[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-3094: Electron negative stain tomography of alpha-synuclein amyloid fibrils -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3094 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Electron negative stain tomography of alpha-synuclein amyloid fibrils | |||||||||
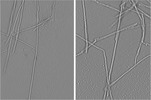
 Map data Map data | negative stain tomogram of alpha-synuclein fibrils | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | alpha-synuclein amyloid fibrils / disaggregation activity | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone / : / neutral lipid metabolic process / regulation of acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / negative regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / negative regulation of norepinephrine uptake / response to desipramine / positive regulation of SNARE complex assembly / positive regulation of hydrogen peroxide catabolic process / supramolecular fiber ...negative regulation of mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone / : / neutral lipid metabolic process / regulation of acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / negative regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / negative regulation of norepinephrine uptake / response to desipramine / positive regulation of SNARE complex assembly / positive regulation of hydrogen peroxide catabolic process / supramolecular fiber / regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling / negative regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy / mitochondrial membrane organization / regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / positive regulation of protein localization to cell periphery / negative regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of exocytosis / regulation of glutamate secretion / dopamine biosynthetic process / response to iron(II) ion / SNARE complex assembly / negative regulation of dopamine metabolic process / positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / regulation of macrophage activation / positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / regulation of locomotion / synaptic vesicle transport / negative regulation of microtubule polymerization / transporter regulator activity / synaptic vesicle priming / dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / protein kinase inhibitor activity / regulation of dopamine secretion / negative regulation of thrombin-activated receptor signaling pathway / dynein complex binding / mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / positive regulation of receptor recycling / cuprous ion binding / nuclear outer membrane / response to magnesium ion / positive regulation of exocytosis / synaptic vesicle exocytosis / positive regulation of endocytosis / kinesin binding / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / enzyme inhibitor activity / cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / response to type II interferon / negative regulation of serotonin uptake / regulation of presynapse assembly / alpha-tubulin binding / beta-tubulin binding / phospholipase binding / behavioral response to cocaine / supramolecular fiber organization / cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus / phospholipid metabolic process / axon terminus / inclusion body / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / Hsp70 protein binding / response to interleukin-1 / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to copper ion / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / SNARE binding / adult locomotory behavior / excitatory postsynaptic potential / protein tetramerization / phosphoprotein binding / microglial cell activation / ferrous iron binding / fatty acid metabolic process / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / synapse organization / PKR-mediated signaling / protein destabilization / phospholipid binding / receptor internalization / tau protein binding / long-term synaptic potentiation / terminal bouton / positive regulation of inflammatory response / synaptic vesicle membrane / actin cytoskeleton / actin binding / growth cone / cellular response to oxidative stress / neuron apoptotic process / cell cortex / histone binding / response to lipopolysaccharide / microtubule binding / chemical synaptic transmission / amyloid fibril formation / molecular adaptor activity / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / oxidoreductase activity / mitochondrial outer membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | electron tomography / negative staining | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gao X / Carroni M / Nussbaum-Krammer C / Mogk A / Nillegoda NB / Szlachcic A / Guilbride DL / Saibil HR / Mayer MP / Bukau B | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2015 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2015Title: Human Hsp70 Disaggregase Reverses Parkinson's-Linked α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils. Authors: Xuechao Gao / Marta Carroni / Carmen Nussbaum-Krammer / Axel Mogk / Nadinath B Nillegoda / Anna Szlachcic / D Lys Guilbride / Helen R Saibil / Matthias P Mayer / Bernd Bukau /   Abstract: Intracellular amyloid fibrils linked to neurodegenerative disease typically accumulate in an age-related manner, suggesting inherent cellular capacity for counteracting amyloid formation in early ...Intracellular amyloid fibrils linked to neurodegenerative disease typically accumulate in an age-related manner, suggesting inherent cellular capacity for counteracting amyloid formation in early life. Metazoan molecular chaperones assist native folding and block polymerization of amyloidogenic proteins, preempting amyloid fibril formation. Chaperone capacity for amyloid disassembly, however, is unclear. Here, we show that a specific combination of human Hsp70 disaggregase-associated chaperone components efficiently disassembles α-synuclein amyloid fibrils characteristic of Parkinson's disease in vitro. Specifically, the Hsc70 chaperone, the class B J-protein DNAJB1, and an Hsp110 family nucleotide exchange factor (NEF) provide ATP-dependent activity that disassembles amyloids within minutes via combined fibril fragmentation and depolymerization. This ultimately generates non-toxic α-synuclein monomers. Concerted, rapid interaction cycles of all three chaperone components with fibrils generate the power stroke required for disassembly. This identifies a powerful human Hsp70 disaggregase activity that efficiently disassembles amyloid fibrils and points to crucial yet undefined biology underlying amyloid-based diseases. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3094.map.gz emd_3094.map.gz | 2.3 GB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3094-v30.xml emd-3094-v30.xml emd-3094.xml emd-3094.xml | 8.9 KB 8.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-3094.png EMD-3094.png | 4.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3094 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3094 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3094 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3094 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3095C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3094.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.7 GB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS SIGNED BYTE Download / File: emd_3094.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.7 GB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS SIGNED BYTE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | negative stain tomogram of alpha-synuclein fibrils | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 3.028 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : alpha-synuclein fibrils formed in vitro
| Entire | Name: alpha-synuclein fibrils formed in vitro |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: alpha-synuclein fibrils formed in vitro
| Supramolecule | Name: alpha-synuclein fibrils formed in vitro / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: amyloid fibers / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: alpha-synuclein
| Macromolecule | Name: alpha-synuclein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Oligomeric state: amyloid fibrils / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 14 KDa / Theoretical: 14 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Alpha-synuclein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | electron tomography |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 50 mM Hepes-KOH pH 7.5, 50 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DTT, 2 mM ATP, 3 mM PEP, 20 ng/microL pyruvate kinase |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: Grids with adsorbed protein floated on 2% w/v uranyl formate for 2 minutes |
| Grid | Details: 200 mesh copper finder grids with thin carbon support glow discharged in atmosphere. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Date | Dec 7, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: OTHER / Average electron dose: 200 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: SIDE ENTRY, EUCENTRIC / Tilt series - Axis1 - Min angle: -60 ° / Tilt series - Axis1 - Max angle: 60 ° / Tilt series - Axis1 - Angle increment: 3 ° |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Software - Name:  IMOD / Number images used: 40 IMOD / Number images used: 40 |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: IMOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller