[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
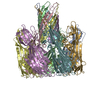
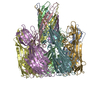
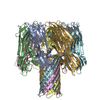
Yorodumi- EMDB-12696: Amyloid beta oligomer displayed on the alpha hemolysin scaffold -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-12696 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Amyloid beta oligomer displayed on the alpha hemolysin scaffold | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Amyloid beta oligomer / alpha hemolysin / Alzheimer's Disease / TOXIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytolysis in another organism / amyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway ...cytolysis in another organism / amyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process / axon midline choice point recognition / astrocyte activation involved in immune response / regulation of synapse structure or activity / NMDA selective glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of spontaneous synaptic transmission / mating behavior / growth factor receptor binding / peptidase activator activity / Golgi-associated vesicle / PTB domain binding / positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / astrocyte projection / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / neuron remodeling / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / nuclear envelope lumen / dendrite development / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / signaling receptor activator activity / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / transition metal ion binding / main axon / The NLRP3 inflammasome / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of multicellular organism growth / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / ECM proteoglycans / regulation of presynapse assembly / positive regulation of T cell migration / neuronal dense core vesicle / response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / positive regulation of chemokine production / Notch signaling pathway / cellular response to manganese ion / swimming behavior / clathrin-coated pit / extracellular matrix organization / neuron projection maintenance / astrocyte activation / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / Mitochondrial protein degradation / response to interleukin-1 / axonogenesis / protein serine/threonine kinase binding / platelet alpha granule lumen / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / cellular response to copper ion / cellular response to cAMP / positive regulation of glycolytic process / central nervous system development / dendritic shaft / trans-Golgi network membrane / endosome lumen / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / adult locomotory behavior / learning / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / locomotory behavior / serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / microglial cell activation / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / TAK1-dependent IKK and NF-kappa-B activation / recycling endosome / synapse organization / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / visual learning / positive regulation of JNK cascade / response to lead ion / Golgi lumen / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / cognition / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / cellular response to amyloid-beta / endocytosis / neuron projection development / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / positive regulation of inflammatory response / calcium ion transport / Platelet degranulation / heparin binding / regulation of translation Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
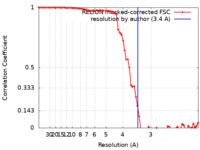
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wu J / Blum TB | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Angew Chem Int Ed Engl / Year: 2021 Journal: Angew Chem Int Ed Engl / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-electron Microscopy Imaging of Alzheimer's Amyloid-beta 42 Oligomer Displayed on a Functionally and Structurally Relevant Scaffold. Authors: Jinming Wu / Thorsten B Blum / Daniel P Farrell / Frank DiMaio / Jan Pieter Abrahams / Jinghui Luo /   Abstract: Amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) oligomers are pathogenic species of amyloid aggregates in Alzheimer's disease. Like certain protein toxins, Aβ oligomers permeabilize cellular membranes, presumably through ...Amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) oligomers are pathogenic species of amyloid aggregates in Alzheimer's disease. Like certain protein toxins, Aβ oligomers permeabilize cellular membranes, presumably through a pore formation mechanism. Owing to their structural and stoichiometric heterogeneity, the structure of these pores remains to be characterized. We studied a functional Aβ42-pore equivalent, created by fusing Aβ42 to the oligomerizing, soluble domain of the α-hemolysin (αHL) toxin. Our data reveal Aβ42-αHL oligomers to share major structural, functional, and biological properties with wild-type Aβ42-pores. Single-particle cryo-EM analysis of Aβ42-αHL oligomers (with an overall 3.3 Å resolution) reveals the Aβ42-pore region to be intrinsically flexible. The Aβ42-αHL oligomers will allow many of the features of the wild-type amyloid oligomers to be studied that cannot be otherwise, and may be a highly specific antigen for the development of immuno-base diagnostics and therapies. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_12696.map.gz emd_12696.map.gz | 21.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-12696-v30.xml emd-12696-v30.xml emd-12696.xml emd-12696.xml | 9.3 KB 9.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_12696_fsc.xml emd_12696_fsc.xml | 7.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_12696.png emd_12696.png | 87.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-12696.cif.gz emd-12696.cif.gz | 5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12696 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12696 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12696 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12696 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 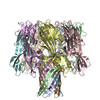 7o1qMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_12696.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_12696.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.03 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
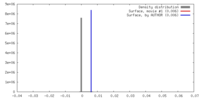
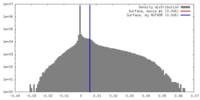
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Abeta42-AHL
| Entire | Name: Abeta42-AHL |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Abeta42-AHL
| Supramolecule | Name: Abeta42-AHL / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Alpha-hemolysin hybridized Abeta
| Macromolecule | Name: Alpha-hemolysin hybridized Abeta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.45927 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: ADSDINIKTG TTDIGSNTTV KTGDLVTYDK ENGMHKKVFY SFIDDKNHNK KLLVIRTKGT IAGQYRVYSE EGANKSGLAW PSAFKVQLQ LPDNEVAQIS DYYPRNDAEF RHDSGYEVHH QKLVFFAEDV GSNKGAIIGL MVGGVVIAYV QPDFKTILES P TDKKVGWK ...String: ADSDINIKTG TTDIGSNTTV KTGDLVTYDK ENGMHKKVFY SFIDDKNHNK KLLVIRTKGT IAGQYRVYSE EGANKSGLAW PSAFKVQLQ LPDNEVAQIS DYYPRNDAEF RHDSGYEVHH QKLVFFAEDV GSNKGAIIGL MVGGVVIAYV QPDFKTILES P TDKKVGWK VIFNNMVNQN WGPYDRDSWN PVYGNQLFMK TRNGSMKAAD NFLDPNKASS LLSSGFSPDF ATVITMDRKA SK QQTNIDV IYERVRDDYQ LHWTSTNWKG TNTKDKWTDR SSERYKIDWE KEEMTN UniProtKB: Alpha-hemolysin, Amyloid-beta precursor protein, Alpha-hemolysin |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4.83 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Details: 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole and 0.38 mM DDM |
| Grid | Material: GOLD |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 55.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)