[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-19132: Structure of dynein-2 intermediate chain DYNC2I2 (WDR34) in compl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of dynein-2 intermediate chain DYNC2I2 (WDR34) in complex with dynein-2 heavy chain DYNC2H1. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Locally refined map, locally sharpened with locscale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | dynein / cilia / intraflagellar transport / complex / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMGMT-mediated DNA damage reversal / nitric-oxide synthase inhibitor activity / deoxyribonuclease inhibitor activity / negative regulation of DNA strand resection involved in replication fork processing / negative regulation of phosphorylation / intraciliary retrograde transport / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase activity / visual behavior / 9+2 motile cilium ...MGMT-mediated DNA damage reversal / nitric-oxide synthase inhibitor activity / deoxyribonuclease inhibitor activity / negative regulation of DNA strand resection involved in replication fork processing / negative regulation of phosphorylation / intraciliary retrograde transport / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase activity / visual behavior / 9+2 motile cilium / cilium movement involved in cell motility / intraciliary transport / spinal cord motor neuron differentiation / dynein light chain binding / dynein heavy chain binding / embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis / Activation of BIM and translocation to mitochondria / motile cilium assembly / DNA-methyltransferase activity / Intraflagellar transport / negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / protein localization to cilium / DNA alkylation repair / positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / coronary vasculature development / non-motile cilium assembly / dorsal/ventral pattern formation / ciliary plasm / dynein complex / determination of left/right symmetry / embryonic limb morphogenesis / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / microtubule motor activity / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / microtubule-based movement / Macroautophagy / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / ciliary base / ciliary tip / forebrain development / pericentriolar material / Golgi organization / dynein intermediate chain binding / cytoskeletal motor activity / tertiary granule membrane / ficolin-1-rich granule membrane / cilium assembly / spermatid development / axoneme / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / Hedgehog 'off' state / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / axon cytoplasm / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / centriole / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / substantia nigra development / enzyme inhibitor activity / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / methyltransferase activity / filopodium / kidney development / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / