[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-28529: Human R-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav2.3 at 3.1 Angstrom... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human R-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav2.3 at 3.1 Angstrom resolution | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | calcium channel | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cav2.3 / Channels / Calcium Ion-Selective / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / NCAM1 interactions / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction ...positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / NCAM1 interactions / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / Mechanical load activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in osteocytes / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / regulation of calcium ion transport / neuronal dense core vesicle / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / sarcoplasmic reticulum / protein localization to plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / Regulation of insulin secretion / GABA-ergic synapse / cellular response to amyloid-beta / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / calcium ion transport / T cell receptor signaling pathway / chemical synaptic transmission / neuronal cell body / calcium ion binding / synapse / extracellular exosome / metal ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gao S / Yao X / Yan N | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structures of the R-type human Ca2.3 channel reveal conformational crosstalk of the intracellular segments. Authors: Xia Yao / Yan Wang / Zhifei Wang / Xiao Fan / Di Wu / Jian Huang / Alexander Mueller / Sarah Gao / Miaohui Hu / Carol V Robinson / Yong Yu / Shuai Gao / Nieng Yan /    Abstract: The R-type voltage-gated Ca (Ca) channels Ca2.3, widely expressed in neuronal and neuroendocrine cells, represent potential drug targets for pain, seizures, epilepsy, and Parkinson's disease. Despite ...The R-type voltage-gated Ca (Ca) channels Ca2.3, widely expressed in neuronal and neuroendocrine cells, represent potential drug targets for pain, seizures, epilepsy, and Parkinson's disease. Despite their physiological importance, there have lacked selective small-molecule inhibitors targeting these channels. High-resolution structures may aid rational drug design. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of human Ca2.3 in complex with α2δ-1 and β3 subunits at an overall resolution of 3.1 Å. The structure is nearly identical to that of Ca2.2, with VSD in the down state and the other three VSDs up. A phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) molecule binds to the interface of VSD and the tightly closed pore domain. We also determined the cryo-EM structure of a Ca2.3 mutant in which a Ca2-unique cytosolic helix in repeat II (designated the CH2 helix) is deleted. This mutant, named ΔCH2, still reserves a down VSD, but PIP2 is invisible and the juxtamembrane region on the cytosolic side is barely discernible. Our structural and electrophysiological characterizations of the wild type and ΔCH2 Ca2.3 show that the CH2 helix stabilizes the inactivated conformation of the channel by tightening the cytosolic juxtamembrane segments, while CH2 helix is not necessary for locking the down state of VSD. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28529.map.gz emd_28529.map.gz | 78.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28529-v30.xml emd-28529-v30.xml emd-28529.xml emd-28529.xml | 25.1 KB 25.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_28529.png emd_28529.png | 110.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28529.cif.gz emd-28529.cif.gz | 9.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28529_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28529_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28529_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28529_half_map_2.map.gz | 65.4 MB 65.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28529 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28529 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28529 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28529 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8eplMC  8epmC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28529.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28529.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | calcium channel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
