[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-3068: Mammalian ribosome bound to the native Sec61 protein-conducting c... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3068 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
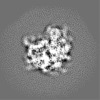
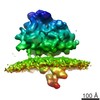
| Title | Mammalian ribosome bound to the native Sec61 protein-conducting channel in the 'non-inserting' state ('conventional' alignment) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Subtomogram average of non-solubilized ribosome-Sec61 complexes in the 'non-inserting' state. Subtomogram alignment was carried out using 'conventional' alignment. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ribosome / Sec61 / Translocon / Endoplasmic Reticulum / Cryoelectron Tomography / Subtomogram Analysis | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationInsertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / membrane docking / endoplasmic reticulum Sec complex / pronephric nephron development / cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Ssh1 translocon complex / Sec61 translocon complex / protein targeting to ER / protein insertion into ER membrane / protein-transporting ATPase activity ...Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / membrane docking / endoplasmic reticulum Sec complex / pronephric nephron development / cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Ssh1 translocon complex / Sec61 translocon complex / protein targeting to ER / protein insertion into ER membrane / protein-transporting ATPase activity / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / signal sequence binding / post-translational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / protein transmembrane transporter activity / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / phospholipid binding / ribosome binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / endoplasmic reticulum / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pfeffer S / Burbaum L / Unverdorben P / Pech M / Chen Y / Zimmermann R / Beckmann R / Foerster F | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2015 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2015Title: Structure of the native Sec61 protein-conducting channel. Authors: Stefan Pfeffer / Laura Burbaum / Pia Unverdorben / Markus Pech / Yuxiang Chen / Richard Zimmermann / Roland Beckmann / Friedrich Förster /  Abstract: In mammalian cells, secretory and membrane proteins are translocated across or inserted into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane by the universally conserved protein-conducting channel Sec61, ...In mammalian cells, secretory and membrane proteins are translocated across or inserted into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane by the universally conserved protein-conducting channel Sec61, which has been structurally studied in isolated, detergent-solubilized states. Here we structurally and functionally characterize native, non-solubilized ribosome-Sec61 complexes on rough ER vesicles using cryo-electron tomography and ribosome profiling. Surprisingly, the 9-Å resolution subtomogram average reveals Sec61 in a laterally open conformation, even though the channel is not in the process of inserting membrane proteins into the lipid bilayer. In contrast to recent mechanistic models for polypeptide translocation and insertion, our results indicate that the laterally open conformation of Sec61 is the only conformation present in the ribosome-bound translocon complex, independent of its functional state. Consistent with earlier functional studies, our structure suggests that the ribosome alone, even without a nascent chain, is sufficient for lateral opening of Sec61 in a lipid environment. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3068.map.gz emd_3068.map.gz | 6.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3068-v30.xml emd-3068-v30.xml emd-3068.xml emd-3068.xml | 11.1 KB 11.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-3068.tif EMD-3068.tif | 209.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3068 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3068 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3068 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3068 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_3068_validation.pdf.gz emd_3068_validation.pdf.gz | 261.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_3068_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_3068_full_validation.pdf.gz | 261 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_3068_validation.xml.gz emd_3068_validation.xml.gz | 6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3068 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3068 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3068 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3068 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 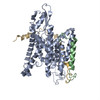 5a6uMC  3069C  3070C  3071C  3072C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3068.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 39.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3068.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 39.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Subtomogram average of non-solubilized ribosome-Sec61 complexes in the 'non-inserting' state. Subtomogram alignment was carried out using 'conventional' alignment. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.62 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Mammalian ribosome bound to the native protein translocon on cani...
| Entire | Name: Mammalian ribosome bound to the native protein translocon on canine pancreatic ER vesicles |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Mammalian ribosome bound to the native protein translocon on cani...
| Supramolecule | Name: Mammalian ribosome bound to the native protein translocon on canine pancreatic ER vesicles type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #1: Membrane-bound 80S ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Membrane-bound 80S ribosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-eukaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: ER protein translocon
| Macromolecule | Name: ER protein translocon / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Recombinant expression: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 / Details: 20mM Hepes, 50mM KCl; 2mM MgCl2 |
| Grid | Details: Lacey carbon molybdenum grid |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE MIXTURE / Chamber humidity: 70 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Method: Blot 3 seconds before plunging. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: Gatan |
| Date | Jun 18, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 3.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Tilt series - Axis1 - Min angle: -20 ° / Tilt series - Axis1 - Max angle: 20 ° |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | Tomogram reconstruction and template matching against a single particle cryo-EM reconstruction of the 80S ribosome were accomplished using PyTom. Subtomograms extracted from cross correlation peaks in the tomogram were classified using constrained principal component analysis focusing on the large ribosomal subunit and the ER membrane. For the retained coordinates, 1 x binned subtomograms were reconstructed individually from the weighted back-projections using the full tilt range, iteratively aligned and classified focusing on the translocon. For the retained coordinates, unbinned subtomograms were reconstructed individually from the weighted back-projections using only a reduced tilt range (-20 deg to +20 deg) and iteratively aligned using a 'conventional' subtomogram alignment procedure. |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 9.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: PyTom, tom_toolbox, av3_toolbox / Number subtomograms used: 17600 |
| CTF correction | Details: Each tilt image |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - #0 - Chain ID: 1 / Chain - #1 - Chain ID: 2 / Chain - #2 - Chain ID: 3 |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: MDFF |
| Details | The Sec61a N-terminal domain along with Sec61b was first fitted as a rigid body prior to flexible fitting. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: pseudo-energy |
| Output model |  PDB-5a6u: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)