[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-13673: Cryo-electron tomogram of podosomes at the basal surface of an un... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-electron tomogram of podosomes at the basal surface of an unroofed primary human macrophage (Volta phase plate, bin 4) | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-electron tomogram of podosomes at the basal surface of an unroofed primary human macrophage | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | electron tomography / cryo EM | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jasnin M | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 3 items Germany, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Elasticity of podosome actin networks produces nanonewton protrusive forces. Authors: Marion Jasnin / Jordan Hervy / Stéphanie Balor / Anaïs Bouissou / Amsha Proag / Raphaël Voituriez / Jonathan Schneider / Thomas Mangeat / Isabelle Maridonneau-Parini / Wolfgang Baumeister ...Authors: Marion Jasnin / Jordan Hervy / Stéphanie Balor / Anaïs Bouissou / Amsha Proag / Raphaël Voituriez / Jonathan Schneider / Thomas Mangeat / Isabelle Maridonneau-Parini / Wolfgang Baumeister / Serge Dmitrieff / Renaud Poincloux /   Abstract: Actin filaments assemble into force-generating systems involved in diverse cellular functions, including cell motility, adhesion, contractility and division. It remains unclear how networks of actin ...Actin filaments assemble into force-generating systems involved in diverse cellular functions, including cell motility, adhesion, contractility and division. It remains unclear how networks of actin filaments, which individually generate piconewton forces, can produce forces reaching tens of nanonewtons. Here we use in situ cryo-electron tomography to unveil how the nanoscale architecture of macrophage podosomes enables basal membrane protrusion. We show that the sum of the actin polymerization forces at the membrane is not sufficient to explain podosome protrusive forces. Quantitative analysis of podosome organization demonstrates that the core is composed of a dense network of bent actin filaments storing elastic energy. Theoretical modelling of the network as a spring-loaded elastic material reveals that it exerts forces of a few tens of nanonewtons, in a range similar to that evaluated experimentally. Thus, taking into account not only the interface with the membrane but also the bulk of the network, is crucial to understand force generation by actin machineries. Our integrative approach sheds light on the elastic behavior of dense actin networks and opens new avenues to understand force production inside cells. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13673.map.gz emd_13673.map.gz | 466.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13673-v30.xml emd-13673-v30.xml emd-13673.xml emd-13673.xml | 11.6 KB 11.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_13673.png emd_13673.png | 245.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13673 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13673 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13673 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13673 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13673.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 552.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13673.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 552.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-electron tomogram of podosomes at the basal surface of an unroofed primary human macrophage | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 16.84 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
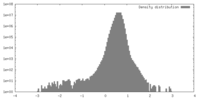
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Podosomes assembled at the basal surface of an unroofed human pri...
| Entire | Name: Podosomes assembled at the basal surface of an unroofed human primary monocyte-derived macrophage |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Podosomes assembled at the basal surface of an unroofed human pri...
| Supramolecule | Name: Podosomes assembled at the basal surface of an unroofed human primary monocyte-derived macrophage type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | electron tomography |
| Aggregation state | cell |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Material: GOLD / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
| Details | Cells were unroofed prior to vitrification |
| Cryo protectant | No |
| Sectioning | Other: NO SECTIONING |
| Fiducial marker | Manufacturer: Aurion / Diameter: 10 nm |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Phase plate: VOLTA PHASE PLATE / Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Details | Bi-directional tilt series were acquired from -30 to +60 degrees and -32 to -60 degrees with a tilt increment of 2 degrees and Volta phase plates |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average exposure time: 1.8 sec. / Average electron dose: 2.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 0.37 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.37 µm / Nominal magnification: 33000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Software - Name:  IMOD / Number images used: 61 IMOD / Number images used: 61 |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)