+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | RAD51 nucleoprotein filament on double-stranded abasic DNA | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | local anisotropy sharpened map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Homologous recombination / DNA replication / abasic DNA / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpresynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton / response to glucoside / mitotic recombination-dependent replication fork processing / DNA recombinase assembly / cellular response to camptothecin / chromosome organization involved in meiotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to cisplatin ...presynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton / response to glucoside / mitotic recombination-dependent replication fork processing / DNA recombinase assembly / cellular response to camptothecin / chromosome organization involved in meiotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to cisplatin / DNA strand invasion / cellular response to hydroxyurea / mitotic recombination / DNA strand exchange activity / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / lateral element / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / Impaired BRCA2 binding to PALB2 / telomere maintenance via recombination / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / reciprocal meiotic recombination / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / nuclear chromosome / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / replication fork processing / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / response to X-ray / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / interstrand cross-link repair / condensed chromosome / DNA polymerase binding / condensed nuclear chromosome / cellular response to ionizing radiation / male germ cell nucleus / meiotic cell cycle / cellular response to gamma radiation / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / PML body / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Meiotic recombination / response to toxic substance / single-stranded DNA binding / site of double-strand break / double-stranded DNA binding / DNA recombination / chromosome, telomeric region / mitochondrial matrix / response to xenobiotic stimulus / DNA repair / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / centrosome / chromatin / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / enzyme binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Appleby R / Pellegrini L | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1 items United Kingdom, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: RAD51 protects abasic sites to prevent replication fork breakage. Authors: Yodhara Wijesekara Hanthi / Miguel Angel Ramirez-Otero / Robert Appleby / Anna De Antoni / Luay Joudeh / Vincenzo Sannino / Salli Waked / Alessandra Ardizzoia / Viviana Barra / Daniele ...Authors: Yodhara Wijesekara Hanthi / Miguel Angel Ramirez-Otero / Robert Appleby / Anna De Antoni / Luay Joudeh / Vincenzo Sannino / Salli Waked / Alessandra Ardizzoia / Viviana Barra / Daniele Fachinetti / Luca Pellegrini / Vincenzo Costanzo /    Abstract: Abasic sites are DNA lesions repaired by base excision repair. Cleavage of unrepaired abasic sites in single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) can lead to chromosomal breakage during DNA replication. How rupture ...Abasic sites are DNA lesions repaired by base excision repair. Cleavage of unrepaired abasic sites in single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) can lead to chromosomal breakage during DNA replication. How rupture of abasic DNA is prevented remains poorly understood. Here, using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), Xenopus laevis egg extracts, and human cells, we show that RAD51 nucleofilaments specifically recognize and protect abasic sites, which increase RAD51 association rate to DNA. In the absence of BRCA2 or RAD51, abasic sites accumulate as a result of DNA base methylation, oxidation, and deamination, inducing abasic ssDNA gaps that make replicating DNA fibers sensitive to APE1. RAD51 assembled on abasic DNA prevents abasic site cleavage by the MRE11-RAD50 complex, suppressing replication fork breakage triggered by an excess of abasic sites or POLθ polymerase inhibition. Our study highlights the critical role of BRCA2 and RAD51 in safeguarding against unrepaired abasic sites in DNA templates stemming from base alterations, ensuring genomic stability. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_19051.map.gz emd_19051.map.gz | 28.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-19051-v30.xml emd-19051-v30.xml emd-19051.xml emd-19051.xml | 26 KB 26 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_19051.png emd_19051.png | 85.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-19051.cif.gz emd-19051.cif.gz | 7.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_19051_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19051_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19051_half_map_2.map.gz emd_19051_half_map_2.map.gz | 23.4 MB 23.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19051 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19051 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19051 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19051 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8rcfMC  8rcdC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_19051.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_19051.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | local anisotropy sharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.304 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
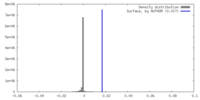
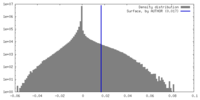
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RAD51 nucleoprotein filament on double-stranded abasic DNA
| Entire | Name: RAD51 nucleoprotein filament on double-stranded abasic DNA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RAD51 nucleoprotein filament on double-stranded abasic DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: RAD51 nucleoprotein filament on double-stranded abasic DNA type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: DNA repair protein
| Supramolecule | Name: DNA repair protein / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: DNA / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 37.009125 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAMQMQLEAN ADTSVEEESF GPQPISRLEQ CGINANDVKK LEEAGFHTVE AVAYAPKKEL INIKGISEAK ADKILAEAAK LVPMGFTTA TEFHQRRSEI IQITTGSKEL DKLLQGGIET GSITEMFGEF RTGKTQICHT LAVTCQLPID RGGGEGKAMY I DTEGTFRP ...String: MAMQMQLEAN ADTSVEEESF GPQPISRLEQ CGINANDVKK LEEAGFHTVE AVAYAPKKEL INIKGISEAK ADKILAEAAK LVPMGFTTA TEFHQRRSEI IQITTGSKEL DKLLQGGIET GSITEMFGEF RTGKTQICHT LAVTCQLPID RGGGEGKAMY I DTEGTFRP ERLLAVAERY GLSGSDVLDN VAYARAFNTD HQTQLLYQAS AMMVESRYAL LIVDSATALY RTDYSGRGEL SA RQMHLAR FLRMLLRLAD EFGVAVVITN QVVAQVDGAA MFAADPKKPI GGNIIAHAST TRLYLRKGRG ETRICKIYDS PCL PEAEAM FAINADGVGD AKD UniProtKB: DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA (5'-D(P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*T...
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (5'-D(P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*GP*(3DR)P*TP*G)-3') type: dna / ID: 2 Details: 3DR refers to an abasic nucleotide. The ribose of the abasic nucleotide is a tetrahydrofurane lacking the hydroxyl group that would naturally be present on position C1 after base hydrolysis. ...Details: 3DR refers to an abasic nucleotide. The ribose of the abasic nucleotide is a tetrahydrofurane lacking the hydroxyl group that would naturally be present on position C1 after base hydrolysis. The sequence consists of 7 x TG(3DR) + TG, as helically averaged version of the DNA sequence: GGTAT(3DR)CA(3DR)TG(3DR)TA(3DR)AC(3DR)TGAGC, which contains 5 central, equally spaced abasic sites flanked by 5 nucleotides. Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 6.282902 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DG)(3DR)(DT)(DG)(3DR)(DT)(DG)(3DR)(DT) (DG)(3DR)(DT)(DG)(3DR)(DT)(DG)(3DR) (DT) (DG)(3DR)(DT)(DG) |
-Macromolecule #3: DNA (5'-D(P*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP...
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (5'-D(P*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*A)-3') type: dna / ID: 3 Details: The sequence consists of 7 x CAC + CA, as helically averaged version of the DNA sequence: GCTCACGTCTACCACTGCATACC Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 6.798423 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DC)(DC)(DA) |
-Macromolecule #4: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 16 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 10084 / Average exposure time: 1.2 sec. / Average electron dose: 52.968 e/Å2 Details: Images were collected in movie mode at 44 frames per movie |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 130000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)