[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-26312: Cryo-EM structure of the pancreatic ATP-sensitive potassium chann... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
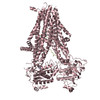
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the pancreatic ATP-sensitive potassium channel bound to ATP with Kir6.2-CTD in the up conformation | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | KATP channel / SUR1 / Kir6.2 / ATP / sulfonylurea receptor / potassium transport / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / metabolic sensor / trafficking defects | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRegulation of insulin secretion / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity / response to resveratrol / inward rectifying potassium channel / sulfonylurea receptor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development / cell body fiber / CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade ...Regulation of insulin secretion / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity / response to resveratrol / inward rectifying potassium channel / sulfonylurea receptor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development / cell body fiber / CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / ATPase-coupled monoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / inward rectifier potassium channel activity / nervous system process / : / ankyrin binding / Ion homeostasis / response to testosterone / response to ATP / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / response to stress / intercalated disc / action potential / axolemma / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / potassium channel activity / ABC-type transporter activity / heat shock protein binding / potassium ion transmembrane transport / cellular response to nutrient levels / T-tubule / regulation of insulin secretion / acrosomal vesicle / response to ischemia / determination of adult lifespan / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / regulation of membrane potential / potassium ion transport / cellular response to glucose stimulus / negative regulation of insulin secretion / sarcolemma / cellular response to nicotine / glucose metabolic process / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / response to estradiol / nuclear envelope / presynaptic membrane / transmembrane transporter binding / response to hypoxia / endosome / response to xenobiotic stimulus / neuronal cell body / apoptotic process / glutamatergic synapse / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / ATP binding / metal ion binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) / Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shyng SL / Sung MW / Driggers CM | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2019 Journal: Elife / Year: 2019Title: Mechanism of pharmacochaperoning in a mammalian K channel revealed by cryo-EM. Authors: Gregory M Martin / Min Woo Sung / Zhongying Yang / Laura M Innes / Balamurugan Kandasamy / Larry L David / Craig Yoshioka / Show-Ling Shyng /  Abstract: ATP-sensitive potassium (K) channels composed of a pore-forming Kir6.2 potassium channel and a regulatory ABC transporter sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) regulate insulin secretion in pancreatic β- ...ATP-sensitive potassium (K) channels composed of a pore-forming Kir6.2 potassium channel and a regulatory ABC transporter sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) regulate insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells to maintain glucose homeostasis. Mutations that impair channel folding or assembly prevent cell surface expression and cause congenital hyperinsulinism. Structurally diverse K inhibitors are known to act as pharmacochaperones to correct mutant channel expression, but the mechanism is unknown. Here, we compare cryoEM structures of a mammalian K channel bound to pharmacochaperones glibenclamide, repaglinide, and carbamazepine. We found all three drugs bind within a common pocket in SUR1. Further, we found the N-terminus of Kir6.2 inserted within the central cavity of the SUR1 ABC core, adjacent the drug binding pocket. The findings reveal a common mechanism by which diverse compounds stabilize the Kir6.2 N-terminus within SUR1's ABC core, allowing it to act as a firm 'handle' for the assembly of metastable mutant SUR1-Kir6.2 complexes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_26312.map.gz emd_26312.map.gz | 2.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-26312-v30.xml emd-26312-v30.xml emd-26312.xml emd-26312.xml | 17.1 KB 17.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_26312.png emd_26312.png | 105.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-26312.cif.gz emd-26312.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26312 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26312 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26312 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26312 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7uaaMC  7tysC  7tytC  7u1eC  7u1qC  7u1sC  7u24C  7u2xC  7u6yC  7u7mC  7uqrC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_26312.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_26312.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.71 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : KATP-ATP-CTDup
