+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | G. haemolysans IgA1 protease | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | protease / IMMUNE SYSTEM | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationserine-type peptidase activity / metalloendopeptidase activity / extracellular region / zinc ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Gemella haemolysans (bacteria) Gemella haemolysans (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.28 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Eisenmesser EZ / Zheng H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2022Title: A substrate-induced gating mechanism is conserved among Gram-positive IgA1 metalloproteases. Authors: Jasmina S Redzic / Jeremy Rahkola / Norman Tran / Todd Holyoak / Eunjeong Lee / Antonio Javier Martín-Galiano / Nancy Meyer / Hongjin Zheng / Elan Eisenmesser /    Abstract: The mucosal adaptive immune response is dependent on the production of IgA antibodies and particularly IgA1, yet opportunistic bacteria have evolved mechanisms to specifically block this response by ...The mucosal adaptive immune response is dependent on the production of IgA antibodies and particularly IgA1, yet opportunistic bacteria have evolved mechanisms to specifically block this response by producing IgA1 proteases (IgA1Ps). Our lab was the first to describe the structures of a metal-dependent IgA1P (metallo-IgA1P) produced from Gram-positive Streptococcus pneumoniae both in the absence and presence of its IgA1 substrate through cryo-EM single particle reconstructions. This prior study revealed an active-site gating mechanism reliant on substrate-induced conformational changes to the enzyme that begged the question of whether such a mechanism is conserved among the wider Gram-positive metallo-IgA1P subfamily of virulence factors. Here, we used cryo-EM to characterize the metallo-IgA1P of a more distantly related family member from Gemella haemolysans, an emerging opportunistic pathogen implicated in meningitis, endocarditis, and more recently bacteremia in the elderly. While the substrate-free structures of these two metallo-IgA1Ps exhibit differences in the relative starting positions of the domain responsible for gating substrate, the enzymes have similar domain orientations when bound to IgA1. Together with biochemical studies that indicate these metallo-IgA1Ps have similar binding affinities and activities, these data indicate that metallo-IgA1P binding requires the specific IgA1 substrate to open the enzymes for access to their active site and thus, largely conform to an "induced fit" model. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_26812.map.gz emd_26812.map.gz | 167.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-26812-v30.xml emd-26812-v30.xml emd-26812.xml emd-26812.xml | 18.6 KB 18.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_26812.png emd_26812.png | 584.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-26812.cif.gz emd-26812.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_26812_half_map_1.map.gz emd_26812_half_map_1.map.gz emd_26812_half_map_2.map.gz emd_26812_half_map_2.map.gz | 165 MB 165 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26812 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26812 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26812 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26812 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7uvkMC  7uvlC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_26812.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_26812.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.83 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
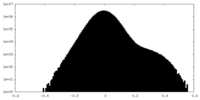
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_26812_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
