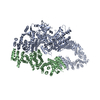
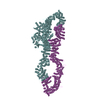
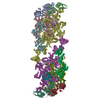
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-23930タイトル Neurofibromin homodimer 複合体 : Neurofibromin homodimerタンパク質・ペプチド : Isoform I of Neurofibromin / / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
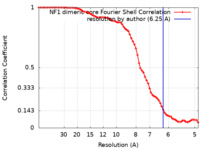
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 6.25 Å Lupton CJ / Bayly-Jones C 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 Not funded
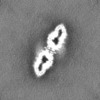
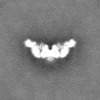
ジャーナル : Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年 : 2021タイトル : The cryo-EM structure of the human neurofibromin dimer reveals the molecular basis for neurofibromatosis type 1.著者 : Christopher J Lupton / Charles Bayly-Jones / Laura D'Andrea / Cheng Huang / Ralf B Schittenhelm / Hari Venugopal / James C Whisstock / Michelle L Halls / Andrew M Ellisdon / 要旨 : Neurofibromin (NF1) mutations cause neurofibromatosis type 1 and drive numerous cancers, including breast and brain tumors. NF1 inhibits cellular proliferation through its guanosine triphosphatase- ... Neurofibromin (NF1) mutations cause neurofibromatosis type 1 and drive numerous cancers, including breast and brain tumors. NF1 inhibits cellular proliferation through its guanosine triphosphatase-activating protein (GAP) activity against rat sarcoma (RAS). In the present study, cryo-electron microscope studies reveal that the human ~640-kDa NF1 homodimer features a gigantic 30 × 10 nm array of α-helices that form a core lemniscate-shaped scaffold. Three-dimensional variability analysis captured the catalytic GAP-related domain and lipid-binding SEC-PH domains positioned against the core scaffold in a closed, autoinhibited conformation. We postulate that interaction with the plasma membrane may release the closed conformation to promote RAS inactivation. Our structural data further allow us to map the location of disease-associated NF1 variants and provide a long-sought-after structural explanation for the extreme susceptibility of the molecule to loss-of-function mutations. Collectively these findings present potential new routes for therapeutic modulation of the RAS pathway. 履歴 登録 2021年5月4日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2021年12月15日 - マップ公開 2021年12月15日 - 更新 2024年5月29日 - 現状 2024年5月29日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 オーストラリア, 1件
オーストラリア, 1件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2021
ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2021
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_23930.map.gz
emd_23930.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-23930-v30.xml
emd-23930-v30.xml emd-23930.xml
emd-23930.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_23930_fsc.xml
emd_23930_fsc.xml FSCデータファイル
FSCデータファイル emd_23930.png
emd_23930.png emd_23930_msk_1.map
emd_23930_msk_1.map マスクマップ
マスクマップ emd-23930.cif.gz
emd-23930.cif.gz emd_23930_additional_1.map.gz
emd_23930_additional_1.map.gz emd_23930_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_23930_half_map_1.map.gz emd_23930_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_23930_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23930
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23930 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23930
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23930 emd_23930_validation.pdf.gz
emd_23930_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_23930_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_23930_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_23930_validation.xml.gz
emd_23930_validation.xml.gz emd_23930_validation.cif.gz
emd_23930_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23930
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23930 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23930
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23930 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_23930.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 38.4 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_23930.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 38.4 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) emd_23930_msk_1.map
emd_23930_msk_1.map 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー
















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)