[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-14763: Cryo-EM structure of aIF1A:aIF5B:Met-tRNAiMet complex from a Pyro... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
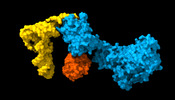
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of aIF1A:aIF5B:Met-tRNAiMet complex from a Pyrococcus abyssi 30S initiation complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Initiation complex / translation initiation / small ribosomal subunit / aIF5b / TRANSLATION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationUDP phosphatase activity / GDP phosphatase activity / proteoglycan biosynthetic process / intron homing / intein-mediated protein splicing / translation initiation factor activity / endonuclease activity / GTPase activity / calcium ion binding / GTP binding ...UDP phosphatase activity / GDP phosphatase activity / proteoglycan biosynthetic process / intron homing / intein-mediated protein splicing / translation initiation factor activity / endonuclease activity / GTPase activity / calcium ion binding / GTP binding / RNA binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |    Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) | |||||||||
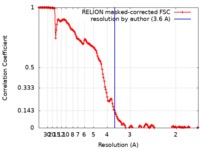
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Coureux PD / Bourgeois G / Mechulam Y / Schmitt E / Kazan R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  France, 1 items France, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2022 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2022Title: Role of aIF5B in archaeal translation initiation. Authors: Ramy Kazan / Gabrielle Bourgeois / Christine Lazennec-Schurdevin / Eric Larquet / Yves Mechulam / Pierre-Damien Coureux / Emmanuelle Schmitt /  Abstract: In eukaryotes and in archaea late steps of translation initiation involve the two initiation factors e/aIF5B and e/aIF1A. In eukaryotes, the role of eIF5B in ribosomal subunit joining is established ...In eukaryotes and in archaea late steps of translation initiation involve the two initiation factors e/aIF5B and e/aIF1A. In eukaryotes, the role of eIF5B in ribosomal subunit joining is established and structural data showing eIF5B bound to the full ribosome were obtained. To achieve its function, eIF5B collaborates with eIF1A. However, structural data illustrating how these two factors interact on the small ribosomal subunit have long been awaited. The role of the archaeal counterparts, aIF5B and aIF1A, remains to be extensively addressed. Here, we study the late steps of Pyrococcus abyssi translation initiation. Using in vitro reconstituted initiation complexes and light scattering, we show that aIF5B bound to GTP accelerates subunit joining without the need for GTP hydrolysis. We report the crystallographic structures of aIF5B bound to GDP and GTP and analyze domain movements associated to these two nucleotide states. Finally, we present the cryo-EM structure of an initiation complex containing 30S bound to mRNA, Met-tRNAiMet, aIF5B and aIF1A at 2.7 Å resolution. Structural data shows how archaeal 5B and 1A factors cooperate to induce a conformation of the initiator tRNA favorable to subunit joining. Archaeal and eukaryotic features of late steps of translation initiation are discussed. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_14763.map.gz emd_14763.map.gz | 288.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-14763-v30.xml emd-14763-v30.xml emd-14763.xml emd-14763.xml | 25.2 KB 25.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_14763_fsc.xml emd_14763_fsc.xml | 15.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_14763.png emd_14763.png | 55.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-14763.cif.gz emd-14763.cif.gz | 7.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_14763_additional_1.map.gz emd_14763_additional_1.map.gz emd_14763_half_map_1.map.gz emd_14763_half_map_1.map.gz emd_14763_half_map_2.map.gz emd_14763_half_map_2.map.gz | 201.7 MB 202.5 MB 202.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14763 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14763 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14763 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14763 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7zkiMC  7yypC  7yznC 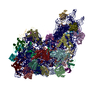 7zagC  7zahC  7zaiC  7zhgC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_14763.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 307.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_14763.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 307.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
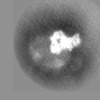
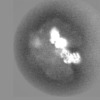
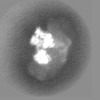
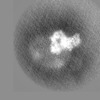
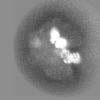
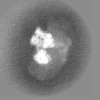
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.86 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
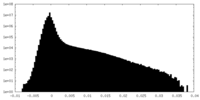
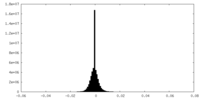
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Not sharpened map
| File | emd_14763_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Not sharpened map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
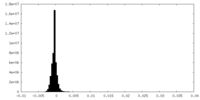
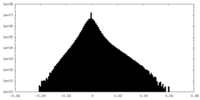
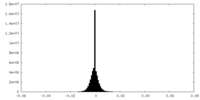
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_14763_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
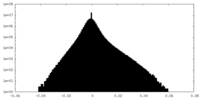
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_14763_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : tRNA-aIF5B-aIF1A moiety of a Pyrococcus abyssi translation initia...
