[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-17764: Catalytic module of yeast GID E3 ligase bound to multiphosphoryla... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
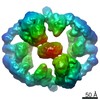
| Title | Catalytic module of yeast GID E3 ligase bound to multiphosphorylated Ubc8~ubiquitin | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | E3 ubiquitin ligase / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / phosphorylation / GID / LIGASE | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationGID complex / mitochondrial outer membrane translocase complex assembly / : / : / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E ...GID complex / mitochondrial outer membrane translocase complex assembly / : / : / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 upon TLR3 ligation / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / Pexophagy / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Regulation of PTEN localization / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / Degradation of CDH1 / Translesion synthesis by POLK / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Josephin domain DUBs / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / Degradation of CRY and PER proteins / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Regulation of signaling by CBL / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / NOTCH3 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Negative regulation of FGFR3 signaling / Fanconi Anemia Pathway / Peroxisomal protein import / Vpu mediated degradation of CD4 / Deactivation of the beta-catenin transactivating complex / Stabilization of p53 / Degradation of DVL / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / Negative regulation of FGFR2 signaling / Dectin-1 mediated noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Negative regulation of FGFR4 signaling / Downregulation of SMAD2/3:SMAD4 transcriptional activity / Degradation of AXIN / Negative regulation of FGFR1 signaling / Regulation of TNFR1 signaling / EGFR downregulation / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
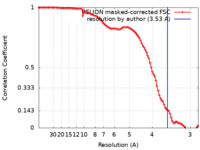
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.53 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chrustowicz J / Sherpa D / Prabu RJ / Schulman BA | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 3 items Germany, European Union, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Multisite phosphorylation dictates selective E2-E3 pairing as revealed by Ubc8/UBE2H-GID/CTLH assemblies. Authors: Jakub Chrustowicz / Dawafuti Sherpa / Jerry Li / Christine R Langlois / Eleftheria C Papadopoulou / D Tung Vu / Laura A Hehl / Özge Karayel / Viola Beier / Susanne von Gronau / Judith ...Authors: Jakub Chrustowicz / Dawafuti Sherpa / Jerry Li / Christine R Langlois / Eleftheria C Papadopoulou / D Tung Vu / Laura A Hehl / Özge Karayel / Viola Beier / Susanne von Gronau / Judith Müller / J Rajan Prabu / Matthias Mann / Gary Kleiger / Arno F Alpi / Brenda A Schulman /   Abstract: Ubiquitylation is catalyzed by coordinated actions of E3 and E2 enzymes. Molecular principles governing many important E3-E2 partnerships remain unknown, including those for RING-family GID/CTLH E3 ...Ubiquitylation is catalyzed by coordinated actions of E3 and E2 enzymes. Molecular principles governing many important E3-E2 partnerships remain unknown, including those for RING-family GID/CTLH E3 ubiquitin ligases and their dedicated E2, Ubc8/UBE2H (yeast/human nomenclature). GID/CTLH-Ubc8/UBE2H-mediated ubiquitylation regulates biological processes ranging from yeast metabolic signaling to human development. Here, cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), biochemistry, and cell biology reveal this exquisitely specific E3-E2 pairing through an unconventional catalytic assembly and auxiliary interactions 70-100 Å away, mediated by E2 multisite phosphorylation. Rather than dynamic polyelectrostatic interactions reported for other ubiquitylation complexes, multiple Ubc8/UBE2H phosphorylation sites within acidic CK2-targeted sequences specifically anchor the E2 C termini to E3 basic patches. Positions of phospho-dependent interactions relative to the catalytic domains correlate across evolution. Overall, our data show that phosphorylation-dependent multivalency establishes a specific E3-E2 partnership, is antagonistic with dephosphorylation, rigidifies the catalytic centers within a flexing GID E3-substrate assembly, and facilitates substrate collision with ubiquitylation active sites. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_17764.map.gz emd_17764.map.gz | 5.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-17764-v30.xml emd-17764-v30.xml emd-17764.xml emd-17764.xml | 29.6 KB 29.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_17764_fsc.xml emd_17764_fsc.xml | 9.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_17764.png emd_17764.png | 108 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_17764_msk_1.map emd_17764_msk_1.map | 76.8 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-17764.cif.gz emd-17764.cif.gz | 8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_17764_additional_1.map.gz emd_17764_additional_1.map.gz emd_17764_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17764_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17764_half_map_2.map.gz emd_17764_half_map_2.map.gz | 66.8 MB 60 MB 60 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17764 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17764 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17764 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17764 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8pmqMC  8pjnC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_17764.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 76.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_17764.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 76.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.427 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_17764_msk_1.map emd_17764_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Map post-processed with DeepEMhancer
| File | emd_17764_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map post-processed with DeepEMhancer | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_17764_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_17764_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of yeast Chelator-GIDSR4 E3 ligase, tetrameric Fbp1 subst...
| Entire | Name: Complex of yeast Chelator-GIDSR4 E3 ligase, tetrameric Fbp1 substrate and multiphosphorylated Ubc8~ubiquitin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of yeast Chelator-GIDSR4 E3 ligase, tetrameric Fbp1 subst...
