[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20850: Focused map of type 3 IP3 receptor N-terminal domain revealing th... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20850 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
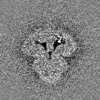
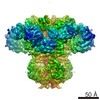
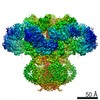
| Title | Focused map of type 3 IP3 receptor N-terminal domain revealing the presence of a self-binding peptide | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Azumaya CM / Linton EA / Risener CJ / Nakagawa T / Karakas E | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2020 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2020Title: Cryo-EM structure of human type-3 inositol triphosphate receptor reveals the presence of a self-binding peptide that acts as an antagonist. Authors: Caleigh M Azumaya / Emily A Linton / Caitlin J Risener / Terunaga Nakagawa / Erkan Karakas /  Abstract: Calcium-mediated signaling through inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptors (IPRs) is essential for the regulation of numerous physiological processes, including fertilization, muscle contraction, ...Calcium-mediated signaling through inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptors (IPRs) is essential for the regulation of numerous physiological processes, including fertilization, muscle contraction, apoptosis, secretion, and synaptic plasticity. Deregulation of IPRs leads to pathological calcium signaling and is implicated in many common diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative, autoimmune, and metabolic diseases. Revealing the mechanism of activation and inhibition of this ion channel will be critical to an improved understanding of the biological processes that are controlled by IPRs. Here, we report structural findings of the human type-3 IPR (IPR-3) obtained by cryo-EM (at an overall resolution of 3.8 Å), revealing an unanticipated regulatory mechanism where a loop distantly located in the primary sequence occupies the IP-binding site and competitively inhibits IP binding. We propose that this inhibitory mechanism must differ qualitatively among IPR subtypes because of their diverse loop sequences, potentially serving as a key molecular determinant of subtype-specific calcium signaling in IPRs. In summary, our structural characterization of human IPR-3 provides critical insights into the mechanistic function of IPRs and into subtype-specific regulation of these important calcium-regulatory channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20850.map.gz emd_20850.map.gz | 138.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20850-v30.xml emd-20850-v30.xml emd-20850.xml emd-20850.xml | 20.3 KB 20.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20850.png emd_20850.png | 83.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_20850_additional.map.gz emd_20850_additional.map.gz emd_20850_additional_1.map.gz emd_20850_additional_1.map.gz emd_20850_half_map_1.map.gz emd_20850_half_map_1.map.gz emd_20850_half_map_2.map.gz emd_20850_half_map_2.map.gz | 138.8 MB 138.8 MB 15.3 MB 15.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20850 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20850 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20850 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20850 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20850.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20850.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.247 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
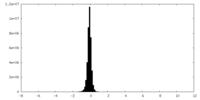
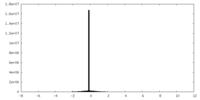
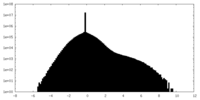
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
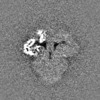
-Additional map: unsharpened map
| File | emd_20850_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | unsharpened map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
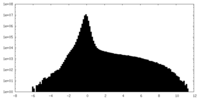
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: unsharpened map