| Entire | Name: KATP-ATP-CTDup |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: KATP-ATP-CTDup
| Supramolecule | Name: KATP-ATP-CTDup / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) |
-Supramolecule #2: Kir6.2
| Supramolecule | Name: Kir6.2 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 / Details: Adenovirus-based infection of INS-1 cells |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) |
-Supramolecule #3: SUR1
| Supramolecule | Name: SUR1 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 / Details: Adenovirus-based infection of INS-1 cells |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: tetramer / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MLSRKGIIPE EYVLTRLAED PTEPRYRTRE RRARFVSKKG NCNVAHKNIR EQGRFLQDVF TTLVDLKWPH TLLIFTMSFL CSWLLFAMV WWLIAFAHGD LAPGEGTNVP CVTSIHSFSS AFLFSIEVQV TIGFGGRMVT EECPLAILIL IVQNIVGLMI N AIMLGCIF ...String: MLSRKGIIPE EYVLTRLAED PTEPRYRTRE RRARFVSKKG NCNVAHKNIR EQGRFLQDVF TTLVDLKWPH TLLIFTMSFL CSWLLFAMV WWLIAFAHGD LAPGEGTNVP CVTSIHSFSS AFLFSIEVQV TIGFGGRMVT EECPLAILIL IVQNIVGLMI N AIMLGCIF MKTAQAHRRA ETLIFSKHAV ITLRHGRLCF MLRVGDLRKS MIISATIHMQ VVRKTTSPEG EVVPLHQVDI PM ENGVGGN SIFLVAPLII YHVIDSNSPL YDLAPSDLHH HQDLEIIVIL EGVVETTGIT TQARTSYLAD EILWGQRFVP IVA EEDGRY SVDYSKFGNT VKVPTPLCTA RQLDEDRSLL DALTLASSRG PLRKRSVAVA KAKPKFSISP DSLS UniProtKB: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11 |
-Macromolecule #2: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 8
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 8 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Details: focused on one SUR1 copy / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPLAFCGTEN HSAAYRVDQG VLNNGCFVDA LNVVPHVFLL FITFPILFIG WGSQSSKVHI HHSTWLHFP GHNLRWILTF ILLFVLVCEI AEGILSDGVT ESRHLHLYMP AGMAFMAAIT S VVYYHNIE TSNFPKLLIA LLIYWTLAFI TKTIKFVKFY DHAIGFSQLR ...String: MPLAFCGTEN HSAAYRVDQG VLNNGCFVDA LNVVPHVFLL FITFPILFIG WGSQSSKVHI HHSTWLHFP GHNLRWILTF ILLFVLVCEI AEGILSDGVT ESRHLHLYMP AGMAFMAAIT S VVYYHNIE TSNFPKLLIA LLIYWTLAFI TKTIKFVKFY DHAIGFSQLR FCLTGLLVIL YG MLLLVEV NVIRVRRYIF FKTPREVKPP EDLQDLGVRF LQPFVNLLSK GTYWWMNAFI KTA HKKPID LRAIAKLPIA MRALTNYQRL CVAFDAQARK DTQSPQGARA IWRALCHAFG RRLI LSSTF RILADLLGFA GPLCIFGIVD HLGKENHVFQ PKTQFLGVYF VSSQEFLGNA YVLAV LLFL ALLLQRTFLQ ASYYVAIETG INLRGAIQTK IYNKIMHMST SNLSMGEMTA GQICNL VAI DTNQLMWFFF LCPNLWTMPV QIIVGVILLY YILGVSALIG AAVIILLAPV QYFVATK LS QAQRTTLEHS NERLKQTNEM LRGMKLLKLY AWESIFCSRV EVTRRKEMTS LRAFAVYT S ISIFMNTAIP IAAVLITFVG HVSFFKESDL SPSVAFASLS LFHILVTPLF LLSSVVRST VKALVSVQKL SEFLSSAEIR EEQCAPREPA PQGQAGKYQA VPLKVVNRKR PAREEVRDLL GPLQRLAPS MDGDADNFCV QIIGGFFTWT PDGIPTLSNI TIRIPRGQLT MIVGQVGCGK S SLLLATLG EMQKVSGAVF WNSNLPDSEG EDPSSPERET AAGSDIRSRG PVAYASQKPW LL NATVEEN ITFESPFNKQ RYKMVIEACS LQPDIDILPH GDQTQIGERG INLSGGQRQR ISV ARALYQ QTNVVFLDDP FSALDVHLSD HLMQAGILEL LRDDKRTVVL VTHKLQYLPH ADWI IAMKD GTIQREGTLK DFQRSECQLF EHWKTLMNRQ DQELEKETVM ERKASEPSQG LPRAM SSRD GLLLDEEEEE EEAAESEEDD NLSSVLHQRA KIPWRACTKY LSSAGILLLS LLVFSQ LLK HMVLVAIDYW LAKWTDSALV LSPAARNCSL SQECDLDQSV YAMVFTLLCS LGIVLCL VT SVTVEWTGLK VAKRLHRSLL NRIILAPMRF FETTPLGSIL NRFSSDCNTI DQHIPSTL E CLSRSTLLCV SALTVISYVT PVFLVALLPL AVVCYFIQKY FRVASRDLQQ LDDTTQLPL VSHFAETVEG LTTIRAFRYE ARFQQKLLEY TDSNNIASLF LTAANRWLEV CMEYIGACVV LIAAATSIS NSLHRELSAG LVGLGLTYAL MVSNYLNWMV RNLADMEIQL GAVKRIHALL K TEAESYEG LLAPSLIPKN WPDQGKIQIQ NLSVRYDSSL KPVLKHVNTL ISPGQKIGIC GR TGSGKSS FSLAFFRMVD MFEGRIIIDG IDIAKLPLHT LRSRLSIILQ DPVLFSGTIR FNL DPEKKC SDSTLWEALE IAQLKLVVKA LPGGLDAIIT EGGENFSQGQ RQLFCLARAF VRKT SIFIM DEATASIDMA TENILQKVVM TAFADRTVVT IAHRVHTILS ADLVMVLKRG AILEF DKPE TLLSQKDSVF ASFVRADK UniProtKB: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 8 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION / Number images used: 33000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: COMMON LINE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7uaa: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
















 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)