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of yeast Chelator-GIDSR4 E3 ligase, tetrameric Fbp1 substrate and multiphosphorylated Ubc8~ubiquitin type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 Details: Map obtained by focus refinement over the catalytic module (Gid2, Gid9) and Ubc8~ubiquitin |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.7 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RMD5
| Macromolecule | Name: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RMD5 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 49.244594 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: MSELLDSFET EFAKFYTDSN LEETNLQKCL DHTHEFKSQL KKLKAHLNKH IQESKPEVYN KLSDKEKQKF KRKRELIIEK LSKSQRQWD HSVKKQIKYV SQQSNRFNKS TLNKLKEFDI DSVYVNKLPK ETMENVNEAI GYHILRYSID NMPLGNKNEA F QYLKDVYG ...String: MSELLDSFET EFAKFYTDSN LEETNLQKCL DHTHEFKSQL KKLKAHLNKH IQESKPEVYN KLSDKEKQKF KRKRELIIEK LSKSQRQWD HSVKKQIKYV SQQSNRFNKS TLNKLKEFDI DSVYVNKLPK ETMENVNEAI GYHILRYSID NMPLGNKNEA F QYLKDVYG ITNKESTEFI EMGQIVHDLK KGDTESCLKW CSNEMESLSS NHTALSSLKF DLYTLSAMQI VKHGNPVELY YQ ITQNAPL DCFRHREKEL MQNVVPLLTK SLIGQPIEDI DSKVNKELKE CTSLFIKEYC AAKHIFFDSP LFLIVLSGLI SFQ FFIKYK TIRELAHVDW TTKDELPFDV KLPDFLTHFH PIFICPVLKE ETTTENPPYS LACHHIISKK ALDRLSKNGT ITFK CPYCP VNTSMSSTKK VRFVML UniProtKB: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RMD5 |
-Macromolecule #2: Protein FYV10
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein FYV10 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 59.975102 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: MAEKSIFNEP DVDFHLKLNQ QLFHIPYELL SKRIKHTQAV INKETKSLHE HTAALNQIFE HNDVEHDELA LAKITEMIRK VDHIERFLN TQIKSYCQIL NRIKKRLEFF HELKDIKSQN SGTSHNGNNE GTRTKLIQWY QSYTNILIGD YLTRNNPIKY N SETKDHWN ...String: MAEKSIFNEP DVDFHLKLNQ QLFHIPYELL SKRIKHTQAV INKETKSLHE HTAALNQIFE HNDVEHDELA LAKITEMIRK VDHIERFLN TQIKSYCQIL NRIKKRLEFF HELKDIKSQN SGTSHNGNNE GTRTKLIQWY QSYTNILIGD YLTRNNPIKY N SETKDHWN SGVVFLKQSQ LDDLIDYDVL LEANRISTSL LHERNLLPLI SWINENKKTL TKKSSILEFQ ARLQEYIELL KV DNYTDAI VCFQRFLLPF VKSNFTDLKL ASGLLIFIKY CNDQKPTSST SSGFDTEEIK SQSLPMKKDR IFQHFFHKSL PRI TSKPAV NTTDYDKSSL INLQSGDFER YLNLLDDQRW SVLNDLFLSD FYSMYGISQN DPLLIYLSLG ISSLKTRDCL HPSD DENGN QETETATTAE KEVEDLQLFT LHSLKRKNCP VCSETFKPIT QALPFAHHIQ SQLFENPILL PNGNVYDSKK LKKLA KTLK KQNLISLNPG QIMDPVDMKI FCESDSIKMY PT UniProtKB: GID complex subunit 9 |
-Macromolecule #3: Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2-24 kDa
| Macromolecule | Name: Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2-24 kDa / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.920771 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: MSSSKRRIET DVMKLLMSDH QVDLINDSMQ EFHVKFLGPK DTPYENGVWR LHVELPDNYP YKSPSIGFVN KIFHPNIDIA SGSIKLDVI NSTWSPLYDL INIVEWMIPG LLKEPNGSDP LNNEAATLQL RDKKLYEEKI KEYIDKYATK EKYQQMFGGD N DSDDSDSG ...String: MSSSKRRIET DVMKLLMSDH QVDLINDSMQ EFHVKFLGPK DTPYENGVWR LHVELPDNYP YKSPSIGFVN KIFHPNIDIA SGSIKLDVI NSTWSPLYDL INIVEWMIPG LLKEPNGSDP LNNEAATLQL RDKKLYEEKI KEYIDKYATK EKYQQMFGGD N DSDDSDSG GDLQEEDSDS DEDMDGTGVS SGDDSVDEL(SEP) EDL(SEP)DIDV(SEP)D DDDYDEVANQ UniProtKB: Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2-24 kDa |
-Macromolecule #4: Ubiquitin
| Macromolecule | Name: Ubiquitin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.576831 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MQIFVKTLTG KTITLEVEPS DTIENVKAKI QDKEGIPPDQ QRLIFAGKQL EDGRTLSDYN IQKESTLHLV LRLRGG UniProtKB: Polyubiquitin-C |
-Macromolecule #5: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 69.24 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.3000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)