[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
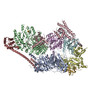
Yorodumi- EMDB-22587: Structure of TFIIH in TFIIH/Rad4-Rad23-Rad33 DNA opening complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22587 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
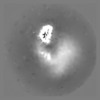
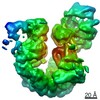
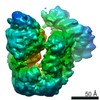
| Title | Structure of TFIIH in TFIIH/Rad4-Rad23-Rad33 DNA opening complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Structure of TFIIH in TFIIH/Rad4-Rad23-Rad33 DNA opening complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TFIIH / Rad4 / Rad4/23 / XPC / NER / Nucleotide Excision Repair / GG-NER / NUCLEAR PROTEIN / NUCLEAR PROTEIN-Transferase complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of mitotic recombination / transcription open complex formation at RNA polymerase II promoter / phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding / RNA polymerase II promoter clearance / positive regulation of mitotic recombination / nucleotide-excision repair factor 3 complex / nucleotide-excision repair, preincision complex assembly / DNA translocase activity / transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding ...regulation of mitotic recombination / transcription open complex formation at RNA polymerase II promoter / phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding / RNA polymerase II promoter clearance / positive regulation of mitotic recombination / nucleotide-excision repair factor 3 complex / nucleotide-excision repair, preincision complex assembly / DNA translocase activity / transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding / DNA 5'-3' helicase / transcription factor TFIIH core complex / transcription factor TFIIH holo complex / transcription preinitiation complex / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / 3'-5' DNA helicase activity / DNA 3'-5' helicase / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / ATPase activator activity / Dual incision in TC-NER / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / transcription by RNA polymerase I / DNA helicase activity / nucleotide-excision repair / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / double-stranded DNA binding / 5'-3' DNA helicase activity / transcription by RNA polymerase II / damaged DNA binding / DNA repair / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | van Eeuwen T / Min JH | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-EM structure of TFIIH/Rad4-Rad23-Rad33 in damaged DNA opening in nucleotide excision repair. Authors: Trevor van Eeuwen / Yoonjung Shim / Hee Jong Kim / Tingting Zhao / Shrabani Basu / Benjamin A Garcia / Craig D Kaplan / Jung-Hyun Min / Kenji Murakami /  Abstract: The versatile nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway initiates as the XPC-RAD23B-CETN2 complex first recognizes DNA lesions from the genomic DNA and recruits the general transcription factor ...The versatile nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway initiates as the XPC-RAD23B-CETN2 complex first recognizes DNA lesions from the genomic DNA and recruits the general transcription factor complex, TFIIH, for subsequent lesion verification. Here, we present a cryo-EM structure of an NER initiation complex containing Rad4-Rad23-Rad33 (yeast homologue of XPC-RAD23B-CETN2) and 7-subunit coreTFIIH assembled on a carcinogen-DNA adduct lesion at 3.9-9.2 Å resolution. A ~30-bp DNA duplex could be mapped as it straddles between Rad4 and the Ssl2 (XPB) subunit of TFIIH on the 3' and 5' side of the lesion, respectively. The simultaneous binding with Rad4 and TFIIH was permitted by an unwinding of DNA at the lesion. Translocation coupled with torque generation by Ssl2 and Rad4 would extend the DNA unwinding at the lesion and deliver the damaged strand to Rad3 (XPD) in an open form suitable for subsequent lesion scanning and verification. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22587.map.gz emd_22587.map.gz | 164.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22587-v30.xml emd-22587-v30.xml emd-22587.xml emd-22587.xml | 30.5 KB 30.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
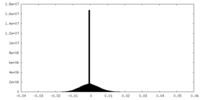
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_22587_fsc.xml emd_22587_fsc.xml | 13.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_22587.png emd_22587.png | 165.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22587.cif.gz emd-22587.cif.gz | 8.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_22587_additional_1.map.gz emd_22587_additional_1.map.gz emd_22587_half_map_1.map.gz emd_22587_half_map_1.map.gz emd_22587_half_map_2.map.gz emd_22587_half_map_2.map.gz | 14.7 MB 179.6 MB 179.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22587 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22587 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22587 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22587 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7k01MC  7k04C  7m2uC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22587.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 226.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22587.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 226.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of TFIIH in TFIIH/Rad4-Rad23-Rad33 DNA opening complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.83 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Additional map
| File | emd_22587_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Additional map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-volume 1
| File | emd_22587_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-volume 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-volume 2
| File | emd_22587_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-volume 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
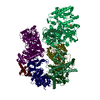
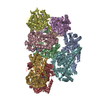
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Ternary complex of TFIIH/Rad4-Rad23-Rad33 with AAF damaged DNA
+Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of TFIIH/Rad4-Rad23-Rad33 with AAF damaged DNA
+Macromolecule #1: General transcription and DNA repair factor IIH subunit TFB1
+Macromolecule #2: General transcription and DNA repair factor IIH subunit TFB4
+Macromolecule #3: DNA repair helicase RAD25
+Macromolecule #4: RNA polymerase II transcription factor B subunit 5
+Macromolecule #5: General transcription and DNA repair factor IIH subunit TFB2
+Macromolecule #6: DNA repair helicase RAD3
+Macromolecule #7: General transcription and DNA repair factor IIH subunit SSL1
+Macromolecule #8: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #9: IRON/SULFUR CLUSTER
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 Component:
Details: Sample dialyzed for 30 minutes into above buffer prior to grid making | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Details: Pelco easyGLOW glow discharge apparatus | ||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: LEICA EM CPC Details: Grids were manually blotted for 2-3 seconds prior to plunge freezing. | ||||||||
| Details | Sample was prepared by Grafix. Sample was monodispersed and well behaved by visual inspection |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum |
| Details | Images collected with image shift |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 6223 / Average exposure time: 2.6 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.8000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




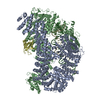

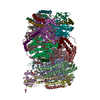
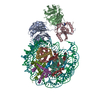
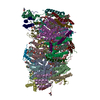













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)