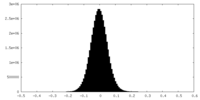
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_26812_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
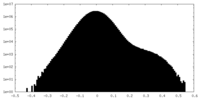
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Gemella haemolysans IgA protease apo
| Entire | Name: Gemella haemolysans IgA protease apo |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Gemella haemolysans IgA protease apo
| Supramolecule | Name: Gemella haemolysans IgA protease apo / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Gemella haemolysans (bacteria) Gemella haemolysans (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: IgA1 Protease
| Macromolecule | Name: IgA1 Protease / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Gemella haemolysans (bacteria) Gemella haemolysans (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 246.235844 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MRKYLEEKYN KFSLRKLTVG VCSMTIGSFF LVSTVQPEDY VVKAADNAIV HYKYVGEDNL TDKEKELIKK EVPSVVSSKE ETYYLVFKP TKTTQLNKLP NTGLNYGVGS MLLGGMLGLV VVVVAKGKNK SRKILSILLV TSLGATTLEL PARAMEDLQL S VYNMDYNL ...String: MRKYLEEKYN KFSLRKLTVG VCSMTIGSFF LVSTVQPEDY VVKAADNAIV HYKYVGEDNL TDKEKELIKK EVPSVVSSKE ETYYLVFKP TKTTQLNKLP NTGLNYGVGS MLLGGMLGLV VVVVAKGKNK SRKILSILLV TSLGATTLEL PARAMEDLQL S VYNMDYNL KVGDKLPEIS SIPGYSFVGF IKNEAETKKE NEEVKEQITS QQHNKKQPEL KENTDENVIE NKQENKTTLK IS DKKEDKK VIENINKKDE KKVQGVNTVN PQDEVLAGKL TKPELLYSDK IIETPLKYNQ IIESNDQLPE GTTRIKQQGK EGK KTEVIR MFTVEGKEVS RELISTKTEE PVSEIIEKGT KKAVSNVITK GQKLVKPAVE VKPEYTGVQA GAIVEPVKAE VPKE YTGVQ AGAIVEPAKV ETPKEYTGVQ AGAIVEPAKA EVSKEYTGVQ AGTIVEPAKA EVPKEYTGVQ AGAIVEPEKV EPQYG GVTS GALVKPEKIE APKEYTGVQA GAVVEPAKAE APKEYRGVQA GAIVEPEKIE SPKEYTGVQA GAVVEPAKAE VPKEYR GVQ AGAIVEPEKI ESPKEYTGEQ SGAIVEPEKV ETTKEYTGIQ AGALVEPEKV EAPKEYTGVQ AGAIVEPEKV EPPKEYT GV QAGAIVEPEK VEAPKEYTGK IEPLKTENPK PTVENNNTAE INNVPKNASA LLRMNFVKGN QVLSGTGSAT FIAPNVLL T VAHNFINNSA DNSTGEFIGD KSKNTYEWQT PDGQKGSFTS EDIHFYNKKD YPKGFIYDLA VITLPQSTRR QHANLVENY SKVNVNDKLN VYGYPRGEYA HLKDTTVEIE QKYANNTYGV QYQGGKAGMS GGGIFNSKGE VIGLHQNGAE NRSGGLILSP TQLDWIRSI IKGKEITPNY DALERHKDEK KDDIKEEKQV DKKLELRNIS NVELYTLENN KYRHVSSLSS VPTNPEAYFM K VKSENFKD VMLPVKSIES ARKDNQDVYK IVGQANDLIQ HENNITLENY TYYLPKTVNS ENGVYTSFKN LVDAMNINPY GT FRLGATM DAREVELSDG QESYINKEFS GKLIGENKGK YYAIYNLKKP LFKALSHATI QDLSIKEANV SSKEDAATIA KEA KNDTTI ANVHSSGVIA GERSIGGLIS QVTDSTISNS SFTGRITNTY DTTATYQIGG LVGKLSGVGA LIEKSISSID MATN ANTGD QVVGGVAGVV DKKATIRNSY VEGNLNNVKP FGKVGGVVGN LWDRETSEVS NSGNLTNVLS DVNVTNGNAI AGYDF NGIK ATNTYSNKNN KVVKVVQVDD EVLSKDSEEQ RGTVLENNIV LEKKIELVPK KNTKIEDFNF SSRYETDYKN LKDADV SRL RVYKNIEKLL PFYNRETIVK YGNLVDANNT LYTKDLVSVV PMKDKEVISD INKNKTSINK LLLHYSDNTS QTLDIKY LQ DFSKVAEYEI ANTKLIYTPN TLLHSYNNIV KAVLNDLKSV QYDSDAVRKV LDISSNIKLT ELYLDEQFTK TKANIEDS L SKLLSADAVI AENSNSIIDN YVIEKIKNNK EALLLGLTYL ERWYNFKYDN TSAKDLVLYH LDFFGKSNSS ALDNVIELG KSGFNNLLAK NNVITYNVLL SKNYGTEGLF KALEGYRKVF LPNVSNNDWF KTQSKAYIVE EKSTIPEVSS KQSKQGTEHS IGVYDRLTS PSWKYQSMVL PLLTLPEEKM IFMIANISTI GFGAYDRYRS SEYPKGDKLN RFVEENAQAA AKRFRDHYDY W YKILDKEN KEKLFRSVLV YDAFRFGNDT NKETQEANFE TNNPVIKNFF GPAGNNVVHN KHGAYATGDA FYYMAYRMLD KS GAVTYTH EMTHNSDREI YLGGYGRRSG LGPEFYAKGL LQAPDHSYDP TITINSVLKY DDSENSTRLQ IADPTQRFTN VED LHNYMH NMFDLIYTLE ILEGRAVAKL DYNEKNDLLR KIENIYKKDP DGNSVYATNA VRRLTSDEIK NLTSFDKLIE NDVI TRRGY IDQGEYERNG YHTINLFSPI YSALSSKIGT PGDLMGRRMA FELLAAKGYK EGMVPYISNQ YEKEAKDRGS KIRSY GKEI GLVTDDLVLE KVFNKKYGSW VEFKKDMYKE RVEQFSKLNR VSFFDPNGPW GRQKNVTVNN ISVLEKMIET AVREDA EDF TAQVYPDTNS RVLKLKKAIF KAYLDQTKDF RTSIFGGK UniProtKB: LPXTG-motif cell wall anchor domain protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 BASE (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source: OTHER |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER / Nominal defocus max: 5.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)