAK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-K |
-Macromolecule #4: Telomerase RNA component
| Macromolecule | Name: Telomerase RNA component / type: rna / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 145.477797 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GGGUUGCGGA GGGUGGGCCU GGGAGGGGUG GUGGCCAUUU UUUGUCUAAC CCUAACUGAG AAGGGCGUAG GCGCCGUGCU UUUGCUCCC CGCGCGCUGU UUUUCUCGCU GACUUUCAGC GGGCGGAAAA GCCUCGGCCU GCCGCCUUCC ACCGUUCAUU C UAGAGCAA ...String: GGGUUGCGGA GGGUGGGCCU GGGAGGGGUG GUGGCCAUUU UUUGUCUAAC CCUAACUGAG AAGGGCGUAG GCGCCGUGCU UUUGCUCCC CGCGCGCUGU UUUUCUCGCU GACUUUCAGC GGGCGGAAAA GCCUCGGCCU GCCGCCUUCC ACCGUUCAUU C UAGAGCAA ACAAAAAAUG UCAGCUGCUG GCCCGUUCGC CCCUCCCGGG GACCUGCGGC GGGUCGCCUG CCCAGCCCCC GA ACCCCGC CUGGAGGCCG CGGUCGGCCC GGGGCUUCUC CGGAGGCACC CACUGCCACC GCGAAGAGUU GGGCUCUGUC AGC CGCGGG UCUCUCGGGG GCGAGGGCGA GGUUCAGGCC UUUCAGGCCG CAGGAAGAGG AACGGAGCGA GUCCCCGCGC GCGG CGCGA UUCCCUGAGC UGUGGGACGU GCACCCAGGA CUCGGCUCAC ACAUGC GENBANK: GENBANK: U85256.1 |
-Macromolecule #5: Primer DNA
| Macromolecule | Name: Primer DNA / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 7.339724 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.9 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 62.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.54 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 297526 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: COMMON LINE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




















