[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-30857: Human calcium sensing receptor adopts an inactive open-open confo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-30857 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
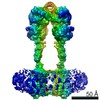
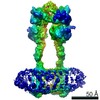
| Title | Human calcium sensing receptor adopts an inactive open-open conformation | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ling SL / Tian CL / Shi P / Liu SL / Meng XY / Liu L / Sun DM / Shi CW | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2021Title: Structural mechanism of cooperative activation of the human calcium-sensing receptor by Ca ions and L-tryptophan. Authors: Shenglong Ling / Pan Shi / Sanling Liu / Xianyu Meng / Yingxin Zhou / Wenjing Sun / Shenghai Chang / Xing Zhang / Longhua Zhang / Chaowei Shi / Demeng Sun / Lei Liu / Changlin Tian /  Abstract: The human calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a class C G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) responsible for maintaining Ca homeostasis in the blood. The general consensus is that extracellular Ca is ...The human calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a class C G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) responsible for maintaining Ca homeostasis in the blood. The general consensus is that extracellular Ca is the principal agonist of CaSR. Aliphatic and aromatic L-amino acids, such as L-Phe and L-Trp, increase the sensitivity of CaSR towards Ca and are considered allosteric activators. Crystal structures of the extracellular domain (ECD) of CaSR dimer have demonstrated Ca and L-Trp binding sites and conformational changes of the ECD upon Ca/L-Trp binding. However, it remains to be understood at the structural level how Ca/L-Trp binding to the ECD leads to conformational changes in transmembrane domains (TMDs) and consequent CaSR activation. Here, we determined the structures of full-length human CaSR in the inactive state, Ca- or L-Trp-bound states, and Ca/L-Trp-bound active state using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. Structural studies demonstrate that L-Trp binding induces the closure of the Venus flytrap (VFT) domain of CaSR, bringing the receptor into an intermediate active state. Ca binding relays the conformational changes from the VFT domains to the TMDs, consequently inducing close contact between the two TMDs of dimeric CaSR, activating the receptor. Importantly, our structural and functional studies reveal that Ca ions and L-Trp activate CaSR cooperatively. Amino acids are not able to activate CaSR alone, but can promote the receptor activation in the presence of Ca. Our data provide complementary insights into the activation of class C GPCRs and may aid in the development of novel drugs targeting CaSR. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_30857.map.gz emd_30857.map.gz | 9.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-30857-v30.xml emd-30857-v30.xml emd-30857.xml emd-30857.xml | 8.9 KB 8.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_30857.png emd_30857.png | 147.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30857 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30857 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30857 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30857 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_30857.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_30857.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human Calcium-Sensing Receptor in an inactive state
| Entire | Name: Human Calcium-Sensing Receptor in an inactive state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human Calcium-Sensing Receptor in an inactive state
| Supramolecule | Name: Human Calcium-Sensing Receptor in an inactive state / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: human calcium sensing receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: human calcium sensing receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Sequence | String: MKTIIALSYI FCLVFADYKD DDDENLYFQG YGPDQRAQKK GDIILGGLFP IHFGVAAKDQ DLKSRPESVE CIRYNFRGFR WLQAMIFAIE EINSSPALLP NLTLGYRIFD TCNTVSKALE ATLSFVAQNK IDSLNLDEFC NCSEHIPSTI AVVGATGSGV STAVANLLGL ...String: MKTIIALSYI FCLVFADYKD DDDENLYFQG YGPDQRAQKK GDIILGGLFP IHFGVAAKDQ DLKSRPESVE CIRYNFRGFR WLQAMIFAIE EINSSPALLP NLTLGYRIFD TCNTVSKALE ATLSFVAQNK IDSLNLDEFC NCSEHIPSTI AVVGATGSGV STAVANLLGL FYIPQVSYAS SSRLLSNKNQ FKSFLRTIPN DEHQATAMAD IIEYFRWNWV GTIAADDDYG RPGIEKFREE AEERDICIDF SELISQYSDE EEIQHVVEVI QNSTAKVIVV FSSGPDLEPL IKEIVRRNIT GKIWLASEAW ASSSLIAMPQ YFHVVGGTIG FALKAGQIPG FREFLKKVHP RKSVHNGFAK EFWEETFNCH LQEGAKGPLP VDTFLRGHEE SGDRFSNSST AFRPLCTGDE NISSVETPYI DYTHLRISYN VYLAVYSIAH ALQDIYTCLP GRGLFTNGSC ADIKKVEAWQ VLKHLRHLNF TNNMGEQVTF DECGDLVGNY SIINWHLSPE DGSIVFKEVG YYNVYAKKGE RLFINEEKIL WSGFSREVPF SNCSRDCLAG TRKGIIEGEP TCCFECVECP DGEYSDETDA SACNKCPDDF WSNENHTSCI AKEIEFLSWT EPFGIALTLF AVLGIFLTAF VLGVFIKFRN TPIVKATNRE LSYLLLFSLL CCFSSSLFFI GEPQDWTCRL RQPAFGISFV LCISCILVKT NRVLLVFEAK IPTSFHRKWW GLNLQFLLVF LCTFMQIVIC VIWLYTAPPS SYRNQELEDE IIFITCHEGS LMALGFLIGY TCLLAAICFF FAFKSRKLPE NFNEAKFITF SMLIFFIVWI SFIPAYASTY GKFVSAVEVI AILAASFGLL ACIFFNKIYI ILFKPSRNTI EEVRCSTAAH AFKVAARATL RRSNVSRKRS SSLGGSTGST PSSSISSKSN SEDPFPQPER QKQQQPLALT QQEQQQQPLT LPQQQRSQQQ PRCKQKVIFG SGTVTFSLSF DEPQKNAMAH RNSTHQNSLE AQKSSDTLTR HEPLLPLQCG ETDLDLTVQE TGLQGPVGGD QRPEVEDPEE LSPALVVSSS QSFVISGGGS TVTENVVNSH HHHHHHHHH |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 62.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 6.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 210908 |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








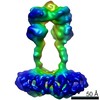

 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