protein processing / kinetochore / apical part of cell / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / mitotic spindle / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / site of double-strand break / scaffold protein binding / methylation / nuclear membrane / microtubule / cytoskeleton / cilium / nuclear body / ciliary basal body / DNA repair / apoptotic process / DNA damage response / Neutrophil degranulation / centrosome / negative regulation of apoptotic process / protein-containing complex binding / nucleolus / enzyme binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mukhopadhyay AG / Toropova K / Daly L / Wells J / Vuolo L / Mladenov M / Seda M / Jenkins D / Stephens DJ / Roberts AJ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 9 items United Kingdom, 9 items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2024 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2024Title: Structure and tethering mechanism of dynein-2 intermediate chains in intraflagellar transport. Authors: Aakash G Mukhopadhyay / Katerina Toropova / Lydia Daly / Jennifer N Wells / Laura Vuolo / Miroslav Mladenov / Marian Seda / Dagan Jenkins / David J Stephens / Anthony J Roberts /  Abstract: Dynein-2 is a large multiprotein complex that powers retrograde intraflagellar transport (IFT) of cargoes within cilia/flagella, but the molecular mechanism underlying this function is still emerging. ...Dynein-2 is a large multiprotein complex that powers retrograde intraflagellar transport (IFT) of cargoes within cilia/flagella, but the molecular mechanism underlying this function is still emerging. Distinctively, dynein-2 contains two identical force-generating heavy chains that interact with two different intermediate chains (WDR34 and WDR60). Here, we dissect regulation of dynein-2 function by WDR34 and WDR60 using an integrative approach including cryo-electron microscopy and CRISPR/Cas9-enabled cell biology. A 3.9 Å resolution structure shows how WDR34 and WDR60 use surprisingly different interactions to engage equivalent sites of the two heavy chains. We show that cilia can assemble in the absence of either WDR34 or WDR60 individually, but not both subunits. Dynein-2-dependent distribution of cargoes depends more strongly on WDR60, because the unique N-terminal extension of WDR60 facilitates dynein-2 targeting to cilia. Strikingly, this N-terminal extension can be transplanted onto WDR34 and retain function, suggesting it acts as a flexible tether to the IFT "trains" that assemble at the ciliary base. We discuss how use of unstructured tethers represents an emerging theme in IFT train interactions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_19132.map.gz emd_19132.map.gz | 3.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-19132-v30.xml emd-19132-v30.xml emd-19132.xml emd-19132.xml | 32.9 KB 32.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_19132_fsc.xml emd_19132_fsc.xml | 19.