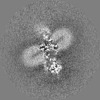
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.114 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
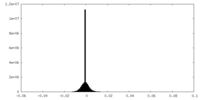
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half Map 1
| File | emd_28529_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map 1 | ||||||||||||
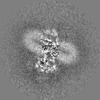
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
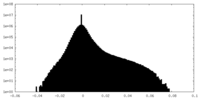
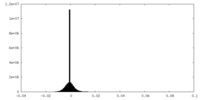
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half Map 2
| File | emd_28529_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
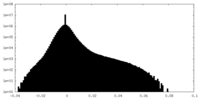
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cav2.3
| Entire | Name: Cav2.3 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cav2.3
| Supramolecule | Name: Cav2.3 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Voltage-dependent R-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1E
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent R-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1E type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 262.055984 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MARFGEAVVA RPGSGDGDSD QSRNRQGTPV PASGQAAAYK QTKAQRARTM ALYNPIPVRQ NCFTVNRSLF IFGEDNIVRK YAKKLIDWP PFEYMILATI IANCIVLALE QHLPEDDKTP MSRRLEKTEP YFIGIFCFEA GIKIVALGFI FHKGSYLRNG W NVMDFIVV ...String: MARFGEAVVA RPGSGDGDSD QSRNRQGTPV PASGQAAAYK QTKAQRARTM ALYNPIPVRQ NCFTVNRSLF IFGEDNIVRK YAKKLIDWP PFEYMILATI IANCIVLALE QHLPEDDKTP MSRRLEKTEP YFIGIFCFEA GIKIVALGFI FHKGSYLRNG W NVMDFIVV LSGILATAGT HFNTHVDLRT LRAVRVLRPL KLVSGIPSLQ IVLKSIMKAM VPLLQIGLLL FFAILMFAII GL EFYSGKL HRACFMNNSG ILEGFDPPHP CGVQGCPAGY ECKDWIGPND GITQFDNILF AVLTVFQCIT MEGWTTVLYN TND ALGATW NWLYFIPLII IGSFFVLNLV LGVLSGEFAK ERERVENRRA FMKLRRQQQI ERELNGYRAW IDKAEEVMLA EENK NAGTS ALEVLRRATI KRSRTEAMTR DSSDEHCVDI SSVGTPLARA SIKSAKVDGV SYFRHKERLL RISIRHMVKS QVFYW IVLS LVALNTACVA IVHHNQPQWL THLLYYAEFL FLGLFLLEMS LKMYGMGPRL YFHSSFNCFD FGVTVGSIFE VVWAIF RPG TSFGISVLRA LRLLRIFKIT KYWASLRNLV VSLMSSMKSI ISLLFLLFLF IVVFALLGMQ LFGGRFNFND GTPSANF DT FPAAIMTVFQ ILTGEDWNEV MYNGIRSQGG VSSGMWSAIY FIVLTLFGNY TLLNVFLAIA VDNLANAQEL TKDEQEEE E AFNQKHALQK AKEVSPMSAP NMPSIERDRR RRHHMSMWEP RSSHLRERRR RHHMSVWEQR TSQLRKHMQM SSQEALNRE EAPTMNPLNP LNPLSSLNPL NAHPSLYRRP RAIEGLALGL ALEKFEEERI SRGGSLKGDG GDRSSALDNQ RTPLSLGQRE PPWLARPCH GNCDPTQQEA GGGEAVVTFE DRARHRQSQR RSRHRRVRTE GKESSSASRS RSASQERSLD EAMPTEGEKD H ELRGNHGA KEPTIQEERA QDLRRTNSLM VSRGSGLAGG LDEADTPLVL PHPELEVGKH VVLTEQEPEG SSEQALLGNV QL DMGRVIS QSEPDLSCIT ANTDKATTES TSVTVAIPDV DPLVDSTVVH ISNKTDGEAS PLKEAEIRED EEEVEKKKQK KEK RETGKA MVPHSSMFIF STTNPIRRAC HYIVNLRYFE MCILLVIAAS SIALAAEDPV LTNSERNKVL RYFDYVFTGV FTFE MVIKM IDQGLILQDG SYFRDLWNIL DFVVVVGALV AFALANALGT NKGRDIKTIK SLRVLRVLRP LKTIKRLPKL KAVFD CVVT SLKNVFNILI VYKLFMFIFA VIAVQLFKGK FFYCTDSSKD TEKECIGNYV DHEKNKMEVK GREWKRHEFH YDNIIW ALL TLFTVSTGEG WPQVLQHSVD VTEEDRGPSR SNRMEMSIFY VVYFVVFPFF FVNIFVALII ITFQEQGDKM MEECSLE KN ERACIDFAIS AKPLTRYMPQ NRHTFQYRVW HFVVSPSFEY TIMAMIALNT VVLMMKYYSA PCTYELALKY LNIAFTMV F SLECVLKVIA FGFLNYFRDT WNIFDFITVI GSITEIILTD SKLVNTSGFN MSFLKLFRAA RLIKLLRQGY TIRILLWTF VQSFKALPYV CLLIAMLFFI YAIIGMQVFG NIKLDEESHI NRHNNFRSFF GSLMLLFRSA TGEAWQEIML SCLGEKGCEP DTTAPSGQN ENERCGTDLA YVYFVSFIFF CSFLMLNLFV AVIMDNFEYL TRDSSILGPH HLDEFVRVWA EYDRAACGRI H YTEMYEML TLMSPPLGLG KRCPSKVAYK RLVLMNMPVA EDMTVHFTST LMALIRTALD IKIAKGGADR QQLDSELQKE TL AIWPHLS QKMLDLLVPM PKASDLTVGK IYAAMMIMDY YKQSKVKKQR QQLEEQKNAP MFQRMEPSSL PQEIIANAKA LPY LQQDPV SGLSGRSGYP SMSPLSPQDI FQLACMDPAD DGQFQERQSL EPEVSELKSV QPSNHGIYLP SDTQEHAGSG RASS MPRLT VDPQVVTDPS SMRRSFSTIR DKRSNSSWLE EFSMERSSEN TYKSRRRSYH SSLRLSAHRL NSDSGHKSDT HRSGG RERG RSKERKHLLS PDVSRCNSEE RGTQADWESP ERRQSRSPSE GRSQTPNRQG TGSLSESSIP SVSDTSTPRR SRRQLP PVP PKPRPLLSYS SLIRHAGSIS PPADGSEEGS PLTSQALESN NACLTESSNS PHPQQSQHAS PQRYISEPYL ALHEDSH AS DCGEEETLTF EAAVATSLGR SNTIGSAPPL RHSWQMPNGH YRRRRRGGPG PGMMCGAVNN LLSDTEEDDK C UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent R-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1E |
