[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-28494: Eag Kv channel with voltage sensor in the intermediate conformation -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Eag Kv channel with voltage sensor in the intermediate conformation | |||||||||
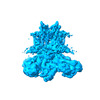
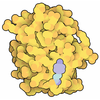
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | voltage-gated potassium channel / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationVoltage gated Potassium channels / potassium channel complex / regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / nuclear inner membrane / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events ...Voltage gated Potassium channels / potassium channel complex / regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / nuclear inner membrane / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / startle response / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / axolemma / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / presynaptic cytosol / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / cellular response to interferon-beta / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Protein methylation / 14-3-3 protein binding / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / titin binding / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / cellular response to calcium ion / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / adenylate cyclase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / sarcomere / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / regulation of cytokinesis / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / potassium ion transport / regulation of membrane potential / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / postsynaptic density membrane / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Stimuli-sensing channels / spindle pole / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / RAS processing / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
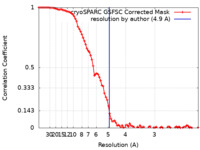
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mandala VS / MacKinnon R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022Title: Voltage-sensor movements in the Eag Kv channel under an applied electric field. Authors: Venkata Shiva Mandala / Roderick MacKinnon /  Abstract: Voltage-dependent ion channels regulate the opening of their pores by sensing the membrane voltage. This process underlies the propagation of action potentials and other forms of electrical activity ...Voltage-dependent ion channels regulate the opening of their pores by sensing the membrane voltage. This process underlies the propagation of action potentials and other forms of electrical activity in cells. The voltage dependence of these channels is governed by the transmembrane displacement of the positive charged S4 helix within their voltage-sensor domains. We use cryo-electron microscopy to visualize this movement in the mammalian Eag voltage-dependent potassium channel in lipid membrane vesicles with a voltage difference across the membrane. Multiple structural configurations show that the applied electric field displaces S4 toward the cytoplasm by two helical turns, resulting in an extended interfacial helix near the inner membrane leaflet. The position of S4 in this down conformation is sterically incompatible with an open pore, thus explaining how movement of the voltage sensor at hyperpolarizing membrane voltages locks the pore shut in this kind of voltage-dependent K (K) channel. The structures solved in lipid bilayer vesicles detail the intricate interplay between K channels and membranes, from showing how arginines are stabilized deep within the membrane and near phospholipid headgroups, to demonstrating how the channel reshapes the inner leaflet of the membrane itself. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28494.map.gz emd_28494.map.gz | 30.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28494-v30.xml emd-28494-v30.xml emd-28494.xml emd-28494.xml | 18 KB 18 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_28494_fsc.xml emd_28494_fsc.xml | 8.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_28494.png emd_28494.png | 69.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28494.cif.gz emd-28494.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28494_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28494_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28494_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28494_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.4 MB 59.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28494 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28494 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28494 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28494 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8ep0MC  8eowC  8ep1C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28494.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28494.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
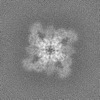
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_28494_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
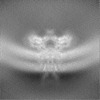
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
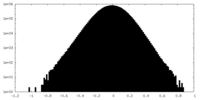
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_28494_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
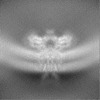
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of Eag Kv channel bound to the inhibitor calmodulin-Ca2+
| Entire | Name: Complex of Eag Kv channel bound to the inhibitor calmodulin-Ca2+ |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of Eag Kv channel bound to the inhibitor calmodulin-Ca2+
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of Eag Kv channel bound to the inhibitor calmodulin-Ca2+ type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 81.664094 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: LVAPQNTFLE NIVRRSNDTN FVLGNAQIVD WPIVYSNDGF CKLSGYHRAE VMQKSSACSF MYGELTDKDT VEKVRQTFEN YEMNSFEIL MYKKNRTPVW FFVKIAPIRN EQDKVVLFLC TFSDITAFKQ PIEDDSCKGW GKFARLTRAL TSSRGVLQQL A PSVQKGEN ...String: LVAPQNTFLE NIVRRSNDTN FVLGNAQIVD WPIVYSNDGF CKLSGYHRAE VMQKSSACSF MYGELTDKDT VEKVRQTFEN YEMNSFEIL MYKKNRTPVW FFVKIAPIRN EQDKVVLFLC TFSDITAFKQ PIEDDSCKGW GKFARLTRAL TSSRGVLQQL A PSVQKGEN VHKHSRLAEV LQLGSDILPQ YKQEAPKTPP HIILHYCVFK TTWDWIILIL TFYTAILVPY NVSFKTRQNN VA WLVVDSI VDVIFLVDIV LNFHTTFVGP AGEVISDPKL IRMNYLKTWF VIDLLSCLPY DVINAFENVD EGISSLFSSL KVV RLLRLG RVARKLDHYI EYGAAVLVLL VCVFGLAAHW MACIWYSIGD YEIFDEDTKT IRNNSWLYQL ALDIGTPYQF NGSG SGKWE GGPSKNSVYI SSLYFTMTSL TSVGFGNIAP STDIEKIFAV AIMMIGSLLY ATIFGNVTTI FQQMYANTNR YHEML NSVR DFLKLYQVPK GLSERVMDYI VSTWSMSRGI DTEKVLQICP KDMRADICVH LNRKVFKEHP AFRLASDGCL RALAME FQT VHCAPGDLIY HAGESVDSLC FVVSGSLEVI QDDEVVAILG KGDVFGDVFW KEATLAQSCA NVRALTYCDL HVIKRDA LQ KVLEFYTAFS HSFSRNLILT YNLRKRIVFR KISDVKREEE ERMKRKNEAP LILPPDHPVR RLFQRFRQQK E UniProtKB: Voltage-gated delayed rectifier potassium channel KCNH1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.063608 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: EEQIAEFKEA FSLFDKDGDG TITTKELGTV MRSLGQNPTE AELQDMINEV DADGNGTIDF PEFLTMMARK MKDTDSEEEI REAFRVFDK DGNGYISAAE LRHVMTNLGE KLTDEEVDEM IREADIDGDG QVNYEEFVQM MTA UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)