+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Closed state of RFC:PCNA bound to a nicked dsDNA | ||||||||||||
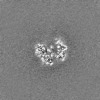
 Map data Map data | Map | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION-DNA complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of DNA metabolic process / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / meiotic mismatch repair / Rad17 RFC-like complex / : / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / Elg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex ...positive regulation of DNA metabolic process / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / meiotic mismatch repair / Rad17 RFC-like complex / : / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / Elg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / : / Polymerase switching / maintenance of DNA trinucleotide repeats / DNA clamp loader activity / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / : / : / : / DNA replication checkpoint signaling / establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / PCNA complex / : / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / lagging strand elongation / DNA damage tolerance / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / sister chromatid cohesion / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / error-free translesion synthesis / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / leading strand elongation / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / translesion synthesis / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / mismatch repair / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / positive regulation of DNA repair / positive regulation of DNA replication / replication fork / nucleotide-excision repair / DNA-templated DNA replication / mitotic cell cycle / chromosome, telomeric region / cell division / DNA repair / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
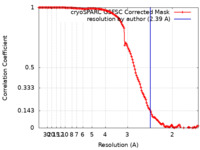
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.39 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Schrecker M / Hite RK | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2022 Journal: Elife / Year: 2022Title: Multistep loading of a DNA sliding clamp onto DNA by replication factor C. Authors: Marina Schrecker / Juan C Castaneda / Sujan Devbhandari / Charanya Kumar / Dirk Remus / Richard K Hite /  Abstract: The DNA sliding clamp proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is an essential co-factor for many eukaryotic DNA metabolic enzymes. PCNA is loaded around DNA by the ATP-dependent clamp loader ...The DNA sliding clamp proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is an essential co-factor for many eukaryotic DNA metabolic enzymes. PCNA is loaded around DNA by the ATP-dependent clamp loader replication factor C (RFC), which acts at single-stranded (ss)/double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) junctions harboring a recessed 3' end (3' ss/dsDNA junctions) and at DNA nicks. To illuminate the loading mechanism we have investigated the structure of RFC:PCNA bound to ATPγS and 3' ss/dsDNA junctions or nicked DNA using cryogenic electron microscopy. Unexpectedly, we observe open and closed PCNA conformations in the RFC:PCNA:DNA complex, revealing that PCNA can adopt an open, planar conformation that allows direct insertion of dsDNA, and raising the question of whether PCNA ring closure is mechanistically coupled to ATP hydrolysis. By resolving multiple DNA-bound states of RFC:PCNA we observe that partial melting facilitates lateral insertion into the central channel formed by RFC:PCNA. We also resolve the Rfc1 N-terminal domain and demonstrate that its single BRCT domain participates in coordinating DNA prior to insertion into the central RFC channel, which promotes PCNA loading on the lagging strand of replication forks in vitro. Combined, our data suggest a comprehensive and fundamentally revised model for the RFC-catalyzed loading of PCNA onto DNA. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27672.map.gz emd_27672.map.gz | 108.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27672-v30.xml emd-27672-v30.xml emd-27672.xml emd-27672.xml | 30.9 KB 30.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27672_fsc.xml emd_27672_fsc.xml | 12.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_27672.png emd_27672.png | 178.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27672.cif.gz emd-27672.cif.gz | 8.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27672_additional_1.map.gz emd_27672_additional_1.map.gz emd_27672_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27672_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27672_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27672_half_map_2.map.gz | 676.4 MB 200.4 MB 200.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27672 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27672 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27672 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27672 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8dr6MC  8dqwC  8dqxC  8dqzC  8dr0C  8dr1C  8dr3C  8dr4C  8dr5C  8dr7C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27672.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27672.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
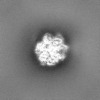
| Annotation | Map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
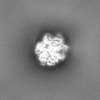
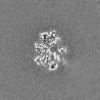
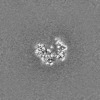
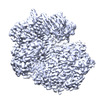
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.826 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
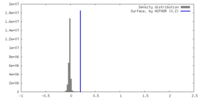
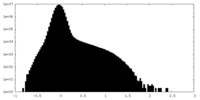
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Density modified and 1.5x resampled
| File | emd_27672_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Density modified and 1.5x resampled | ||||||||||||
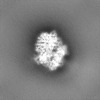
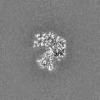
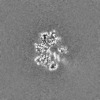
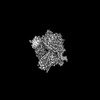
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
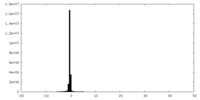
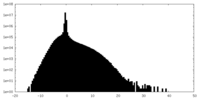
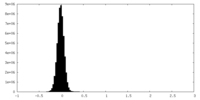
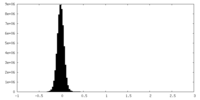
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_27672_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
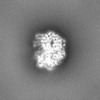
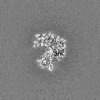
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_27672_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Closed state of RFC:PCNA bound to a nicked dsDNA
+Supramolecule #1: Closed state of RFC:PCNA bound to a nicked dsDNA
+Macromolecule #1: Replication factor C subunit 1
+Macromolecule #2: Replication factor C subunit 4
+Macromolecule #3: Replication factor C subunit 3
+Macromolecule #4: Replication factor C subunit 2
+Macromolecule #5: Replication factor C subunit 5
+Macromolecule #6: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
+Macromolecule #7: DNA (32-MER)
+Macromolecule #8: DNA (5'-D(P*CP*CP*CP*CP*CP*CP*GP*GP*CP*CP*CP*CP*CP*CP*CP*GP*GP*C)-3')
+Macromolecule #9: DNA (5'-D(P*TP*TP*AP*GP*GP*GP*GP*GP*GP*GP*GP*GP*A)-3')
+Macromolecule #10: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
+Macromolecule #11: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #12: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #13: water
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/mL | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 Component:
| ||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GRAPHENE OXIDE / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: GRAPHENE OXIDE / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS | ||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 297 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 66.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)