+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
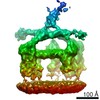
| Title | C1 complex binding to a tetrameric C-reactive protein platform | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Map low pass filtered to 16 A. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | C-reactive protein / C1 / Complex / Complement / Classical pathway / CRP / activation / IMMUNE SYSTEM | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 24.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sharp TH / Noone DP | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis for surface activation of the classical complement cascade by the short pentraxin C-reactive protein. Authors: Dylan P Noone / Marjolein M E Isendoorn / Sebastiaan M W R Hamers / Mariska E Keizer / Jip Wulffelé / Tijn T van der Velden / Douwe J Dijkstra / Leendert A Trouw / Dmitri V Filippov / Thomas H Sharp /   Abstract: Human C-reactive protein (CRP) is a pentameric complex involved in immune defense and regulation of autoimmunity. CRP is also a therapeutic target, with both administration and depletion of serum CRP ...Human C-reactive protein (CRP) is a pentameric complex involved in immune defense and regulation of autoimmunity. CRP is also a therapeutic target, with both administration and depletion of serum CRP being pursued as a possible treatment for autoimmune and cardiovascular diseases, among others. CRP binds to phosphocholine (PC) moieties on membranes to activate the complement system via the C1 complex, but it is unknown how CRP, or any pentraxin, binds to C1. Here, we present a cryoelectron tomography (cryoET)-derived structure of CRP bound to PC ligands and the C1 complex. To gain control of CRP binding, a synthetic mimotope of PC was synthesized and used to decorate cell-mimetic liposome surfaces. Structure-guided mutagenesis of CRP yielded a fully active complex able to bind PC-coated liposomes that was ideal for cryoET and subtomogram averaging. In contrast to antibodies, which form Fc-mediated hexameric platforms to bind and activate the C1 complex, CRP formed rectangular platforms assembled from four laterally associated CRP pentamers that bind only four of the six available globular C1 head groups. Potential residues mediating lateral association of CRP were identified from interactions between unit cells in existing crystal structures, which rationalized previously unexplained mutagenesis data regarding CRP-mediated complement activation. The structure also enabled interpretation of existing biochemical data regarding interactions mediating C1 binding and identified additional residues for further mutagenesis studies. These structural data therefore provide a possible mechanism for regulation of complement by CRP, which limits complement progression and has consequences for how the innate immune system influences autoimmunity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_18830.map.gz emd_18830.map.gz | 16.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-18830-v30.xml emd-18830-v30.xml emd-18830.xml emd-18830.xml | 17.8 KB 17.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_18830_fsc.xml emd_18830_fsc.xml | 6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_18830.png emd_18830.png | 86.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_18830_msk_1.map emd_18830_msk_1.map | 18.1 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-18830.cif.gz emd-18830.cif.gz | 4.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_18830_additional_1.map.gz emd_18830_additional_1.map.gz emd_18830_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18830_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18830_half_map_2.map.gz emd_18830_half_map_2.map.gz | 2.3 MB 16.4 MB 15.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18830 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18830 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18830 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18830 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_18830_validation.pdf.gz emd_18830_validation.pdf.gz | 899.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_18830_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_18830_full_validation.pdf.gz | 899.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_18830_validation.xml.gz emd_18830_validation.xml.gz | 12.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_18830_validation.cif.gz emd_18830_validation.cif.gz | 16.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-18830 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-18830 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-18830 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-18830 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_18830.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 18.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_18830.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 18.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map low pass filtered to 16 A. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 3.48 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_18830_msk_1.map emd_18830_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : C1 complex bound to a membrane bound tetrameric CRP platform
| Entire | Name: C1 complex bound to a membrane bound tetrameric CRP platform |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: C1 complex bound to a membrane bound tetrameric CRP platform
| Supramolecule | Name: C1 complex bound to a membrane bound tetrameric CRP platform type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1226 kDa/nm |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: EMS Lacey Carbon / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Details: 25 mA | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 65 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP | ||||||||||||
| Details | CRP was an R188A mutant expressed in human cells. C1 was purchased from complement technology (Texas, USA) and purified from human serum. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.54 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 6.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 4.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





