| File | emd_20850_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | unsharpened map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_20850_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_20850_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3
| Entire | Name: inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3
| Supramolecule | Name: inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.2 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3
| Macromolecule | Name: inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSSFLHIGDI VSLYAEGSVN GFISTLGLVD DRCVVEPAAG DLDNPPKKFR DCLFKVCPMN RYSAQKQYWK AKQTKQDKEK IADVVLLQKL QHAAQMEQKQ NDTENKKVHG DVVKYGSVIQ LLHMKSNKYL TVNKRLPALL EKNAMRVTLD ATGNEGSWLF IQPFWKLRSN ...String: MSSFLHIGDI VSLYAEGSVN GFISTLGLVD DRCVVEPAAG DLDNPPKKFR DCLFKVCPMN RYSAQKQYWK AKQTKQDKEK IADVVLLQKL QHAAQMEQKQ NDTENKKVHG DVVKYGSVIQ LLHMKSNKYL TVNKRLPALL EKNAMRVTLD ATGNEGSWLF IQPFWKLRSN GDNVVVGDKV ILNPVNAGQP LHASNYELSD NAGCKEVNSV NCNTSWKINL FMQFRDHLEE VLKGGDVVRL FHAEQEKFLT CDEYKGKLQV FLRTTLRQSA TSATSSNALW EVEVVHHDPC RGGAGHWNGL YRFKHLATGN YLAAEENPSY KGDASDPKAA GMGAQGRTGR RNAGEKIKYC LVAVPHGNDI ASLFELDPTT LQKTDSFVPR NSYVRLRHLC TNTWIQSTNV PIDIEEERPI RLMLGTCPTK EDKEAFAIVS VPVSEIRDLD FANDASSMLA SAVEKLNEGF ISQNDRRFVI QLLEDLVFFV SDVPNNGQNV LDIMVTKPNR ERQKLMREQN ILKQVFGILK APFREKGGEG PLVRLEELSD QKNAPYQHMF RLCYRVLRHS QEDYRKNQEH IAKQFGMMQS QIGYDILAED TITALLHNNR KLLEKHITKT EVETFVSLVR KNREPRFLDY LSDLCVSNHI AIPVTQELIC KCVLDPKNSD ILIRTELRPV KEMAQSHEYL SIEYSEEEVW LTWTDKNNEH HEKSVRQLAQ EARAGNAHDE NVLSYYRYQL KLFARMCLDR QYLAIDEISQ QLGVDLIFLC MADEMLPFDL RASFCHLMLH VHVDRDPQEL VTPVKFARLW TEIPTAITIK DYDSNLNASR DDKKNKFANT MEFVEDYLNN VVSEAVPFAN EEKNKLTFEV VSLAHNLIYF GFYSFSELLR LTRTLLGIID CVQGPPAMLQ AYEDPGGKNV RRSIQGVGHM MSTMVLSRKQ SVFSAPSLSA GASAAEPLDR SKFEENEDIV VMETKLKILE ILQFILNVRL DYRISYLLSV FKKEFVEVFP MQDSGADGTA PAFDSTTANM NLDRIGEQAE AMFGVGKTSS MLEVDDEGGR MFLRVLIHLT MHDYAPLVSG ALQLLFKHFS QRQEAMHTFK QVQLLISAQD VENYKVIKSE LDRLRTMVEK SELWVDKKGS GKGEEVEAGA AKDKKERPTD EEGFLHPPGE KSSENYQIVK GILERLNKMC GVGEQMRKKQ QRLLKNMDAH KVMLDLLQIP YDKGDAKMME ILRYTHQFLQ KFCAGNPGNQ ALLHKHLHLF LTPGLLEAET MQHIFLNNYQ LCSEISEPVL QHFVHLLATH GRHVQYLDFL HTVIKAEGKY VKKCQDMIMT ELTNAGDDVV VFYNDKASLA HLLDMMKAAR DGVEDHSPLM YHISLVDLLA ACAEGKNVYT EIKCTSLLPL EDVVSVVTHE DCITEVKMAY VNFVNHCYVD TEVEMKEIYT SNHIWTLFEN FTLDMARVCS KREKRVADPT LEKYVLSVVL DTINAFFSSP FSENSTSLQT HQTIVVQLLQ STTRLLECPW LQQQHKGSVE ACIRTLAMVA KGRAILLPMD LDAHISSMLS SGASCAAAAQ RNASSYKATT RAFPRVTPTA NQWDYKNIIE KLQDIITALE ERLKPLVQAE LSVLVDVLHW PELLFLEGSE AYQRCESGGF LSKLIQHTKD LMESEEKLCI KVLRTLQQML LKKTKYGDRG NQLRKMLLQN YLQNRKSTSR GDLPDPIGTG LDPDWSAIAA TQCRLDKEGA TKLVCDLITS TKNEKIFQES IGLAIHLLDG GNTEIQKSFH NLMMSDKKSE RFFKVLHDRM KRAQQETKST VAVNMNDLGS QPHEDREPVD PTTKGRVASF SIPGSSSRYS LGPSLRRGHE VSERVQSSEM GTSVLIMQPI LRFLQLLCEN HNRDLQNFLR CQNNKTNYNL VCETLQFLDI MCGSTTGGLG LLGLYINEDN VGLVIQTLET LTEYCQGPCH ENQTCIVTHE SNGIDIITAL ILNDISPLCK YRMDLVLQLK DNASKLLLAL MESRHDSENA ERILISLRPQ ELVDVIKKAY LQEEERENSE VSPREVGHNI YILALQLSRH NKQLQHLLKP VKRIQEEEAE GISSMLSLNN KQLSQMLKSS APAQEEEEDP LAYYENHTSQ IEIVRQDRSM EQIVFPVPGI CQFLTEETKH RLFTTTEQDE QGSKVSDFFD QSSFLHNEME WQRKLRSMPL IYWFSRRMTL WGSISFNLAV FINIIIAFFY PYMEGASTGV LDSPLISLLF WILICFSIAA LFTKRYSIRP LIVALILRSI YYLGIGPTLN ILGALNLTNK IVFVVSFVGN RGTFIRGYKA MVMDMEFLYH VGYILTSVLG LFAHELFYSI LLFDLIYREE TLFNVIKSVT RNGRSILLTA LLALILVYLF SIVGFLFLKD DFILEVDRLP NNHSTASPLG MPHGAAAFVD TCSGDKMDCV SGLSVPEVLE EDRELDSTER ACDTLLMCIV TVMNHGLRNG GGVGDILRKP SKDESLFPAR VVYDLLFFFI VIIIVLNLIF GVIIDTFADL RSEKQKKEEI LKTTCFICGL ERDKFDNKTV SFEEHIKLEH NMWNYLYFIV LVRVKNKTDY TGPESYVAQM IKNKNLDWFP RMRAMSLVSN EGEGEQNEIR ILQDKLNSTM KLVSHLTAQL NELKEQMTEQ RKRRQRLGFV DVQNCISRGE NLYFQSAWSH PQFEKGGGSG GGSGGSAWSH PQFEK |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.3 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: The grid was blotted for 3 seconds at force 1. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.2 mm / Nominal magnification: 31000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





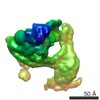


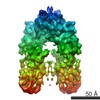
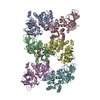
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)