[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-23882: Vascular KATP channel: Kir6.1 SUR2B quatrefoil-like conformation 2 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23882 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
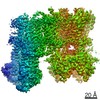
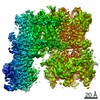
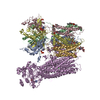
| Title | Vascular KATP channel: Kir6.1 SUR2B quatrefoil-like conformation 2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | KATP / potassium channel / vascular / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcardiac pacemaker cell differentiation / atrioventricular node cell differentiation / vascular process in circulatory system / substrate-dependent cell migration, cell contraction / reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / oxygen metabolic process / synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / reactive gliosis / response to decreased oxygen levels ...cardiac pacemaker cell differentiation / atrioventricular node cell differentiation / vascular process in circulatory system / substrate-dependent cell migration, cell contraction / reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / oxygen metabolic process / synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / reactive gliosis / response to decreased oxygen levels / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / potassium channel activator activity / ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity / response to peptide / glutamate secretion, neurotransmission / response to resveratrol / inward rectifying potassium channel / membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / sulfonylurea receptor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / response to potassium ion / CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade / cardiac conduction / response to oxygen levels / NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly / response to hydrogen sulfide / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / ATPase-coupled monoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / cellular respiration / cellular response to chemical stress / coronary vasculature development / vasculature development / cardiac muscle cell contraction / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / cellular response to potassium ion / circulatory system development / nervous system process / heterocyclic compound binding / : / syntaxin binding / blood circulation / Ion homeostasis / sulfonylurea receptor binding / neuromuscular process / blood vessel development / response to ATP / p38MAPK cascade / response to exogenous dsRNA / cellular response to ATP / establishment of cell polarity / myofibril / fatty acid oxidation / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / response to stress / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / transmission of nerve impulse / protein secretion / action potential / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / potassium channel regulator activity / potassium channel activity / fatty acid transport / ABC-type transporter activity / fat cell differentiation / heart morphogenesis / ATP metabolic process / skeletal muscle tissue development / negative regulation of blood pressure / response to cytokine / potassium ion transmembrane transport / presynaptic active zone membrane / T-tubule / acrosomal vesicle / regulation of heart rate / cellular response to calcium ion / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / blood vessel diameter maintenance / response to ischemia / sarcomere / response to activity / determination of adult lifespan / mitochondrion organization / regulation of membrane potential / potassium ion transport / kidney development / response to hydrogen peroxide / microglial cell activation / sarcolemma / response to insulin / response to estrogen / transmembrane transport / calcium ion transmembrane transport / regulation of blood pressure / vasodilation / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / MAPK cascade / presynapse / heart development Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sung MW / Shyng SL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021Title: Vascular K channel structural dynamics reveal regulatory mechanism by Mg-nucleotides. Authors: Min Woo Sung / Zhongying Yang / Camden M Driggers / Bruce L Patton / Barmak Mostofian / John D Russo / Daniel M Zuckerman / Show-Ling Shyng /  Abstract: Vascular tone is dependent on smooth muscle K channels comprising pore-forming Kir6.1 and regulatory SUR2B subunits, in which mutations cause Cantú syndrome. Unique among K isoforms, they lack ...Vascular tone is dependent on smooth muscle K channels comprising pore-forming Kir6.1 and regulatory SUR2B subunits, in which mutations cause Cantú syndrome. Unique among K isoforms, they lack spontaneous activity and require Mg-nucleotides for activation. Structural mechanisms underlying these properties are unknown. Here, we determined cryogenic electron microscopy structures of vascular K channels bound to inhibitory ATP and glibenclamide, which differ informatively from similarly determined pancreatic K channel isoform (Kir6.2/SUR1). Unlike SUR1, SUR2B subunits adopt distinct rotational "propeller" and "quatrefoil" geometries surrounding their Kir6.1 core. The glutamate/aspartate-rich linker connecting the two halves of the SUR-ABC core is observed in a quatrefoil-like conformation. Molecular dynamics simulations reveal MgADP-dependent dynamic tripartite interactions between this linker, SUR2B, and Kir6.1. The structures captured implicate a progression of intermediate states between MgADP-free inactivated, and MgADP-bound activated conformations wherein the glutamate/aspartate-rich linker participates as mobile autoinhibitory domain, suggesting a conformational pathway toward K channel activation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23882.map.gz emd_23882.map.gz | 2.