[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-29172: Cryo-EM structure of Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphat... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphate synthase homotetramer in complex with uridine diphosphate and glucose-6-phosphate | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (Tps1) homotetramer bound to UDP and G6P | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Glycosyltransferase / Complex / TRANSFERASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationalpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase complex (UDP-forming) / alpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase (UDP-forming) / trehalose-phosphatase activity / alpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase (UDP-forming) activity / trehalose biosynthetic process / cellular response to heat / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Washington EJ / Brennan RG | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024Title: Structures of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase, Tps1, from the fungal pathogen : a target for novel antifungals. Authors: Erica J Washington / Ye Zhou / Allen L Hsu / Matthew Petrovich / Jennifer L Tenor / Dena L Toffaletti / Ziqiang Guan / John R Perfect / Mario J Borgnia / Alberto Bartesaghi / Richard G Brennan Abstract: Invasive fungal diseases are a major threat to human health, resulting in more than 1.5 million annual deaths worldwide. The arsenal of antifungal therapeutics remains limited and is in dire need of ...Invasive fungal diseases are a major threat to human health, resulting in more than 1.5 million annual deaths worldwide. The arsenal of antifungal therapeutics remains limited and is in dire need of novel drugs that target additional biosynthetic pathways that are absent from humans. One such pathway involves the biosynthesis of trehalose. Trehalose is a disaccharide that is required for pathogenic fungi to survive in their human hosts. In the first step of trehalose biosynthesis, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (Tps1) converts UDP-glucose and glucose-6-phosphate to trehalose-6-phosphate. Here, we report the structures of full-length Tps1 (CnTps1) in unliganded form and in complex with uridine diphosphate and glucose-6-phosphate. Comparison of these two structures reveals significant movement towards the catalytic pocket by the N-terminus upon ligand binding and identifies residues required for substrate-binding, as well as residues that stabilize the tetramer. Intriguingly, an intrinsically disordered domain (IDD), which is conserved amongst Cryptococcal species and closely related Basidiomycetes, extends from each subunit of the tetramer into the "solvent" but is not visible in density maps. We determined that the IDD is not required for Tps1-dependent thermotolerance and osmotic stress survival. Studies with UDP-galactose highlight the exquisite substrate specificity of CnTps1. , these studies expand our knowledge of trehalose biosynthesis in and highlight the potential of developing antifungal therapeutics that disrupt the synthesis of this disaccharide or the formation of a functional tetramer and the use of cryo-EM in the structural characterization of CnTps1-ligand/drug complexes. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Fungal infections are responsible for over a million deaths worldwide each year. Biosynthesis of a disaccharide, trehalose, is required for multiple pathogenic fungi to ...SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Fungal infections are responsible for over a million deaths worldwide each year. Biosynthesis of a disaccharide, trehalose, is required for multiple pathogenic fungi to transition from the environment to the human host. Enzymes in the trehalose biosynthesis pathway are absent in humans and, therefore, are potentially significant targets for novel antifungal therapeutics. One enzyme in the trehalose biosynthesis is trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (Tps1). Here, we describe the cryo-electron microscopy structures of the CnTps1 homo-tetramer in the unliganded form and in complex with a substrate and a product. These structures and subsequent biochemical analysis reveal key details of substrate-binding residues and substrate specificity. These structures should facilitate structure-guided design of inhibitors against CnTps1. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_29172.map.gz emd_29172.map.gz | 59.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-29172-v30.xml emd-29172-v30.xml emd-29172.xml emd-29172.xml | 15.3 KB 15.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_29172_fsc.xml emd_29172_fsc.xml | 9.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_29172.png emd_29172.png | 118.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-29172.cif.gz emd-29172.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_29172_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29172_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29172_half_map_2.map.gz emd_29172_half_map_2.map.gz | 59 MB 59 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29172 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29172 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29172 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29172 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 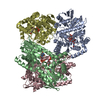 8fhwMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_29172.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_29172.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (Tps1) homotetramer bound to UDP and G6P | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
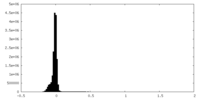
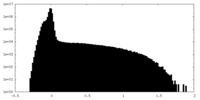
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (Tps1) homotetramer bound to...
| File | emd_29172_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (Tps1) homotetramer bound to UDP and G6P Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (Tps1) homotetramer bound to...
| File | emd_29172_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (Tps1) homotetramer bound to UDP and G6P Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphat...
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphate synthase homotetramer in complex with uridine diphosphate and glucose-6-phosphate |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphat...
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of Cryptococcus neoformans trehalose-6-phosphate synthase homotetramer in complex with uridine diphosphate and glucose-6-phosphate type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 307 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Alpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase (UDP-forming)
| Macromolecule | Name: Alpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase (UDP-forming) type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: UDP G6P / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 76.8155 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MHHHHHHSSG VDLGTENLYF QSNAMTTMSN DIPNSPTSTS FTGTFSPAAT AANTAANART SDAPSPTTSS SGPKLETSKE QRLIVVSNR LPVTISKDDN GEYHFKMSSG GLVSALSGCK KTMSFTWIGW PGKDIPMQDR ETVNRRLLDE YNCYPVYLSD E LADSHYNG ...String: MHHHHHHSSG VDLGTENLYF QSNAMTTMSN DIPNSPTSTS FTGTFSPAAT AANTAANART SDAPSPTTSS SGPKLETSKE QRLIVVSNR LPVTISKDDN GEYHFKMSSG GLVSALSGCK KTMSFTWIGW PGKDIPMQDR ETVNRRLLDE YNCYPVYLSD E LADSHYNG FSNSILWPLF HYHPGEMNFD AAHWLAYREA NMRFADVVSS LVQAGDMVWV QDYHLMLLPM LLRSMITGES AQ GEMVRQE LGRVKEGVDD TVVKEVLKMG PGVAQAEDEG VEMLDDVEEE GGEMDVKSSP KRPHYARGMS TFQKQELVAK EKG KEGIRI GFFLHTPFPS SEIYRILPVR REILLGVLQC DLIGFHTYDY ARHFLSSCTR ILGLETQPNG IEFDGRYCQV GTFP IGIDP NQFIEGLQKE SIVKRLRSLE ARFEGVKVII GVDRLDYIKG IPQKLQALET FLTQHPEWIG KVVLVQLAIP SRQDV EEYQ DLRACVNELV GRINGRFGTV ESVPIHYMHK SVPFEELTAM YALADACLVT STRDGMNLVA YEYISSQAER HGSMIL SEF AGAAQSFNGS LLINPWDVQS TADAINQALT LSPQQRKTNW QKLFNYVSKY TAEAWGVSFV NELNRLSGQR PSGPTGL AG RRKSGSLSRT SSKASIQRRK SSQSGIVTGL GAAAGAAVNW AQAQVQGGSQ T UniProtKB: alpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase (UDP-forming) |
-Macromolecule #2: URIDINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: URIDINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: UDP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 404.161 Da |
| Chemical component information | 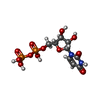 ChemComp-UDP: |
-Macromolecule #3: 6-O-phosphono-alpha-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 6-O-phosphono-alpha-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: G6P |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 260.136 Da |
| Chemical component information | 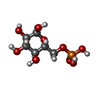 ChemComp-G6P: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.75 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)