-Macromolecule #2: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-3
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-3 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 54.607852 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MYDDSYVPGF EDSEAGSADS YTSRPSLDSD VSLEEDRESA RREVESQAQQ QLERAKHKPV AFAVRTNVSY CGVLDEECPV QGSGVNFEA KDFLHIKEKY SNDWWIGRLV KEGGDIAFIP SPQRLESIRL KQEQKARRSG NPSSLSDIGN RRSPPPSLAK Q KQKQAEHV ...String: MYDDSYVPGF EDSEAGSADS YTSRPSLDSD VSLEEDRESA RREVESQAQQ QLERAKHKPV AFAVRTNVSY CGVLDEECPV QGSGVNFEA KDFLHIKEKY SNDWWIGRLV KEGGDIAFIP SPQRLESIRL KQEQKARRSG NPSSLSDIGN RRSPPPSLAK Q KQKQAEHV PPYDVVPSMR PVVLVGPSLK GYEVTDMMQK ALFDFLKHRF DGRISITRVT ADLSLAKRSV LNNPGKRTII ER SSARSSI AEVQSEIERI FELAKSLQLV VLDADTINHP AQLAKTSLAP IIVFVKVSSP KVLQRLIRSR GKSQMKHLTV QMM AYDKLV QCPPESFDVI LDENQLEDAC EHLAEYLEVY WRATHHPAPG PGLLGPPSAI PGLQNQQLLG ERGEEHSPLE RDSL MPSDE ASESSRQAWT GSSQRSSRHL EEDYADAYQD LYQPHRQHTS GLPSANGHDP QDRLLAQDSE HNHSDRNWQR NRPWP KDSY UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-3 |
-Macromolecule #3: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 124.692469 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAAGCLLALT LTLFQSLLIG PSSEEPFPSA VTIKSWVDKM QEDLVTLAKT ASGVNQLVDI YEKYQDLYTV EPNNARQLVE IAARDIEKL LSNRSKALVR LALEAEKVQA AHQWREDFAS NEVVYYNAKD DLDPEKNDSE PGSQRIKPVF IEDANFGRQI S YQHAAVHI ...String: MAAGCLLALT LTLFQSLLIG PSSEEPFPSA VTIKSWVDKM QEDLVTLAKT ASGVNQLVDI YEKYQDLYTV EPNNARQLVE IAARDIEKL LSNRSKALVR LALEAEKVQA AHQWREDFAS NEVVYYNAKD DLDPEKNDSE PGSQRIKPVF IEDANFGRQI S YQHAAVHI PTDIYEGSTI VLNELNWTSA LDEVFKKNRE EDPSLLWQVF GSATGLARYY PASPWVDNSR TPNKIDLYDV RR RPWYIQG AASPKDMLIL VDVSGSVSGL TLKLIRTSVS EMLETLSDDD FVNVASFNSN AQDVSCFQHL VQANVRNKKV LKD AVNNIT AKGITDYKKG FSFAFEQLLN YNVSRANCNK IIMLFTDGGE ERAQEIFNKY NKDKKVRVFT FSVGQHNYDR GPIQ WMACE NKGYYYEIPS IGAIRINTQE YLDVLGRPMV LAGDKAKQVQ WTNVYLDALE LGLVITGTLP VFNITGQFEN KTNLK NQLI LGVMGVDVSL EDIKRLTPRF TLCPNGYYFA IDPNGYVLLH PNLQPKPIGV GIPTINLRKR RPNIQNPKSQ EPVTLD FLD AELENDIKVE IRNKMIDGES GEKTFRTLVK SQDERYIDKG NRTYTWTPVN GTDYSLALVL PTYSFYYIKA KLEETIT QA RYSETLKPDN FEESGYTFIA PRDYCNDLKI SDNNTEFLLN FNEFIDRKTP NNPSCNADLI NRVLLDAGFT NELVQNYW S KQKNIKGVKA RFVVTDGGIT RVYPKEAGEN WQENPETYED SFYKRSLDND NYVFTAPYFN KSGPGAYESG IMVSKAVEI YIQGKLLKPA VVGIKIDVNS WIENFTKTSI RDPCAGPVCD CKRNSDVMDC VILDDGGFLL MANHDDYTNQ IGRFFGEIDP SLMRHLVNI SVYAFNKSYD YQSVCEPGAA PKQGAGHRSA YVPSVADILQ IGWWATAAAW SILQQFLLSL TFPRLLEAVE M EDDDFTAS LSKQSCITEQ TQYFFDNDSK SFSGVLDCGN CSRIFHGEKL MNTNLIFIMV ESKGTCPCDT RLLIQAEQTS DG PNPCDMV KQPRYRKGPD VCFDNNVLED YTDCGGVSGL NPSLWYIIGI QFLLLWLVSG STHRLL UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 |
-Macromolecule #6: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #7: CHOLESTEROL
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: CLR |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 386.654 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CLR: |
-Macromolecule #8: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: 3PE |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 748.065 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-3PE: |
-Macromolecule #9: [(2R)-1-octadecanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tr...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2R)-1-octadecanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(oxidanyl)-4,5-diphosphonooxy-cyclohexyl]oxy-phospho ryl]oxy-propan-2-yl] (8Z)-icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoate type: ligand / ID: 9 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PT5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.047088 KDa |
-Macromolecule #10: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 10 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.9000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)