+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21028 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
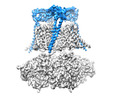
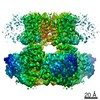
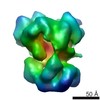
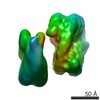
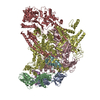
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Ca2+-free hsSlo1-beta4 channel complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | B factor-sharpened Ca2 -free hsSlo1-beta4 channel complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | High conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel / Slo1 channel / BK channel / MaxiK channel / Slo1 beta subunit / beta4 subunit / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCa2+ activated K+ channels / calcium-activated potassium channel activity / regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / translation release factor activity, codon specific / cGMP effects / action potential / potassium channel regulator activity / detection of calcium ion / regulation of vasoconstriction ...Ca2+ activated K+ channels / calcium-activated potassium channel activity / regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / translation release factor activity, codon specific / cGMP effects / action potential / potassium channel regulator activity / detection of calcium ion / regulation of vasoconstriction / neuronal action potential / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transport / chemical synaptic transmission / synapse / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Tao X / MacKinnon R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2019 Journal: Elife / Year: 2019Title: Molecular structures of the human Slo1 K channel in complex with β4. Authors: Xiao Tao / Roderick MacKinnon /  Abstract: Slo1 is a Ca- and voltage-activated K channel that underlies skeletal and smooth muscle contraction, audition, hormone secretion and neurotransmitter release. In mammals, Slo1 is regulated by ...Slo1 is a Ca- and voltage-activated K channel that underlies skeletal and smooth muscle contraction, audition, hormone secretion and neurotransmitter release. In mammals, Slo1 is regulated by auxiliary proteins that confer tissue-specific gating and pharmacological properties. This study presents cryo-EM structures of Slo1 in complex with the auxiliary protein, β4. Four β4, each containing two transmembrane helices, encircle Slo1, contacting it through helical interactions inside the membrane. On the extracellular side, β4 forms a tetrameric crown over the pore. Structures with high and low Ca concentrations show that identical gating conformations occur in the absence and presence of β4, implying that β4 serves to modulate the relative stabilities of 'pre-existing' conformations rather than creating new ones. The effects of β4 on scorpion toxin inhibition kinetics are explained by the crown, which constrains access but does not prevent binding. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21028.map.gz emd_21028.map.gz | 48.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21028-v30.xml emd-21028-v30.xml emd-21028.xml emd-21028.xml | 18.1 KB 18.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21028.png emd_21028.png | 141.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21028.cif.gz emd-21028.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21028 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21028 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21028 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21028 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6v35MC  6v22C  6v38C  6v3gC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21028.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21028.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | B factor-sharpened Ca2 -free hsSlo1-beta4 channel complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : hsSlo1 alpha subunit-beta4 subunit complex
| Entire | Name: hsSlo1 alpha subunit-beta4 subunit complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: hsSlo1 alpha subunit-beta4 subunit complex
| Supramolecule | Name: hsSlo1 alpha subunit-beta4 subunit complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: human high conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel Slo1 (BK) alpha subunit and beta4 subunit |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 580 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit alpha-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit alpha-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 119.988062 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MDALIIPVTM EVPCDSRGQR MWWAFLASSM VTFFGGLFII LLWRTLKYLW TVCCHCGGKT KEAQKINNGS SQADGTLKPV DEKEEAVAA EVGWMTSVKD WAGVMISAQT LTGRVLVVLV FALSIGALVI YFIDSSNPIE SCQNFYKDFT LQIDMAFNVF F LLYFGLRF ...String: MDALIIPVTM EVPCDSRGQR MWWAFLASSM VTFFGGLFII LLWRTLKYLW TVCCHCGGKT KEAQKINNGS SQADGTLKPV DEKEEAVAA EVGWMTSVKD WAGVMISAQT LTGRVLVVLV FALSIGALVI YFIDSSNPIE SCQNFYKDFT LQIDMAFNVF F LLYFGLRF IAANDKLWFW LEVNSVVDFF TVPPVFVSVY LNRSWLGLRF LRALRLIQFS EILQFLNILK TSNSIKLVNL LS IFISTWL TAAGFIHLVE NSGDPWENFQ NNQALTYWEC VYLLMVTMST VGYGDVYAKT TLGRLFMVFF ILGGLAMFAS YVP EIIELI GNRKKYGGSY SAVSGRKHIV VCGHITLESV SNFLKDFLHK DRDDVNVEIV FLHNISPNLE LEALFKRHFT QVEF YQGSV LNPHDLARVK IESADACLIL ANKYCADPDA EDASNIMRVI SIKNYHPKIR IITQMLQYHN KAHLLNIPSW NWKEG DDAI CLAELKLGFI AQSCLAQGLS TMLANLFSMR SFIKIEEDTW QKYYLEGVSN EMYTEYLSSA FVGLSFPTVC ELCFVK LKL LMIAIEYKSA NRESRILINP GNHLKIQEGT LGFFIASDAK EVKRAFFYCK ACHDDITDPK RIKKCGCKRL EDEQPST LS PKKKQRNGGM RNSPNTSPKL MRHDPLLIPG NDQIDNMDSN VKKYDSTGMF HWCAPKEIEK VILTRSEAAM TVLSGHVV V CIFGDVSSAL IGLRNLVMPL RASNFHYHEL KHIVFVGSIE YLKREWETLH NFPKVSILPG TPLSRADLRA VNINLCDMC VILSANQNNI DDTSLQDKEC ILASLNIKSM QFDDSIGVLQ ANSQGFTPPG MDRSSPDNSP VHGMLRQPSI TTGVNIPIIT ELVNDTNVQ FLDQDDDDDP DTELYLTQPF ACGTAFAVSV LDSLMSATYF NDNILTLIRT LVTGGATPEL EALIAEENAL R GGYSTPQT LANRDRCRVA QLALLDGPFA DLGDGGCYGD LFCKALKTYN MLCFGIYRLR DAHLSTPSQC TKRYVITNPP YE FELVPTD LIFCLMQFDS NSLEVLFQ UniProtKB: Peptide chain release factor subunit 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-4
| Macromolecule | Name: Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.991756 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAKLRVAYEY TEAEDKSIRL GLFLIISGVV SLFIFGFCWL SPALQDLQAT EANCTVLSVQ QIGEVFECTF TCGADCRGTS QYPCVQVYV NNSESNSRAL LHSDEHQLLT NPKCSYIPPC KRENQKNLES VMNWQQYWKD EIGSQPFTCY FNQHQRPDDV L LHRTHDEI ...String: MAKLRVAYEY TEAEDKSIRL GLFLIISGVV SLFIFGFCWL SPALQDLQAT EANCTVLSVQ QIGEVFECTF TCGADCRGTS QYPCVQVYV NNSESNSRAL LHSDEHQLLT NPKCSYIPPC KRENQKNLES VMNWQQYWKD EIGSQPFTCY FNQHQRPDDV L LHRTHDEI VLLHCFLWPL VTFVVGVLIV VLTICAKSLA VKAEAMKKRK FSSNSLEVLF Q UniProtKB: Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-4 |
-Macromolecule #3: (1R)-2-{[(S)-{[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl]o...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1R)-2-{[(S)-{[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-1-[(hexadecanoyloxy)methyl]ethyl (9Z)-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 40 / Formula: PGW |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 749.007 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: CHOLESTEROL
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: CLR |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 386.654 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CLR: |
-Macromolecule #5: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 8.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 12 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: Blot for 4 seconds before plunging.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-50 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 3405 / Average exposure time: 15.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 89.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















