[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24846: Human KATP channel in open conformation, focused on Kir and one S... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-24846 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human KATP channel in open conformation, focused on Kir and one SUR, position 5 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | focused on Kir and one SUR after sharpening (B-factor: 58.6), position 5 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / KATP / ATP-sensitive potassium channel / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of neuroblast migration / positive regulation of uterine smooth muscle relaxation / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / Defective ABCC8 can cause hypo- and hyper-glycemias / potassium ion-transporting ATPase complex / negative regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability / ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity / glutamate secretion, neurotransmission / response to resveratrol / inward rectifying potassium channel ...negative regulation of neuroblast migration / positive regulation of uterine smooth muscle relaxation / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / Defective ABCC8 can cause hypo- and hyper-glycemias / potassium ion-transporting ATPase complex / negative regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability / ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity / glutamate secretion, neurotransmission / response to resveratrol / inward rectifying potassium channel / sulfonylurea receptor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development / positive regulation of tight junction disassembly / CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / ATPase-coupled monoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / positive regulation of potassium ion transport / response to pH / negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance / : / ankyrin binding / negative regulation of glial cell proliferation / response to zinc ion / neuromuscular process / intracellular glucose homeostasis / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / action potential / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / potassium channel activity / ABC-type transporter activity / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / cellular response to nutrient levels / T-tubule / potassium ion transmembrane transport / negative regulation of angiogenesis / response to ischemia / determination of adult lifespan / potassium ion transport / Regulation of insulin secretion / female pregnancy / ADP binding / negative regulation of insulin secretion / sarcolemma / visual learning / response to insulin / transmembrane transport / memory / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / synaptic vesicle membrane / presynaptic membrane / response to lipopolysaccharide / transmembrane transporter binding / response to hypoxia / response to xenobiotic stimulus / apoptotic process / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
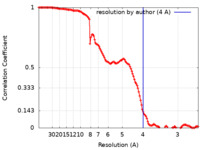
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao C / MacKinnon R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021Title: Molecular structure of an open human K channel. Authors: Chen Zhao / Roderick MacKinnon /  Abstract: K channels are metabolic sensors that translate intracellular ATP/ADP balance into membrane excitability. The molecular composition of K includes an inward-rectifier potassium channel (Kir) and an ...K channels are metabolic sensors that translate intracellular ATP/ADP balance into membrane excitability. The molecular composition of K includes an inward-rectifier potassium channel (Kir) and an ABC transporter-like sulfonylurea receptor (SUR). Although structures of K have been determined in many conformations, in all cases, the pore in Kir is closed. Here, we describe human pancreatic K (hK) structures with an open pore at 3.1- to 4.0-Å resolution using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Pore opening is associated with coordinated structural changes within the ATP-binding site and the channel gate in Kir. Conformational changes in SUR are also observed, resulting in an area reduction of contact surfaces between SUR and Kir. We also observe that pancreatic hK exhibits the unique (among inward-rectifier channels) property of PIP-independent opening, which appears to be correlated with a docked cytoplasmic domain in the absence of PIP. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24846.map.gz emd_24846.map.gz | 173.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24846-v30.xml emd-24846-v30.xml emd-24846.xml emd-24846.xml | 17.6 KB 17.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_24846_fsc.xml emd_24846_fsc.xml | 12.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_24846.png emd_24846.png | 141.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24846.cif.gz emd-24846.cif.gz | 7.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24846 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24846 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24846 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24846 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 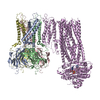 7s61MC 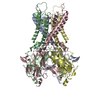 7s5tC  7s5vC  7s5xC  7s5yC  7s5zC  7s60C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24846.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 184 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24846.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 184 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