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_19132.png emd_19132.png | 112 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_19132_msk_1.map emd_19132_msk_1.map | 103 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-19132.cif.gz emd-19132.cif.gz | 10.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_19132_additional_1.map.gz emd_19132_additional_1.map.gz emd_19132_additional_2.map.gz emd_19132_additional_2.map.gz emd_19132_additional_3.map.gz emd_19132_additional_3.map.gz emd_19132_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19132_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19132_half_map_2.map.gz emd_19132_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.6 MB 95.6 MB 4.8 MB 95.7 MB 95.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19132 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19132 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19132 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19132 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8rggMC  8rghC  8rgiC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_19132.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_19132.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Locally refined map, locally sharpened with locscale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
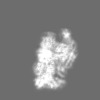
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.828 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
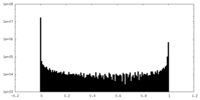
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_19132_msk_1.map emd_19132_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
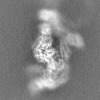
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
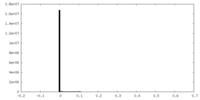
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Locally refined map, unsharpened
| File | emd_19132_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Locally refined map, unsharpened | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Globally refined map, unsharpened
| File | emd_19132_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Globally refined map, unsharpened | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Composite map of locally refined WDR34 and WDR60 map regions.
| File | emd_19132_additional_3.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Composite map of locally refined WDR34 and WDR60 map regions. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_19132_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_19132_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Dynein-2 complex
| Entire | Name: Dynein-2 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Dynein-2 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Dynein-2 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Methylated-DNA--protein-cysteine methyltransferase,Cytoplasmic dy...
