[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-13989: Infectious mouse-adapted RML scrapie prion fibril purified from t... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Infectious mouse-adapted RML scrapie prion fibril purified from terminally-infected mouse brains | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Ex vivo RML prion fibril | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Prion / Amyloid / PrP / Prion protein / mouse RML scrapie strain / ex vivo prion / PROTEIN FIBRIL | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationInsertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / lamin binding / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / glycosaminoglycan binding / type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / ATP-dependent protein binding ...Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / lamin binding / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / glycosaminoglycan binding / type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / ATP-dependent protein binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / cupric ion binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation / negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation / response to amyloid-beta / negative regulation of type II interferon production / cuprous ion binding / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / response to cadmium ion / side of membrane / inclusion body / neuron projection maintenance / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / molecular function activator activity / cellular response to copper ion / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / molecular condensate scaffold activity / protein homooligomerization / protein destabilization / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / cellular response to amyloid-beta / terminal bouton / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / signaling receptor activity / protein-folding chaperone binding / regulation of protein localization / amyloid-beta binding / response to oxidative stress / protease binding / nuclear membrane / microtubule binding / molecular adaptor activity / transmembrane transporter binding / learning or memory / intracellular signal transduction / postsynaptic density / membrane raft / copper ion binding / dendrite / negative regulation of apoptotic process / protein-containing complex binding / cell surface / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
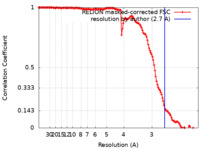
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Manka SW / Zhang W | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 4 items United Kingdom, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: 2.7 Å cryo-EM structure of ex vivo RML prion fibrils. Authors: Szymon W Manka / Wenjuan Zhang / Adam Wenborn / Jemma Betts / Susan Joiner / Helen R Saibil / John Collinge / Jonathan D F Wadsworth /  Abstract: Mammalian prions propagate as distinct strains and are composed of multichain assemblies of misfolded host-encoded prion protein (PrP). Here, we present a near-atomic resolution cryo-EM structure of ...Mammalian prions propagate as distinct strains and are composed of multichain assemblies of misfolded host-encoded prion protein (PrP). Here, we present a near-atomic resolution cryo-EM structure of PrP fibrils present in highly infectious prion rod preparations isolated from the brains of RML prion-infected mice. We found that prion rods comprise single-protofilament helical amyloid fibrils that coexist with twisted pairs of the same protofilaments. Each rung of the protofilament is formed by a single PrP monomer with the ordered core comprising PrP residues 94-225, which folds to create two asymmetric lobes with the N-linked glycans and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor projecting from the C-terminal lobe. The overall architecture is comparable to that of recently reported PrP fibrils isolated from the brain of hamsters infected with the 263K prion strain. However, there are marked conformational variations that could result from differences in PrP sequence and/or represent distinguishing features of the distinct prion strains. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13989.map.gz emd_13989.map.gz | 10.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13989-v30.xml emd-13989-v30.xml emd-13989.xml emd-13989.xml | 12.7 KB 12.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13989_fsc.xml emd_13989_fsc.xml | 13.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_13989.png emd_13989.png | 89.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13989.cif.gz emd-13989.cif.gz | 5.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13989 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13989 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13989 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13989 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7qigMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10992 (Title: Infectious mouse-adapted RML scrapie prion fibrils purified from terminally-infected mouse brains EMPIAR-10992 (Title: Infectious mouse-adapted RML scrapie prion fibrils purified from terminally-infected mouse brainsData size: 1.0 TB Data #1: Aligned multi-frame micrographs of RML prion fibrils [micrographs - single frame]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13989.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13989.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Ex vivo RML prion fibril | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.067 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
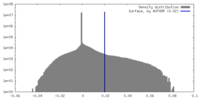
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Amyloid fibril of mouse PrP from RML--infected mouse brain
| Entire | Name: Amyloid fibril of mouse PrP from RML--infected mouse brain |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Amyloid fibril of mouse PrP from RML--infected mouse brain
| Supramolecule | Name: Amyloid fibril of mouse PrP from RML--infected mouse brain type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Major prion protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Major prion protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.290103 KDa |
| Sequence | String: THNQWNKPSK PKTNLKHVAG AAAAGAVVGG LGGYMLGSAM SRPMIHFGND WEDRYYRENM YRYPNQVYYR PVDQYSNQNN FVHDCVNIT IKQHTVTTTT KGENFTETDV KMMERVVEQM CVTQYQKESQ AYY UniProtKB: Major prion protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: C-flat-2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 45 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 49.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7qig: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)