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23882-v30.xml emd-23882-v30.xml emd-23882.xml emd-23882.xml | 14.2 KB 14.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23882.png emd_23882.png | 101.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23882.cif.gz emd-23882.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23882 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23882 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23882 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23882 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mjqMC  7mitC  7mjoC  7mjpC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23882.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23882.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.653 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Vascular KATP channel: Kir6.1 SUR2B quatrefoil-like conformation 2
| Entire | Name: Vascular KATP channel: Kir6.1 SUR2B quatrefoil-like conformation 2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Vascular KATP channel: Kir6.1 SUR2B quatrefoil-like conformation 2
| Supramolecule | Name: Vascular KATP channel: Kir6.1 SUR2B quatrefoil-like conformation 2 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 889 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 8
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 8 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 48.023871 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet monkey) Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet monkey) |
| Sequence | String: MLARKSIIPE EYVLARIAAE NLRKPRIRDR LPKARFIAKS GACNLAHKNI REQGRFLQDI FTTLVDLKWR HTLVIFTMSF LCSWLLFAI MWWLVAFAHG DIYAYMEKGI TEKSGLESAV CVTNVRSFTS AFLFSIEVQV TIGFGGRMMT EECPLAITVL I LQNIVGLI ...String: MLARKSIIPE EYVLARIAAE NLRKPRIRDR LPKARFIAKS GACNLAHKNI REQGRFLQDI FTTLVDLKWR HTLVIFTMSF LCSWLLFAI MWWLVAFAHG DIYAYMEKGI TEKSGLESAV CVTNVRSFTS AFLFSIEVQV TIGFGGRMMT EECPLAITVL I LQNIVGLI INAVMLGCIF MKTAQAHRRA ETLIFSRHAV IAVRNGKLCF MFRVGDLRKS MIISASVRIQ VVKKTTTPEG EV VPIHQQD IPVDNPIESN NIFLVAPLII CHVIDKRSPL YDISATDLVN QDLEVIVILE GVVETTGITT QARTSYIAEE IQW GHRFVS IVTEEEGVYS VDYSKFGNTV RVAAPRCSAR ELDEKPSILI QTLQKSELSH QNSLRKRNSM RRNNSMRRSN SIRR NNSSL MVPKVQFMTP EGNQCPSES UniProtKB: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 8 |
-Macromolecule #2: Isoform SUR2B of ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 9
| Macromolecule | Name: Isoform SUR2B of ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 9 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 174.488562 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet monkey) Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet monkey) |
| Sequence | String: MSLSFCGNNI SSYNIYHGVL QNPCFVDALN LVPHVFLLFI TFPILFIGWG SQSSKVQIHH NTWLHFPGHN LRWILTFALL FVHVCEIAE GIVSDSQRAS RHLHLFMPAV MGFVATTTSI VYYHNIETSN FPKLLLALFL YWVMAFITKT IKLVKYWQLG W GMSDLRFC ...String: MSLSFCGNNI SSYNIYHGVL QNPCFVDALN LVPHVFLLFI TFPILFIGWG SQSSKVQIHH NTWLHFPGHN LRWILTFALL FVHVCEIAE GIVSDSQRAS RHLHLFMPAV MGFVATTTSI VYYHNIETSN FPKLLLALFL YWVMAFITKT IKLVKYWQLG W GMSDLRFC ITGVMVILNG LLMAVEINVI RVRRYVFFMN PQKVKPPEDL QDLGVRFLQP FVNLLSKATY WWMNTLIISA HR KPIDLKA IGKLPIAMRA VTNYVCLKEA YEEQKKKAAD HPNRTPSIWL AMYRAFGRPI LLSSTFRYLA DLLGFAGPLC ISG IVQRVN EPKNNTTRFS ETLSSKEFLE NAHVLAVLLF LALILQRTFL QASYYVTIET GINLRGALLA MIYNKILRLS TSNL SMGEM TLGQINNLVA IETNQLMWFL FLCPNLWAMP VQIIMGVILL YNLLGSSALV GAAVIVLLAP IQYFIATKLA EAQKS TLDY STERLKKTNE ILKGIKLLKL YAWEHIFCKS VEETRMKELS SLKTFALYTS LSIFMNAAIP IAAVLATFVT HAYASG NNL KPAEAFASLS LFHILVTPLF LLSTVVRFAV KAIISVQKLN EFLLSDEIGE DSWRTGEGTL PFESCKKHTG VQSKPIN RK QPGRYHLDNY EQARRLRPAE TEDVAIKVTN GYFSWGSGLA TLSNIDIRIP TGQLTMIVGQ VGCGKSSLLL AILGEMQT L EGKVYWNNVN ESEPSFEATR SRSRYSVAYA AQKPWLLNAT VEENITFGSS FNRQRYKAVT DACSLQPDID LLPFGDQTE IGERGINLSG GQRQRICVAR ALYQNTNIVF LDDPFSALDI HLSDHLMQEG ILKFLQDDKR TVVLVTHKLQ YLTHADWIIA MKDGSVLRE GTLKDIQTKD VELYEHWKTL MNRQDQELEK DMEADQTTLE RKTLRRAMYS REAKAQMEDE DEEEEEEEDE D DNMSTVMR LRTKMPWKTC WWYLTSGGFF LLFLMIFSKL LKHSVIVAID YWLATWTSEY SINDPGKADQ TFYVAGFSIL CG AGIFLCL VTSLTVEWMG LTAAKNLHHN LLNKIILGPI RFFDTTPLGL ILNRFSADTN IIDQHIPPTL ESLTRSTLLC LSA IGMISY ATPVFLIALA PLGVAFYFIQ KYFRVASKDL QELDDSTQLP LLCHFSETAE GLTTIRAFRH ETRFKQRMLE LTDT NNIAY LFLSAANRWL EVRTDYLGAC IVLTASIASI SGSSNSGLVG LGLLYALTIT NYLNWVVRNL ADLEVQMGAV KKVNS FLTM ESENYEGTMD PSQVPEHWPQ EGEIKIHDLC VRYENNLKPV LKHVKAYIKP GQKVGICGRT GSGKSSLSLA FFRMVD IFD GKIVIDGIDI SKLPLHTLRS RLSIILQDPI LFSGSIRFNL DPECKCTDDR LWEALEIAQL KNMVKSLPGG LDATVTE GG ENFSVGQRQL FCLARAFVRK SSILIMDEAT ASIDMATENI LQKVVMTAFA DRTVVTIAHR VHTILTADLV IVMKRGNI L EYDTPESLLA QEDGVFASFV RADM UniProtKB: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 9 |
-Macromolecule #4: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Support film - Material: GRAPHENE OXIDE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3.0) / Number images used: 22038 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: COMMON LINE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)