| Macromolecule | Name: Methylated-DNA--protein-cysteine methyltransferase,Cytoplasmic dynein 2 heavy chain 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: DYNC2H1 with N-terminal SNAPf tag / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 515.223031 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GDKDCEMKRT TLDSPLGKLE LSGCEQGLHR IIFLGKGTSA ADAVEVPAPA AVLGGPEPLM QATAWLNAYF HQPEAIEEFP VPALHHPVF QQESFTRQVL WKLLKVVKFG EVISYSHLAA LAGNPAATAA VKTALSGNPV PILIPCHRVV QGDLDVGGYE G GLAVKEWL ...String: GDKDCEMKRT TLDSPLGKLE LSGCEQGLHR IIFLGKGTSA ADAVEVPAPA AVLGGPEPLM QATAWLNAYF HQPEAIEEFP VPALHHPVF QQESFTRQVL WKLLKVVKFG EVISYSHLAA LAGNPAATAA VKTALSGNPV PILIPCHRVV QGDLDVGGYE G GLAVKEWL LAHEGHRLGK PGLGGSLEVL FQGPDYDIPT TLEVLFQGPA NGTADVRKLF IFTTTQNYFG LMSELWDQPL LC NCLEINN FLDDGNQMLL RVQRSDAGIS FSNTIEFGDT KDKVLVFFKL RPEVITDENL HDNILVSSML ESPISSLYQA VRQ VFAPML LKDQEWSRNF DPKLQNLLSE LEAGLGIVLR RSDTNLTKLK FKEDDTRGIL TPSDEFQFWI EQAHRGNKQI SKER ANYFK ELFETIAREF YNLDSLSLLE VVDLVETTQD VVDDVWRQTE HDHYPESRML HLLDIIGGSF GRFVQKKLGT LNLWE DPYY LVKESLKAGI SICEQWVIVC NHLTGQVWQR YVPHPWKNEK YFPETLDKLG KRLEEVLAIR TIHEKFLYFL PASEEK IIC LTRVFEPFTG LNPVQYNPYT EPLWKAAVSQ YEKIIAPAEQ KIAGKLKNYI SEIQDSPQQL LQAFLKYKEL VKRPTIS KE LMLERETLLA RLVDSIKDFR LDFENRCRGI PGDASGPLSG KNLSEVVNSI VWVRQLELKV DDTIKIAEAL LSDLPGFR C FHQSAKDLLD QLKLYEQEQF DDWSRDIQSG LSDSRSGLCI EASSRIMELD SNDGLLKVHY SDRLVILLRE VRQLSALGF VIPAKIQQVA NIAQKFCKQA IILKQVAHFY NSIDQQMIQS QRPMMLQSAL AFEQIIKNSK AGSGGKSQIT WDNPKELEGY IQKLQNAAE RLATENRKLR KWHTTFCEKV VVLMNIDLLR QQQRWKDGLQ ELRTGLATVE AQGFQASDMH AWKQHWNHQL Y KALEHQYQ MGLEALNENL PEINIDLTYK QGRLQFRPPF EEIRAKYYRE MKRFIGIPNQ FKGVGEAGDE SIFSIMIDRN AS GFLTIFS KAEDLFRRLS AVLHQHKEWI VIGQVDMEAL VEKHLFTVHD WEKNFKALKI KGKEVERLPS AVKVDCLNIN CNP VKTVID DLIQKLFDLL VLSLKKSIQA HLHEIDTFVT EAMEVLTIMP QSVEEIGDAN LQYSKLQERK PEILPLFQEA EDKN RLLRT VAGGGLETIS NLKAKWDKFE LMMESHQLMI KDQIEVMKGN VKSRLQIYYQ ELEKFKARWD QLKPGDDVIE TGQHN TLDK SAKLIKEKKI EFDDLEVTRK KLVDDCHHFR LEEPNFSLAS SISKDIESCA QIWAFYEEFQ QGFQEMANED WITFRT KTY LFEEFLMNWH DRLRKVEEHS VMTVKLQSEV DKYKIVIPIL KYVRGEHLSP DHWLDLFRLL GLPRGTSLEK LLFGDLL RV ADTIVAKAAD LKDLNSRAQG EVTIREALRE LDLWGVGAVF TLIDYEDSQS RTMKLIKDWK DIVNQVGDNR CLLQSLKD S PYYKGFEDKV SIWERKLAEL DEYLQNLNHI QRKWVYLEPI FGRGALPKEQ TRFNRVDEDF RSIMTDIKKD NRVTTLTTH AGIRNSLLTI LDQLQRCQRS LNEFLEEKRS AFPRFYFIGD DDLLEILGQS TNPSVIQSHL KKLFAGINSV CFDEKSKHIT AMKSLEGEV VPFKNKVPLS NNVETWLNDL ALEMKKTLEQ LLKECVTTGR SSQGAVDPSL FPSQILCLAE QIKFTEDVEN A IKDHSLHQ IETQLVNKLE QYTNIDTSSE DPGNTESGIL ELKLKALILD IIHNIDVVKQ LNQIQVHTTE DWAWKKQLRF YM KSDHTCC VQMVDSEFQY TYEYQGNASK LVYTPLTDKC YLTLTQAMKM GLGGNPYGPA GTGKTESVKA LGGLLGRQVL VFN CDEGID VKSMGRIFVG LVKCGAWGCF DEFNRLEESV LSAVSMQIQT IQDALKNHRT VCELLGKEVE VNSNSGIFIT MNPA GKGYG GRQKLPDNLK QLFRPVAMSH PDNELIAEVI LYSEGFKDAK VLSRKLVAIF NLSRELLTPQ QHYDWGLRAL KTVLR GSGN LLRQLNKSGT TQNANESHIV VQALRLNTMS KFTFTDCTRF DALIKDVFPG IELKEVEYDE LSAALKQVFE EANYEI IPN QIKKALELYE QLCQRMGVVI VGPSGAGKST LWRMLRAALC KTGKVVKQYT MNPKAMPRYQ LLGHIDMDTR EWSDGVL TN SARQVVREPQ DVSSWIICDG DIDPEWIESL NSVLDDNRLL TMPSGERIQF GPNVNFVFET HDLSCASPAT ISRMGMIF L SDEETDLNSL IKSWLRNQPA EYRNNLENWI GDYFEKALQW VLKQNDYVVE TSLVGTVMNG LSHLHGCRDH DEFIINLIR GLGGNLNMKS RLEFTKEVFH WARESPPDFH KPMDTYYDST RGRLATYVLK KPEDLTADDF SNGLTLPVIQ TPDMQRGLDY FKPWLSSDT KQPFILVGPE GCGKGMLLRY AFSQLRSTQI ATVHCSAQTT