| Entire | Name: tRNA-aIF5B-aIF1A moiety of a Pyrococcus abyssi translation initiation complex with 30S ribosomal subunit,tRNA, mRNA and initiation factors 1A and 5B. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: tRNA-aIF5B-aIF1A moiety of a Pyrococcus abyssi translation initia...
| Supramolecule | Name: tRNA-aIF5B-aIF1A moiety of a Pyrococcus abyssi translation initiation complex with 30S ribosomal subunit,tRNA, mRNA and initiation factors 1A and 5B. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: tRNA-Met
| Supramolecule | Name: tRNA-Met / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Translation initiation factor 1A and Probable translation initiat...
| Supramolecule | Name: Translation initiation factor 1A and Probable translation initiation factor IF-2 type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) |
-Macromolecule #1: Met-tRNAiMet
| Macromolecule | Name: Met-tRNAiMet / type: rna / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.833904 KDa |
| Sequence | String: AGCGGGG(4SU)GG AGCAGCCUGG (H2U)AGCUCGUCG GG(OMC)UCAUAAC CCGAAGAUCG UCGG(5MU)(PSU)CAAA UCCGGCCCC CGCUACCA GENBANK: GENBANK: CP026027.1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Translation initiation factor 1A
| Macromolecule | Name: Translation initiation factor 1A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) / Strain: GE5 / Orsay Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) / Strain: GE5 / Orsay |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.336709 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSSSHHHHH HSSGLVPRGS HMPKKERKVE GDEVIRVPLP EGNQLFGVVE QALGAGWMDV RCEDGKIRRC RIPGKLRRRV WIRVGDLVI VQPWPVQSDK RGDIVYRYTQ TQVDWLLRKG KITQEFLTGG SLLVE UniProtKB: Translation initiation factor 1A |
-Macromolecule #3: Translation initiation factor 5B
| Macromolecule | Name: Translation initiation factor 5B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) / Strain: GE5 / Orsay Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) / Strain: GE5 / Orsay |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 69.122945 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MMTKRIRQPI IAVLGHVDHG KTTLLDRIRK TNVAAKEAGG ITQHIGATEV PIEVVKKIAG PLIKLWKAE IKLPGLLFID TPGHEAFTSL RARGGSLADL AVLVVDINEG FQPQTIESIE ILRKYRTPFV VAANKIDRIK G WVIEEDEP ...String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MMTKRIRQPI IAVLGHVDHG KTTLLDRIRK TNVAAKEAGG ITQHIGATEV PIEVVKKIAG PLIKLWKAE IKLPGLLFID TPGHEAFTSL RARGGSLADL AVLVVDINEG FQPQTIESIE ILRKYRTPFV VAANKIDRIK G WVIEEDEP FLMNIKKQDQ RAVQELETKL WELIGKFYEF GFQANRFDRV QNFTRELAIV PISAKYGIGI AELLVLIAGL SQ RYLEEKL KIEVEGPARG TILEVREEPG LGHTIDVIIY DGTLHKDDTI VVGGKDKAIV TKIRALLKPK PLDEIRDPRF RFD YVDEVT AAAGVKIAAP GLEEALAGSP VIAAPTPEDV EKAKQEILEQ IERVVISTDK VGVIVKADTL GSLEALSKEL QEKE IPIRK ADVGNVSKTD VMEALSVKEE EPKYGVILGF NVKVNEDAEE VAKAKDVKIF VGNVIYKLIE DYEEWVKEEE EKKKR ELLS KVTFPGVIRL YPDERYVFRR SNPAIVGIEV IEGRIKPGVT LIKQNGQKVG VIRSIKSRDE FLQEAKKGQA VAIAIE GAI VGRHIHPGET LYVDLSRDDA ITLLKHLRDT LEDTDIKALK MIAKVKAKED PFWRAI UniProtKB: Apyrase, Probable translation initiation factor IF-2, Probable translation initiation factor IF-2 |
-Macromolecule #4: METHIONINE
| Macromolecule | Name: METHIONINE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MET |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 149.211 Da |
| Chemical component information | 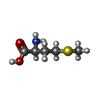 ChemComp-MET: |
-Macromolecule #5: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-GUANYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-GUANYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: GNP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 522.196 Da |
| Chemical component information | 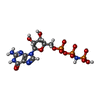 ChemComp-GNP: |
-Macromolecule #6: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.7 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Support film - Film thickness: 2 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 39.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)