[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-21925: Structural basis of alphaE-catenin - F-actin catch bond behavior -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21925 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
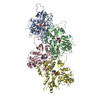
| Title | Structural basis of alphaE-catenin - F-actin catch bond behavior | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | alphaE-catenin - F-actin catch bond behavior | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | alphaE-catenin / catch bond / adherens junction / CELL ADHESION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / Adherens junctions interactions / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / epithelial cell-cell adhesion / gamma-catenin binding / zonula adherens / gap junction assembly / cellular response to indole-3-methanol / vinculin binding ...negative regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / Adherens junctions interactions / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / epithelial cell-cell adhesion / gamma-catenin binding / zonula adherens / gap junction assembly / cellular response to indole-3-methanol / vinculin binding / flotillin complex / Myogenesis / apical junction assembly / catenin complex / negative regulation of cell motility / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleus / axon regeneration / negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / smoothened signaling pathway / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / intercalated disc / actin monomer binding / neuroblast proliferation / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / ovarian follicle development / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / acrosomal vesicle / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / actin filament / filopodium / adherens junction / cell motility / beta-catenin binding / response to estrogen / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / male gonad development / calcium-dependent protein binding / actin filament binding / intracellular protein localization / actin cytoskeleton / lamellipodium / regulation of cell population proliferation / cell body / cadherin binding / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / apoptotic process / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / negative regulation of apoptotic process / structural molecule activity / magnesium ion binding / Golgi apparatus / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.56 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xu XP / Pokutta S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2020 Journal: Elife / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis of αE-catenin-F-actin catch bond behavior. Authors: Xiao-Ping Xu / Sabine Pokutta / Megan Torres / Mark F Swift / Dorit Hanein / Niels Volkmann / William I Weis /   Abstract: Cell-cell and cell-matrix junctions transmit mechanical forces during tissue morphogenesis and homeostasis. α-Catenin links cell-cell adhesion complexes to the actin cytoskeleton, and mechanical ...Cell-cell and cell-matrix junctions transmit mechanical forces during tissue morphogenesis and homeostasis. α-Catenin links cell-cell adhesion complexes to the actin cytoskeleton, and mechanical load strengthens its binding to F-actin in a direction-sensitive manner. Specifically, optical trap experiments revealed that force promotes a transition between weak and strong actin-bound states. Here, we describe the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the F-actin-bound αE-catenin actin-binding domain, which in solution forms a five-helix bundle. In the actin-bound structure, the first helix of the bundle dissociates and the remaining four helices and connecting loops rearrange to form the interface with actin. Deletion of the first helix produces strong actin binding in the absence of force, suggesting that the actin-bound structure corresponds to the strong state. Our analysis explains how mechanical force applied to αE-catenin or its homolog vinculin favors the strongly bound state, and the dependence of catch bond strength on the direction of applied force. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21925.map.gz emd_21925.map.gz | 6.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21925-v30.xml emd-21925-v30.xml emd-21925.xml emd-21925.xml | 18.2 KB 18.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21925.png emd_21925.png | 276.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21925.cif.gz emd-21925.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21925 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21925 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21925 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21925 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6wvtMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21925.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 17.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21925.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 17.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | alphaE-catenin - F-actin catch bond behavior | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.035 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of alphaE-catenin actin binding domain with F-actin
| Entire | Name: Complex of alphaE-catenin actin binding domain with F-actin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of alphaE-catenin actin binding domain with F-actin
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of alphaE-catenin actin binding domain with F-actin type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Supramolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Catenin alpha-1
| Supramolecule | Name: Catenin alpha-1 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 42.109973 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MCDEDETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIE(HIC)G IIT NWDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLD SG DGVTHNVPIY ...String: MCDEDETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIE(HIC)G IIT NWDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLD SG DGVTHNVPIY EGYALPHAIM RLDLAGRDLT DYLMKILTER GYSFVTTAER EIVRDIKEKL CYVALDFENE MATAASSS S LEKSYELPDG QVITIGNERF RCPETLFQPS FIGMESAGIH ETTYNSIMKC DIDIRKDLYA NNVMSGGTTM YPGIADRMQ KEITALAPST MKIKIIAPPE RKYSVWIGGS ILASLSTFQQ MWITKQEYDE AGPSIVHRKC F UniProtKB: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #2: Catenin alpha-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Catenin alpha-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.999281 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: AIMAQLPQEQ KAKIAEQVAS FQEEKSKLDA EVSKWDDSGN DIIVLAKQMC MIMMEMTDFT RGKGPLKNTS DVISAAKKIA EAGSRMDKL GRTIADHCPD SACKQDLLAY LQRIALYCHQ LNICSKVKAE VQNLGGELVV SGVDSAMSLI QAAKNLMNAV V QTVKASYV ...String: AIMAQLPQEQ KAKIAEQVAS FQEEKSKLDA EVSKWDDSGN DIIVLAKQMC MIMMEMTDFT RGKGPLKNTS DVISAAKKIA EAGSRMDKL GRTIADHCPD SACKQDLLAY LQRIALYCHQ LNICSKVKAE VQNLGGELVV SGVDSAMSLI QAAKNLMNAV V QTVKASYV ASTKYQKSQG MASLNLPAVS WKMKAPEKKP LVKREKQDET QTKIKRASQK KHVNPVQALS EFKAMDSI UniProtKB: Catenin alpha-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | helical array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 2-7 / Number grids imaged: 3 / Number real images: 5573 / Average exposure time: 1.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.8000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 75000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 27.4 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: -166.9 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.56 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3) / Number images used: 422822 |
|---|---|
| Segment selection | Number selected: 728331 |
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER Details: in-house rabbit skeletal actin filament reconstruction filtered to 4 nm |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3) |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




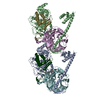
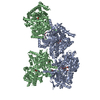
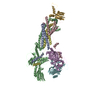
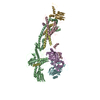





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)