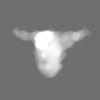
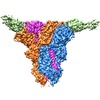
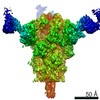
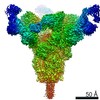
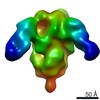
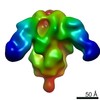
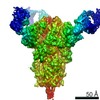
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-21377タイトル Cryo-electron microscopy structure of mouse coronavirus spike protein complexed with its murine receptor CryoEM density map of MHV spike ectodomain complex with its receptor CEACAM1a 複合体 : MHV Spike and CEACAM1a Complex複合体 : Spike glycoproteinタンパク質・ペプチド : Spike glycoprotein複合体 : Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1タンパク質・ペプチド : Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1リガンド : 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
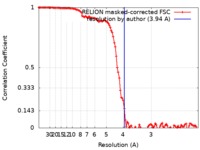
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 / Mus musculus (ハツカネズミ)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.94 Å Shang J / Wan YS 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 National Institutes of Health/National Institute Of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIH/NIAID) R01AI089728
ジャーナル : PLoS Pathog / 年 : 2020タイトル : Structure of mouse coronavirus spike protein complexed with receptor reveals mechanism for viral entry.著者 : Jian Shang / Yushun Wan / Chang Liu / Boyd Yount / Kendra Gully / Yang Yang / Ashley Auerbach / Guiqing Peng / Ralph Baric / Fang Li / 要旨 : Coronaviruses recognize a variety of receptors using different domains of their envelope-anchored spike protein. How these diverse receptor recognition patterns affect viral entry is unknown. Mouse ... Coronaviruses recognize a variety of receptors using different domains of their envelope-anchored spike protein. How these diverse receptor recognition patterns affect viral entry is unknown. Mouse hepatitis coronavirus (MHV) is the only known coronavirus that uses the N-terminal domain (NTD) of its spike to recognize a protein receptor, CEACAM1a. Here we determined the cryo-EM structure of MHV spike complexed with mouse CEACAM1a. The trimeric spike contains three receptor-binding S1 heads sitting on top of a trimeric membrane-fusion S2 stalk. Three receptor molecules bind to the sides of the spike trimer, where three NTDs are located. Receptor binding induces structural changes in the spike, weakening the interactions between S1 and S2. Using protease sensitivity and negative-stain EM analyses, we further showed that after protease treatment of the spike, receptor binding facilitated the dissociation of S1 from S2, allowing S2 to transition from pre-fusion to post-fusion conformation. Together these results reveal a new role of receptor binding in MHV entry: in addition to its well-characterized role in viral attachment to host cells, receptor binding also induces the conformational change of the spike and hence the fusion of viral and host membranes. Our study provides new mechanistic insight into coronavirus entry and highlights the diverse entry mechanisms used by different viruses. 履歴 登録 2020年2月11日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2020年3月4日 - マップ公開 2020年3月4日 - 更新 2024年11月6日 - 現状 2024年11月6日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Murine coronavirus (strain A59) (ウイルス) /
Murine coronavirus (strain A59) (ウイルス) / 
 データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 1件
米国, 1件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: PLoS Pathog / 年: 2020
ジャーナル: PLoS Pathog / 年: 2020

 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_21377.map.gz
emd_21377.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-21377-v30.xml
emd-21377-v30.xml emd-21377.xml
emd-21377.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_21377_fsc.xml
emd_21377_fsc.xml FSCデータファイル
FSCデータファイル emd_21377.png
emd_21377.png emd_21377_msk_1.map
emd_21377_msk_1.map マスクマップ
マスクマップ emd-21377.cif.gz
emd-21377.cif.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21377
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21377 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21377
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21377 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_21377.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 125 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_21377.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 125 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) emd_21377_msk_1.map
emd_21377_msk_1.map 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Murine coronavirus (strain A59) (ウイルス) / 株: A59
Murine coronavirus (strain A59) (ウイルス) / 株: A59
 Murine coronavirus (strain A59) (ウイルス) / 株: A59
Murine coronavirus (strain A59) (ウイルス) / 株: A59 Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM (ウイルス)
Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM (ウイルス)
 Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM (ウイルス)
Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM (ウイルス)
 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)