[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20505: A complex structure of arrestin-2 bound to neurotensin receptor 1 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20505 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
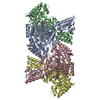
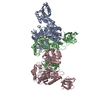
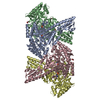
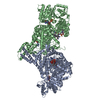
| Title | A complex structure of arrestin-2 bound to neurotensin receptor 1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | cryo-EM structure / beta-arrestin / neurotensin receptor / beta-arrestin-GPCR complex / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationG protein-coupled neurotensin receptor activity / inositol phosphate catabolic process / symmetric synapse / angiotensin receptor binding / D-aspartate import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / Activation of SMO / regulation of membrane depolarization / positive regulation of arachidonate secretion ...G protein-coupled neurotensin receptor activity / inositol phosphate catabolic process / symmetric synapse / angiotensin receptor binding / D-aspartate import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / Activation of SMO / regulation of membrane depolarization / positive regulation of arachidonate secretion / L-glutamate import across plasma membrane / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange / positive regulation of inhibitory postsynaptic potential / arrestin family protein binding / negative regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / positive regulation of glutamate secretion / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / temperature homeostasis / : / response to lipid / stress fiber assembly / positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy / positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / pseudopodium / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of receptor internalization / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / neuropeptide signaling pathway / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / clathrin-coated pit / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / enzyme inhibitor activity / GTPase activator activity / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / dendritic shaft / adult locomotory behavior / learning / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / G protein-coupled receptor binding / G protein-coupled receptor activity / cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane / terminal bouton / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / endocytic vesicle membrane / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / protein transport / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / cytoplasmic vesicle / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / G alpha (s) signalling events / perikaryon / dendritic spine / G alpha (q) signalling events / chemical synaptic transmission / molecular adaptor activity / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / transcription coactivator activity / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / Ub-specific processing proteases / nuclear body / protein ubiquitination / positive regulation of apoptotic process / membrane raft / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Golgi membrane / lysosomal membrane / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of gene expression / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process / chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / cell surface / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / signal transduction / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yin W / Li Z | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  China, 2 items China, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2019 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2019Title: A complex structure of arrestin-2 bound to a G protein-coupled receptor. Authors: Wanchao Yin / Zhihai Li / Mingliang Jin / Yu-Ling Yin / Parker W de Waal / Kuntal Pal / Yanting Yin / Xiang Gao / Yuanzheng He / Jing Gao / Xiaoxi Wang / Yan Zhang / Hu Zhou / Karsten ...Authors: Wanchao Yin / Zhihai Li / Mingliang Jin / Yu-Ling Yin / Parker W de Waal / Kuntal Pal / Yanting Yin / Xiang Gao / Yuanzheng He / Jing Gao / Xiaoxi Wang / Yan Zhang / Hu Zhou / Karsten Melcher / Yi Jiang / Yao Cong / X Edward Zhou / Xuekui Yu / H Eric Xu /    Abstract: Arrestins comprise a family of signal regulators of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which include arrestins 1 to 4. While arrestins 1 and 4 are visual arrestins dedicated to rhodopsin, arrestins ...Arrestins comprise a family of signal regulators of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which include arrestins 1 to 4. While arrestins 1 and 4 are visual arrestins dedicated to rhodopsin, arrestins 2 and 3 (Arr2 and Arr3) are β-arrestins known to regulate many nonvisual GPCRs. The dynamic and promiscuous coupling of Arr2 to nonvisual GPCRs has posed technical challenges to tackle the basis of arrestin binding to GPCRs. Here we report the structure of Arr2 in complex with neurotensin receptor 1 (NTSR1), which reveals an overall assembly that is strikingly different from the visual arrestin-rhodopsin complex by a 90° rotation of Arr2 relative to the receptor. In this new configuration, intracellular loop 3 (ICL3) and transmembrane helix 6 (TM6) of the receptor are oriented toward the N-terminal domain of the arrestin, making it possible for GPCRs that lack the C-terminal tail to couple Arr2 through their ICL3. Molecular dynamics simulation and crosslinking data further support the assembly of the Arr2‒NTSR1 complex. Sequence analysis and homology modeling suggest that the Arr2‒NTSR1 complex structure may provide an alternative template for modeling arrestin-GPCR interactions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20505.map.gz emd_20505.map.gz | 58.