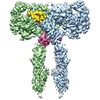
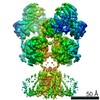
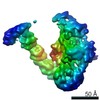
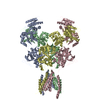
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-20522タイトル Cryo-EM structure of full-length insulin receptor bound to 4 insulin. 3D refinement was focused on the extracellular region. Cryo-EM structure of full-length insulin receptor bound to 4 insulin. 3D refinement was focused on the entire extracellular region. 複合体 : Full-length insulin receptor/insulin complexタンパク質・ペプチド : Insulin receptorタンパク質・ペプチド : Insulin / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.2 Å Uchikawa E / Choi E ジャーナル : Elife / 年 : 2019タイトル : Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex.著者 : Emiko Uchikawa / Eunhee Choi / Guijun Shang / Hongtao Yu / Xiao-Chen Bai / 要旨 : Insulin signaling controls metabolic homeostasis. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of full-length insulin receptor (IR) and insulin complex in the active state. This structure unexpectedly ... Insulin signaling controls metabolic homeostasis. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of full-length insulin receptor (IR) and insulin complex in the active state. This structure unexpectedly reveals that maximally four insulins can bind the 'T'-shaped IR dimer at four distinct sites related by 2-fold symmetry. Insulins 1 and 1' bind to sites 1 and 1', formed by L1 of one IR protomer and α-CT and FnIII-1 of the other. Insulins 2 and 2' bind to sites 2 and 2' on FnIII-1 of each protomer. Mutagenesis and cellular assays show that both sites 1 and 2 are required for optimal insulin binding and IR activation. We further identify a homotypic FnIII-2-FnIII-2 interaction in mediating the dimerization of membrane proximal domains in the active IR dimer. Our results indicate that binding of multiple insulins at two distinct types of sites disrupts the autoinhibited apo-IR dimer and stabilizes the active dimer. 履歴 登録 2019年7月27日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2019年9月4日 - マップ公開 2019年9月4日 - 更新 2024年10月23日 - 現状 2024年10月23日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 引用
引用 ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2019
ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2019
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_20522.map.gz
emd_20522.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-20522-v30.xml
emd-20522-v30.xml emd-20522.xml
emd-20522.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_20522.png
emd_20522.png emd-20522.cif.gz
emd-20522.cif.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20522
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20522 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20522
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20522 emd_20522_validation.pdf.gz
emd_20522_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_20522_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_20522_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_20522_validation.xml.gz
emd_20522_validation.xml.gz emd_20522_validation.cif.gz
emd_20522_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-20522
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-20522 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-20522
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-20522 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_20522.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 103 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_20522.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 103 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 画像解析
画像解析
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















