+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
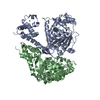
| Title | SV40 T-Antigen helicase hexamer | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SV40 T-Antigen / VIRAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Betapolyomavirus macacae Betapolyomavirus macacae | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.8 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yuan Z / Langston L / Georgescu R / Li H / O'Donnell M | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022Title: SV40 T-antigen uses a DNA shearing mechanism to initiate origin unwinding. Authors: Lance D Langston / Zuanning Yuan / Roxana Georgescu / Huilin Li / Michael E O'Donnell /  Abstract: Duplication of DNA genomes requires unwinding of the double-strand (ds) DNA so that each single strand (ss) can be copied by a DNA polymerase. The genomes of eukaryotic cells are unwound by two ring- ...Duplication of DNA genomes requires unwinding of the double-strand (ds) DNA so that each single strand (ss) can be copied by a DNA polymerase. The genomes of eukaryotic cells are unwound by two ring-shaped hexameric helicases that initially encircle dsDNA but transition to ssDNA for function as replicative helicases. How the duplex is initially unwound, and the role of the two helicases in this process, is poorly understood. We recently described an initiation mechanism for eukaryotes in which the two helicases are directed inward toward one another and shear the duplex open by pulling on opposite strands of the duplex while encircling dsDNA [L. D. Langston, M. E. O'Donnell, , e46515 (2019)]. Two head-to-head T-Antigen helicases are long known to be loaded at the SV40 origin. We show here that T-Antigen tracks head (N-tier) first on ssDNA, opposite the direction proposed for decades. We also find that SV40 T-Antigen tracks directionally while encircling dsDNA and mainly tracks on one strand of the duplex in the same orientation as during ssDNA translocation. Further, two inward directed T-Antigen helicases on dsDNA are able to melt a 150-bp duplex. These findings explain the "rabbit ear" DNA loops observed at the SV40 origin by electron microscopy and reconfigure how the DNA loops emerge from the double hexamer relative to earlier models. Thus, the mechanism of DNA shearing by two opposing helicases is conserved in a eukaryotic viral helicase and may be widely used to initiate origin unwinding of dsDNA genomes. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28195.map.gz emd_28195.map.gz | 4.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28195-v30.xml emd-28195-v30.xml emd-28195.xml emd-28195.xml | 13.7 KB 13.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_28195.png emd_28195.png | 137.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28195.cif.gz emd-28195.cif.gz | 4.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28195_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28195_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28195_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28195_half_map_2.map.gz | 48.8 MB 48.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28195 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28195 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28195 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28195 | HTTPS FTP |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28195.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28195.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
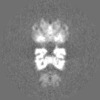
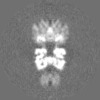
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.16 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
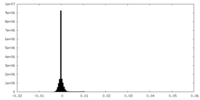
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_28195_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
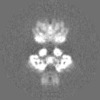
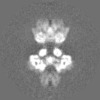
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
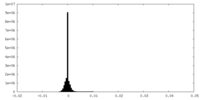
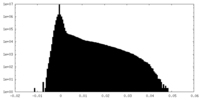
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_28195_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
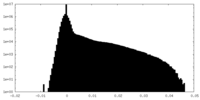
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : SV40 T-Antigen
| Entire | Name: SV40 T-Antigen |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: SV40 T-Antigen
| Supramolecule | Name: SV40 T-Antigen / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Betapolyomavirus macacae Betapolyomavirus macacae |
-Macromolecule #1: SV40 large antigen
| Macromolecule | Name: SV40 large antigen / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: DEXTRO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Betapolyomavirus macacae Betapolyomavirus macacae |
| Sequence | String: MDKVLNREES LQLMDLLGLE RSAWGNIPLM RKAYLKKCKE FHPDKGGDEE KMKKMNTLYK KMEDGVKYAH QPDFGGFWDA TEIPTYGTDE WEQWWNAFNE ENLFCSEEMP SSDDEATADS QHSTPPKKKR KVEDPKDFPS ELLSFLSHAV FSNRTLACFA IYTTKEKAAL ...String: MDKVLNREES LQLMDLLGLE RSAWGNIPLM RKAYLKKCKE FHPDKGGDEE KMKKMNTLYK KMEDGVKYAH QPDFGGFWDA TEIPTYGTDE WEQWWNAFNE ENLFCSEEMP SSDDEATADS QHSTPPKKKR KVEDPKDFPS ELLSFLSHAV FSNRTLACFA IYTTKEKAAL LYKKIMEKYS VTFISRHNSY NHNILFFLTP HRHRVSAINN YAQKLCTFSF LICKGVNKEY LMYSALTRDP FSVIEESLPG GLKEHDFNPE EAEETKQVSW KLVTEYAMET KCDDVLLLLG MYLEFQYSFE MCLKCIKKEQ PSHYKYHEKH YANAAIFADS KNQKTICQQA VDTVLAKKRV DSLQLTREQM LTNRFNDLLD RMDIMFGSTG SADIEEWMAG VAWLHCLLPK MDSVVYDFLK CMVYNIPKKR YWLFKGPIDS GKTTLAAALL ELCGGKALNV NLPLDRLNFE LGVAIDQFLV VFEDVKGTGG ESRDLPSGQG INNLDNLRDY LDGSVKVNLE KKHLNKRTQI FPPGIVTMNE FSVPKTLQAR FVKQIDFRAK DYLKHCLERS EFLLEKRIIQ SGIALLLMLI WYRPVAEFAQ SIQSRIVEWK ERLDKEFSLS VYQKMKFNVA MGIGVLDWLR NSDDDDEDSQ ENADKNEDGG EKNMEDSGHE TGIDSQSQGS FQAPQSSQSV HDHNQPYHIC RGFTCFKKPP TPPPEPET |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 0.0025 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.0015 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 22375 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)