[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20070: Structural basis for human coronavirus attachment to sialic acid ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20070 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structural basis for human coronavirus attachment to sialic acid receptors. Apo-HCoV-OC43 S | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Coronavirus spike glycoprotein / sialic acid / HCoV-OC43 / fusion protein / VIRAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Betacoronavirus / Betacoronavirus /  Human coronavirus OC43 Human coronavirus OC43 | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Tortorici MA / Walls AC | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2019Title: Structural basis for human coronavirus attachment to sialic acid receptors. Authors: M Alejandra Tortorici / Alexandra C Walls / Yifei Lang / Chunyan Wang / Zeshi Li / Danielle Koerhuis / Geert-Jan Boons / Berend-Jan Bosch / Félix A Rey / Raoul J de Groot / David Veesler /    Abstract: Coronaviruses cause respiratory tract infections in humans and outbreaks of deadly pneumonia worldwide. Infections are initiated by the transmembrane spike (S) glycoprotein, which binds to host ...Coronaviruses cause respiratory tract infections in humans and outbreaks of deadly pneumonia worldwide. Infections are initiated by the transmembrane spike (S) glycoprotein, which binds to host receptors and fuses the viral and cellular membranes. To understand the molecular basis of coronavirus attachment to oligosaccharide receptors, we determined cryo-EM structures of coronavirus OC43 S glycoprotein trimer in isolation and in complex with a 9-O-acetylated sialic acid. We show that the ligand binds with fast kinetics to a surface-exposed groove and that interactions at the identified site are essential for S-mediated viral entry into host cells, but free monosaccharide does not trigger fusogenic conformational changes. The receptor-interacting site is conserved in all coronavirus S glycoproteins that engage 9-O-acetyl-sialogycans, with an architecture similar to those of the ligand-binding pockets of coronavirus hemagglutinin esterases and influenza virus C/D hemagglutinin-esterase fusion glycoproteins. Our results demonstrate these viruses evolved similar strategies to engage sialoglycans at the surface of target cells. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
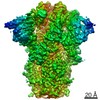
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20070.map.gz emd_20070.map.gz | 6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20070-v30.xml emd-20070-v30.xml emd-20070.xml emd-20070.xml | 14.1 KB 14.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20070.png emd_20070.png | 55.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20070.cif.gz emd-20070.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_20070_additional.map.gz emd_20070_additional.map.gz | 230.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20070 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20070 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20070 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20070 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6ohwMC  0557C  6nzkC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20070.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20070.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Unsharpened map
| File | emd_20070_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
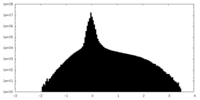
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : HCoV-OC43 spike glycoprotein ectodomain in complex with 9-O-acety...
| Entire | Name: HCoV-OC43 spike glycoprotein ectodomain in complex with 9-O-acetyl sialic acid |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: HCoV-OC43 spike glycoprotein ectodomain in complex with 9-O-acety...
| Supramolecule | Name: HCoV-OC43 spike glycoprotein ectodomain in complex with 9-O-acetyl sialic acid type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Betacoronavirus Betacoronavirus |
-Macromolecule #1: Spike surface glycoprotein
| Macromolecule | Name: Spike surface glycoprotein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Human coronavirus OC43 Human coronavirus OC43 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 146.438312 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MPMGSLQPLA TLYLLGMLVA SVLAVIGDLK CTSDNINDKD TGPPPISTDT VDVTNGLGTY YVLDRVYLNT TLFLNGYYPT SGSTYRNMA LKGSVLLSRL WFKPPFLSDF INGIFAKVKN TKVIKDRVMY SEFPAITIGS TFVNTSYSVV VQPRTINSTQ D GDNKLQGL ...String: MPMGSLQPLA TLYLLGMLVA SVLAVIGDLK CTSDNINDKD TGPPPISTDT VDVTNGLGTY YVLDRVYLNT TLFLNGYYPT SGSTYRNMA LKGSVLLSRL WFKPPFLSDF INGIFAKVKN TKVIKDRVMY SEFPAITIGS TFVNTSYSVV VQPRTINSTQ D GDNKLQGL LEVSVCQYNM CEYPQTICHP NLGNHRKELW HLDTGVVSCL YKRNFTYDVN ADYLYFHFYQ EGGTFYAYFT DT GVVTKFL FNVYLGMALS HYYVMPLTCN SKLTLEYWVT PLTSRQYLLA FNQDGIIFNA VDCMSDFMSE IKCKTQSIAP PTG VYELNG YTVQPIADVY RRKPNLPNCN IEAWLNDKSV PSPLNWERKT FSNCNFNMSS LMSFIQADSF TCNNIDAAKI YGMC FSSIT IDKFAIPNGR KVDLQLGNLG YLQSFNYRID TTATSCQLYY NLPAANVSVS RFNPSTWNKR FGFIEDSVFK PRPAG VLTN HDVVYAQHCF KAPKNFCPCK LNGSCVGSGP GKNNGIGTCP AGTNYLTCDN LCTPDPITFT GTYKCPQTKS LVGIGE HCS GLAVKSDYCG GNSCTCRPQA FLGWSADSCL QGDKCNIFAN FILHDVNSGL TCSTDLQKAN TDIILGVCVN YDLYGIL GQ GIFVEVNATY YNSWQNLLYD SNGNLYGFRD YITNRTFMIR SCYSGRVSAA FHANSSEPAL LFRNIKCNYV FNNSLTRQ L QPINYFDSYL GCVVNAYNST AISVQTCDLT VGSGYCVDYS KNGGSGGAIT TGYRFTNFEP FTVNSVNDSL EPVGGLYEI QIPSEFTIGN MVEFIQTSSP KVTIDCAAFV CGDYAACKSQ LVEYGSFCDN INAILTEVNE LLDTTQLQVA NSLMNGVTLS TKLKDGVNF NVDDINFSPV LGCLGSECSK ASSRSAIEDL LFDKVKLSDV GFVEAYNNCT GGAEIRDLIC VQSYKGIKVL P PLLSENQF SGYTLAATSA SLFPPWTAAA GVPFYLNVQY RINGLGVTMD VLSQNQKLIA NAFNNALYAI QEGFDATNSA LV KIQAVVN ANAEALNNLL QQLSNRFGAI SASLQEILSR LDALEAEAQI DRLINGRLTA LNAYVSQQLS DSTLVKFSAA QAM EKVNEC VKSQSSRINF CGNGNHIISL VQNAPYGLYF IHFSYVPTKY VTARVSPGLC IAGDRGIAPK SGYFVNVNNT WMYT GSGYY YPEPITENNV VVMSTCAVNY TKAPYVMLNT SIPNLPDFKE ELDQWFKNQT SVAPDLSLDY INVTFLDLLI KRMKQ IEDK IEEIESKQKK IENEIARIKK IKLVPRGSLE WSHPQFEK UniProtKB: Spike glycoprotein |
-Macromolecule #5: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 15 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #6: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 186 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C3 (3 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Number images used: 105919 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: RELION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




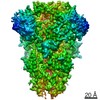
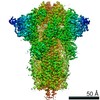
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)