SRHLLQKLSQ TCMVISTNTG RVYRPKDCER L VLYLKDIN LPKLDKWGTS TLVAFLQQVL TYQGFYDENL EWVGLENIQI VASMSAGGRL GRHKLTTRFT SIVRLCSIDY PE REQLQTI YGAYLEPVLH KNLKNHSIWG SSSKIYLLAG SMVQVYEQVR AKFTVDDYSH YFFTPCILTQ WVLGLFRYDL EGG SSNHPL DYVLEIVAYE ARRLFRDKIV GAKELHLFDI ILTSVFQGDW GSDILDNMSD SFYVTWGARH NSGARAAPGQ PLPP HGKPL GKLNSTDLKD VIKKGLIHYG RDNQNLDILL FHEVLEYMSR IDRVLSFPGG SLLLAGRSGV GRRTITSLVS HMHGA VLFS PKISRGYELK QFKNDLKHVL QLAGIEAQQV VLLLEDYQFV HPTFLEMINS LLSSGEVPGL YTLEELEPLL LPLKDQ ASQ DGFFGPVFNY FTYRIQQNLH IVLIMDSANS NFMINCESNP ALHKKCQVLW MEGWSNSSMK KIPEMLFSET GGGEKYN DK KRKEEKKKNS VDPDFLKSFL LIHESCKAYG ATPSQYMTFL HVYSAISSSK KKELLKRQSH LQAGVSKLNE AKALVDEL N RKAGEQSVLL KTKQDEADAA LQMITVSMQD ASEQKTELER LKHRIAEEVV KIEERKNKID DELKEVQPLV NEAKLAVGN IKPESLSEIR SLRMPPDVIR DILEGVLRLM GIFDTSWVSM KSFLAKRGVR EDIATFDARN ISKEIRESVE ELLFKNKGSF DPKNAKRAS TAAAPLAAWV KANIQYSHVL ERIHPLETEQ AGLESNLKKT EDRKRKLEEL LNSVGQKVSE LKEKFQSRTS E AAKLEAEV SKAQETIKAA EVLINQLDRE HKRWNAQVVE ITEELATLPK RAQLAAAFIT YLSAAPESLR KTCLEEWTKS AG LEKFDLR RFLCTESEQL IWKSEGLPSD DLSIENALVI LQSRVCPFLI DPSSQATEWL KTHLKDSRLE VINQQDSNFI TAL ELAVRF GKTLIIQEMD GVEPVLYPLL RRDLVAQGPR YVVQIGDKII DYNEEFRLFL STRNPNPFIP PDAASIVTEV NFTT TRSGL RGQLLALTIQ HEKPDLEEQK TKLLQQEEDK KIQLAKLEES LLETLATSQG NILENKDLIE SLNQTKASSA LIQES LKES YKLQISLDQE RDAYLPLAES ASKMYFIISD LSKINNMYRF SLAAFLRLFQ RALQNKQDSE NTEQRIQSLI SSLQHM VYE YICRCLFKAD QLMFALHFVR GMHPELFQEN EWDTFTGVVV GDMLRKADSQ QKIRDQLPSW IDQERSWAVA TLKIALP SL YQTLCFEDAA LWRTYYNNSM CEQEFPSILA KKVSLFQQIL VVQVLRPDRL QSAMALFACK TLGLKEVSPL PLNLKRLY K ETLEIEPILI IISPGADPSQ ELQELANAER SGECYHQVAM GQGQADLAIQ MLKECARNGD WLCLKNLHLV VSWLPVLEK ELNTLQPKDT FRLWLTAEVH PNFTPILLQS SLKITYESPP GLKKNLMRTY ESWTPEQISK KDNTHRAHAL FSLAWFHAAC QERRNYIPQ GWTKFYEFSL SDLRAGYNII DRLFDGAKDV QWEFVHGLLE NAIYGGRIDN YFDLRVLQSY LKQFFNSSVI D VFNQRNKK SIFPYSVSLP QSCSILDYRA VIEKIPEDDK PSFFGLPANI ARSSQRMISS QVISQLRILG RSITAGSKFD RE IWSNELS PVLNLWKKLN QNSNLIHQKV PPPNDRQGSP ILSFIILEQF NAIRLVQSVH QSLAALSKVI RGTTLLSSEV QKL ASALLN QKCPLAWQSK WEGPEDPLQY LRGLVARALA IQNWVDKAEK QALLSETLDL SELFHPDTFL NALRQETARA VGRS VDSLK FVASWKGRLQ EAKLQIKISG LLLEGCSFDG NQLSENQLDS PSVSSVLPCF MGWIPQDACG PYSPDECISL PVYTS AERD RVVTNIDVPC GGNQDQWIQC GAALFLKNQ UniProtKB: Methylated-DNA--protein-cysteine methyltransferase, Cytoplasmic dynein 2 heavy chain 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Cytoplasmic dynein 2 intermediate chain 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Cytoplasmic dynein 2 intermediate chain 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 122.865156 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MEPGKRRTKD DTWKADDLRK HLWAIQSGGS KEERKHREKK LRKESEMDLP EHKEPRCRDP DQDARSRDRV AEVHTAKESP RGERDRDRQ RERRRDAKDR EKEKLKEKHR EAEKSHSRGK DREKEKDRRA RKEELRQTVA HHNLLGQETR DRQLLERAER K GRSVSKVR ...String: MEPGKRRTKD DTWKADDLRK HLWAIQSGGS KEERKHREKK LRKESEMDLP EHKEPRCRDP DQDARSRDRV AEVHTAKESP RGERDRDRQ RERRRDAKDR EKEKLKEKHR EAEKSHSRGK DREKEKDRRA RKEELRQTVA HHNLLGQETR DRQLLERAER K GRSVSKVR SEEKDEDSER GDEDRERRYR ERKLQYGDSK DNPLKYWLYK EEGERRHRKP REPDRDKKHR