[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-1954: Negative stain reconstruction of the Vibrio cholerae toxin coregu... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1954 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Negative stain reconstruction of the Vibrio cholerae toxin coregulated pilus (TCP) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | TCP - negative stain | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Vibrio cholerae / Type IV pili / helical filaments / helical symmetry / autoagglutination | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 21.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li J / Egelman EH / Craig L | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2012 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2012Title: Structure of the Vibrio cholerae Type IVb Pilus and stability comparison with the Neisseria gonorrhoeae type IVa pilus. Authors: Juliana Li / Edward H Egelman / Lisa Craig /  Abstract: Type IV pili are multifunctional filaments displayed on many bacterial pathogens. Members of the Type IVa pilus subclass are found on a diverse group of human pathogens, whereas Type IVb pili are ...Type IV pili are multifunctional filaments displayed on many bacterial pathogens. Members of the Type IVa pilus subclass are found on a diverse group of human pathogens, whereas Type IVb pili are found almost exclusively on enteric bacteria. The Type IVa and IVb subclasses are distinguished by differences in the pilin subunits, including the fold of the globular domain. To understand the implications of the distinct pilin folds, we compared the stabilities of pilin subunits and pilus filaments for the Type IVa GC pilus from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and the Type IVb toxin-coregulated pilus (TCP) from Vibrio cholerae. We show that while recombinant TCP pilin is more stable than GC pilin, the GC pili are more resistant to proteolysis, heat and chemical denaturation than TCP, remaining intact in 8 M urea. To understand these differences, we determined the TCP structure by electron microscopy and three-dimensional image reconstruction. TCP have an architecture similar to that of GC pili, with subunits arranged in a right-handed 1-start helix and related by an 8.4-Å axial rise and a 96.8° azimuthal rotation. However, the TCP subunits are not as tightly packed as GC pilins, and the distinct Type IVb pilin fold exposes a segment of the α-helical core of TCP. Hydrophobic interactions dominate for both pilus subtypes, but base stacking by aromatic residues conserved among the Type IVa pilins may contribute to GC pilus stability. The extraordinary stability of GC pili may represent an adaptation of the Type IVa pili to harsh environments and the need to retract against external forces. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1954.map.gz emd_1954.map.gz | 1.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1954-v30.xml emd-1954-v30.xml emd-1954.xml emd-1954.xml | 10.2 KB 10.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  em-1954.jpg em-1954.jpg | 33.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1954 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1954 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1954 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1954 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1954.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 29.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1954.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 29.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | TCP - negative stain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Toxin coregulated pilus (TCP)
| Entire | Name: Toxin coregulated pilus (TCP) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Toxin coregulated pilus (TCP)
| Supramolecule | Name: Toxin coregulated pilus (TCP) / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: Polymer / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 42 MDa / Theoretical: 42 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: TcpA
| Macromolecule | Name: TcpA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Type IV pilin / Oligomeric state: polymer / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 21 KDa / Theoretical: 21 KDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Details: PBS (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 2 mM KH2PO4 pH 7.4), 10 mM EDTA |
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Details: 1% phosphotungstic acid, pH 7 |
| Grid | Details: carbon-coated copper grids (EMS) |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: corrected at 100KX |
| Details | Low dose mode |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: NIKON COOLSCAN / Digitization - Sampling interval: 2.49 µm / Number real images: 15 / Average electron dose: 10 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 30000 / Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 30000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Eucentric / Specimen holder model: SIDE ENTRY, EUCENTRIC |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 8.5 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 96.8 ° Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 21.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: IHRSR Details: reconstruction was obtained from 8,034 overlapping particles (200 pixels length with a 190-pixel overlap, 80 pixels in width, padded to 200 pixels) |
|---|
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Details | PDBEntryID_givenInChain. Protocol: Rigid body. The TcpA pilin subunit was docked manually using the program Chimera. The filament was generated by applying the symmetry parameters to the docked subunit. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





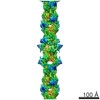
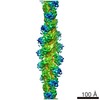
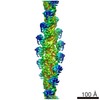
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