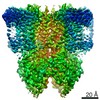
| Annotation | focused on Kir and one SUR after sharpening (B-factor: 58.6), position 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human KATP channel composed of Kir6.2 (C166S G334D) and SUR1
| Entire | Name: Human KATP channel composed of Kir6.2 (C166S G334D) and SUR1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human KATP channel composed of Kir6.2 (C166S G334D) and SUR1
| Supramolecule | Name: Human KATP channel composed of Kir6.2 (C166S G334D) and SUR1 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 881.87 kDa/nm |
-Supramolecule #2: Kir6.2 (C166S G334D) subunit of human KATP
| Supramolecule | Name: Kir6.2 (C166S G334D) subunit of human KATP / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: SUR1 subunit of human KATP
| Supramolecule | Name: SUR1 subunit of human KATP / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 43.622746 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MLSRKGIIPE EYVLTRLAED PAKPRYRARQ RRARFVSKKG NCNVAHKNIR EQGRFLQDVF TTLVDLKWPH TLLIFTMSFL CSWLLFAMA WWLIAFAHGD LAPSEGTAEP CVTSIHSFSS AFLFSIEVQV TIGFGGRMVT EECPLAILIL IVQNIVGLMI N AIMLGSIF ...String: MLSRKGIIPE EYVLTRLAED PAKPRYRARQ RRARFVSKKG NCNVAHKNIR EQGRFLQDVF TTLVDLKWPH TLLIFTMSFL CSWLLFAMA WWLIAFAHGD LAPSEGTAEP CVTSIHSFSS AFLFSIEVQV TIGFGGRMVT EECPLAILIL IVQNIVGLMI N AIMLGSIF MKTAQAHRRA ETLIFSKHAV IALRHGRLCF MLRVGDLRKS MIISATIHMQ VVRKTTSPEG EVVPLHQVDI PM ENGVGGN SIFLVAPLII YHVIDANSPL YDLAPSDLHH HQDLEIIVIL EGVVETTGIT TQARTSYLAD EILWGQRFVP IVA EEDGRY SVDYSKFDNT VKVPTPLCTA RQLDEDHSLL EALTLASARG PLRKRSVPMA KAKPKFSISP DSLS UniProtKB: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11 |
-Macromolecule #2: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 8
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 8 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 177.237266 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGPLAFCGSE NHSAAYRVDQ GVLNNGCFVD ALNVVPHVFL LFITFPILFI GWGSQSSKVH IHHSTWLHFP GHNLRWILTF MLLFVLVCE IAEGILSDGV TESHHLHLYM PAGMAFMAAV TSVVYYHNIE TSNFPKLLIA LLVYWTLAFI TKTIKFVKFL D HAIGFSQL ...String: MGPLAFCGSE NHSAAYRVDQ GVLNNGCFVD ALNVVPHVFL LFITFPILFI GWGSQSSKVH IHHSTWLHFP GHNLRWILTF MLLFVLVCE IAEGILSDGV TESHHLHLYM PAGMAFMAAV TSVVYYHNIE TSNFPKLLIA LLVYWTLAFI TKTIKFVKFL D HAIGFSQL RFCLTGLLVI LYGMLLLVEV NVIRVRRYIF FKTPREVKPP EDLQDLGVRF LQPFVNLLSK GTYWWMNAFI KT AHKKPID LRAIGKLPIA MRALTNYQRL CEAFDAQVRK DIQGTQGARA IWQALSHAFG RRLVLSSTFR ILADLLGFAG PLC IFGIVD HLGKENDVFQ PKTQFLGVYF VSSQEFLANA YVLAVLLFLA LLLQRTFLQA SYYVAIETGI NLRGAIQTKI YNKI MHLST SNLSMGEMTA GQICNLVAID TNQLMWFFFL CPNLWAMPVQ IIVGVILLYY ILGVSALIGA AVIILLAPVQ YFVAT KLSQ AQRSTLEYSN ERLKQTNEML RGIKLLKLYA WENIFRTRVE TTRRKEMTSL RAFAIYTSIS IFMNTAIPIA AVLITF VGH VSFFKEADFS PSVAFASLSL FHILVTPLFL LSSVVRSTVK ALVSVQKLSE FLSSAEIREE QCAPHEPTPQ GPASKYQ AV PLRVVNRKRP AREDCRGLTG PLQSLVPSAD GDADNCCVQI MGGYFTWTPD GIPTLSNITI RIPRGQLTMI VGQVGCGK S SLLLAALGEM QKVSGAVFWS SLPDSEIGED PSPERETATD LDIRKRGPVA YASQKPWLLN ATVEENIIFE SPFNKQRYK MVIEACSLQP DIDILPHGDQ TQIGERGINL SGGQRQRISV ARALYQHANV VFLDDPFSAL DIHLSDHLMQ AGILELLRDD KRTVVLVTH KLQYLPHADW IIAMKDGTIQ REGTLKDFQR SECQLFEHWK TLMNRQDQEL EKETVTERKA TEPPQGLSRA M SSRDGLLQ DEEEEEEEAA ESEEDDNLSS MLHQRAEIPW RACAKYLSSA GILLLSLLVF SQLLKHMVLV AIDYWLAKWT DS ALTLTPA ARNCSLSQEC TLDQTVYAMV FTVLCSLGIV LCLVTSVTVE WTGLKVAKRL HRSLLNRIIL APMRFFETTP LGS ILNRFS SDCNTIDQHI PSTLECLSRS TLLCVSALAV ISYVTPVFLV ALLPLAIVCY FIQKYFRVAS RDLQQLDDTT QLPL LSHFA ETVEGLTTIR AFRYEARFQQ KLLEYTDSNN IASLFLTAAN RWLEVRMEYI GACVVLIAAV TSISNSLHRE LSAGL VGLG LTYALMVSNY LNWMVRNLAD MELQLGAVKR IHGLLKTEAE SYEGLLAPSL IPKNWPDQGK IQIQNLSVRY DSSLKP VLK HVNALIAPGQ KIGICGRTGS GKSSFSLAFF RMVDTFEGHI IIDGIDIAKL PLHTLRSRLS IILQDPVLFS GTIRFNL DP ERKCSDSTLW EALEIAQLKL VVKALPGGLD AIITEGGENF SQGQRQLFCL ARAFVRKTSI FIMDEATASI DMATENIL Q KVVMTAFADR TVVTIAHRVH TILSADLVIV LKRGAILEFD KPEKLLSRKD SVFASFVRAD K UniProtKB: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 8 |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 6.83 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 289 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 57.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




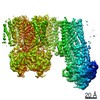
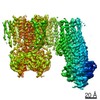
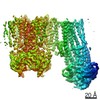
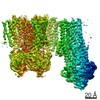

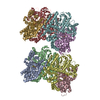

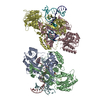








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)