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20505-v30.xml emd-20505-v30.xml emd-20505.xml emd-20505.xml | 18.7 KB 18.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20505.png emd_20505.png | 26 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20505.cif.gz emd-20505.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20505 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20505 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20505 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20505 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6pwcMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20505.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20505.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.031 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Fusion complex of Bril-NTSR1-beta-arrestin1-fab30
| Entire | Name: Fusion complex of Bril-NTSR1-beta-arrestin1-fab30 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Fusion complex of Bril-NTSR1-beta-arrestin1-fab30
| Supramolecule | Name: Fusion complex of Bril-NTSR1-beta-arrestin1-fab30 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Neurotensin receptor type 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Neurotensin receptor type 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.555387 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: APSSELDVNT DIYSKVLVTA VYLALFVVGT VGNTVTAFTL ARKKSLQSLQ STVHYHLGSL ALSDLLTLLL AMPVELYNFI WVHHPWAFG DAGCRGYYFL RDACTYATAL NVASLSVERY LAICHPFKAK TLMSRSRTKK FISAIWLASA LLAVPMLFTM G EQNRSADG ...String: APSSELDVNT DIYSKVLVTA VYLALFVVGT VGNTVTAFTL ARKKSLQSLQ STVHYHLGSL ALSDLLTLLL AMPVELYNFI WVHHPWAFG DAGCRGYYFL RDACTYATAL NVASLSVERY LAICHPFKAK TLMSRSRTKK FISAIWLASA LLAVPMLFTM G EQNRSADG QHAGGLVCTP TIHTATVKVV IQVNTFMSFI FPMVVISVLN TIIANKLTVM VRQAAEQGQV CTVGGEHSTF SM AIEPGRV QALRHGVRVL RAVVIAFVVC WLPYHVRRLM FCYISDEQWT PFLYDFYHYF YMVTNALFYV SSTINPILYN LVS ANFRHI FLATLACLCP VWRRRRKRPA FSRKADSVSS NHTLSSNATR ETLY UniProtKB: Neurotensin receptor type 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Neurotensin peptide
| Macromolecule | Name: Neurotensin peptide / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 819.007 Da |
| Sequence | String: RRPYIL |
-Macromolecule #3: Beta-arrestin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Beta-arrestin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.161359 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVDPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTCA FRYGREDLDV LGLTFRKDLF CANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPCSVTL QPGPEDTGKA CGVDYEVKAF CAENLEEKIH K RNSVRLVI ...String: MGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVDPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTCA FRYGREDLDV LGLTFRKDLF CANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPCSVTL QPGPEDTGKA CGVDYEVKAF CAENLEEKIH K RNSVRLVI RKVQYAPERP GPQPTAETTR QFLMSDKPLH LEASLDKEIY YHGEPISVNV HVTNNTNKTV KKIKISVRQY AD ICLFNTA QYKCPVAMEE ADDTVAPSST FCKVYTLTPF LCNNREKRGL ALDGKLKHED TNLASSTLLR EGANREILGI IVS YKVKVK LVVSRGGLLG DLASSDVAVE LPFTLMHPKP KEEPPHREVP ENETPVDTNL IELDTNDDDA AAEDFAR UniProtKB: Beta-arrestin-1 |
-Macromolecule #4: Fab30 heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab30 heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.689643 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MEISEVQLVE SGGGLVQPGG SLRLSCAASG FNVYSSSIHW VRQAPGKGLE WVASISSYYC YTYYADSVKG RFTISADTSK NTAYLQMNS LRAEDTAVYY CARSRQFWYS GLDYWGQGTL VTVSSASTKG PSVFPLAPSS KSTSGGTAAL GCLVKDYFPE P VTVSWNSG ...String: MEISEVQLVE SGGGLVQPGG SLRLSCAASG FNVYSSSIHW VRQAPGKGLE WVASISSYYC YTYYADSVKG RFTISADTSK NTAYLQMNS LRAEDTAVYY CARSRQFWYS GLDYWGQGTL VTVSSASTKG PSVFPLAPSS KSTSGGTAAL GCLVKDYFPE P VTVSWNSG ALTSGVHTFP AVLQSSGLYS LSSVVTVPSS SLGTQTYICN VNHKPSNTKV DKKVEPKSCD KTHHHHHHHH |
-Macromolecule #5: Fab30 light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab30 light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.435064 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSGT DFTLTISSLQ PEDFATYYC QQYKYVPVTF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN FYPREAKVQW KVDNALQSGN S QESVTEQD ...String: SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSGT DFTLTISSLQ PEDFATYYC QQYKYVPVTF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN FYPREAKVQW KVDNALQSGN S QESVTEQD SKDSTYSLSS TLTLSKADYE KHKVYACEVT HQGLSSPVTK SFNRGEC |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 BASE (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 68.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















