+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: EMDB / ID: EMD-1324 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Spontaneous reverse movement of mRNA-bound tRNA through the ribosome. | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | none | |||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
| 生物種 |  | |||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 12.0 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Konevega AL / Fischer N / Semenkov YP / Stark H / Wintermeyer W / Rodnina MV | |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2007 ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2007タイトル: Spontaneous reverse movement of mRNA-bound tRNA through the ribosome. 著者: Andrey L Konevega / Niels Fischer / Yuri P Semenkov / Holger Stark / Wolfgang Wintermeyer / Marina V Rodnina /  要旨: During the translocation step of protein synthesis, a complex of two transfer RNAs bound to messenger RNA (tRNA-mRNA) moves through the ribosome. The reaction is promoted by an elongation factor, ...During the translocation step of protein synthesis, a complex of two transfer RNAs bound to messenger RNA (tRNA-mRNA) moves through the ribosome. The reaction is promoted by an elongation factor, called EF-G in bacteria, which, powered by GTP hydrolysis, induces an open, unlocked conformation of the ribosome that allows for spontaneous tRNA-mRNA movement. Here we show that, in the absence of EF-G, there is spontaneous backward movement, or retrotranslocation, of two tRNAs bound to mRNA. Retrotranslocation is driven by the gain in affinity when a cognate E-site tRNA moves into the P site, which compensates the affinity loss accompanying the movement of peptidyl-tRNA from the P to the A site. These results lend support to the diffusion model of tRNA movement during translocation. In the cell, tRNA movement is biased in the forward direction by EF-G, which acts as a Brownian ratchet and prevents backward movement. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | EMマップ:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| 添付画像 |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_1324.map.gz emd_1324.map.gz | 7.5 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-1324-v30.xml emd-1324-v30.xml emd-1324.xml emd-1324.xml | 7.7 KB 7.7 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  1324.gif 1324.gif | 54 KB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1324 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1324 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1324 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1324 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_1324_validation.pdf.gz emd_1324_validation.pdf.gz | 252.3 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_1324_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_1324_full_validation.pdf.gz | 251.4 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_1324_validation.xml.gz emd_1324_validation.xml.gz | 5.5 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1324 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1324 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1324 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1324 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_1324.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 7.8 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_1324.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 7.8 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | none | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 2.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
CCP4マップ ヘッダ情報:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-添付データ
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : E. Coli 70S-tRNA complex prior to retrotranslocation 70S-fMetVal-...
| 全体 | 名称: E. Coli 70S-tRNA complex prior to retrotranslocation 70S-fMetVal-tRNAVal |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1000: E. Coli 70S-tRNA complex prior to retrotranslocation 70S-fMetVal-...
| 超分子 | 名称: E. Coli 70S-tRNA complex prior to retrotranslocation 70S-fMetVal-tRNAVal タイプ: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 2 |
|---|
-超分子 #1: E. Coli 70S
| 超分子 | 名称: E. Coli 70S / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / Ribosome-details: ribosome-prokaryote: ALL |
|---|
-分子 #1: fMet-Val-tRNAVal
| 分子 | 名称: fMet-Val-tRNAVal / タイプ: rna / ID: 1 / 分類: TRANSFER / Structure: OTHER / Synthetic?: No |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 詳細: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 70 mM NH4Cl, 30 mM KCl, 7 mM MgCl2, 0.6 mM spermine, 0.4 mM spermidine. |
|---|---|
| グリッド | 詳細: 200 mesh copper grid |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / 手法: Manual blotting |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI/PHILIPS CM200FEG |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | カテゴリ: CCD フィルム・検出器のモデル: GENERIC TVIPS (4k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 19 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 200 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: SPOT SCAN / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2.0 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1.0 µm / 倍率(公称値): 166000 |
| 試料ステージ | 試料ホルダー: Eucentric / 試料ホルダーモデル: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
- 画像解析
画像解析
| 詳細 | Particles selected semiautomatically. |
|---|---|
| CTF補正 | 詳細: local |
| 最終 再構成 | 想定した対称性 - 点群: C1 (非対称) / アルゴリズム: OTHER / 解像度のタイプ: BY AUTHOR / 解像度: 12.0 Å / 解像度の算出法: OTHER / ソフトウェア - 名称: Imagic / 使用した粒子像数: 11732 |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー







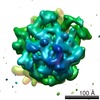
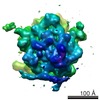

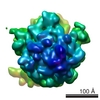

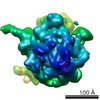


 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