EKSSTREKRE KY SKEKSNS FSDKGEERHK EKRHKEGFHF DDERHQSNVD RKEKSAKDEP RKREFQNGEH RNRGASSKRD GTSSQHAENL VRN HGKDKD SRRKHGHEEG SSVWWKLDQR PGGEETVEIE KEETDLENAR ADAYTASCED DFEDYEDDFE VCDGDDDESS NEPE SREKL EELPLAQKKE IQEIQRAINA ENERIGELSL KLFQKRGRTE FEKEPRTDTN SSPSRASVCG IFVDFASASH RQKSR TQAL KQKMRSTKLL RLIDLDFSFT FSLLDLPPVN EYDMYIRNFG KKNTKQAYVQ CNEDNVERDI QTEEIETREV WTQHPG EST VVSGGSEQRD TSDAVVMPKI DTPRLCSFLR AACQVMAVLL EEDRLAAEPS WNLRAQDRAL YFSDSSSQLN TSLPFLQ NR KVSSLHTSRV QRQMVVSVHD LPEKSFVPLL DSKYVLCVWD IWQPSGPQKV LICESQVTCC CLSPLKAFLL FAGTAHGS V VVWDLREDSR LHYSVTLSDG FWTFRTATFS TDGILTSVNH RSPLQAVEPI STSVHKKQSF VLSPFSTQEE MSGLSFHIA SLDESGVLNV WVVVELPKAD IAGSISDLGL MPGGRVKLVH SALIQLGDSL SHKGNEFWGT TQTLNVKFLP SDPNHFIIGT DMGLISHGT RQDLRVAPKL FKPQQHGIRP VKVNVIDFSP FGEPIFLAGC SDGSIRLHQL SSAFPLLQWD SSTDSHAVTG L QWSPTRPA VFLVQDDTSN IYIWDLLQSD LGPVAKQQVS PNRLVAMAAV GEPEKAGGSF LALVLARASG SIDIQHLKRR WA APEVDEC NRLRLLLQEA LWPEGKLHK UniProtKB: Cytoplasmic dynein 2 intermediate chain 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Cytoplasmic dynein 2 intermediate chain 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Cytoplasmic dynein 2 intermediate chain 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 Details: DYNC2I2 (also known as WDR34) with C-terminal Strep tag Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 60.639129 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MATRAQPGPL SQAGSAGVAA LATVGVASGP GPGRPGPLQD ETLGVASVPS QWRAVQGIRG ETKSCQTASI ATASASAQAR NHVDAQVQT EAPVPVSVQP PSQYDIPRLA AFLRRVEAMV IRELNKNWQS HAFDGFEVNW TEQQQMVSCL YTLGYPPAQA Q GLHVTSIS ...String: MATRAQPGPL SQAGSAGVAA LATVGVASGP GPGRPGPLQD ETLGVASVPS QWRAVQGIRG ETKSCQTASI ATASASAQAR NHVDAQVQT EAPVPVSVQP PSQYDIPRLA AFLRRVEAMV IRELNKNWQS HAFDGFEVNW TEQQQMVSCL YTLGYPPAQA Q GLHVTSIS WNSTGSVVAC AYGRLDHGDW STLKSFVCAW NLDRRDLRPQ QPSAVVEVPS AVLCLAFHPT QPSHVAGGLY SG EVLVWDL SRLEDPLLWR TGLTDDTHTD PVSQVVWLPE PGHSHRFQVL SVATDGKVLL WQGIGVGQLQ LTEGFALVMQ QLP RSTKLK KHPRGETEVG ATAVAFSSFD PRLFILGTEG GFPLKCSLAA GEAALTRMPS SVPLRAPAQF TFSPHGGPIY SVSC SPFHR NLFLSAGTDG HVHLYSMLQA PPLTSLQLSL KYLFAVRWSP VRPLVFAAAS GKGDVQLFDL QKSSQKPTVL IKQTQ DESP VYCLEFNSQQ TQLLAAGDAQ GTVKVWQLST EFTEQGPREA EDLDCLAAEV AAWSHPQFEK GSAGSAAGSG AGWSHP QFE K UniProtKB: Cytoplasmic dynein 2 intermediate chain 2 |
-Macromolecule #4: Dynein light chain roadblock-type 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Dynein light chain roadblock-type 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.934576 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAEVEETLKR LQSQKGVQGI IVVNTEGIPI KSTMDNPTTT QYASLMHSFI LKARSTVRDI DPQNDLTFLR IRSKKNEIMV APDKDYFLI VIQNPTE UniProtKB: Dynein light chain roadblock-type 1 |
-Macromolecule #5: Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic
| Macromolecule | Name: Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.381899 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MCDRKAVIKN ADMSEEMQQD SVECATQALE KYNIEKDIAA HIKKEFDKKY NPTWHCIVGR NFGSYVTHET KHFIYFYLGQ VAILLFKSG UniProtKB: Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)