+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-11996 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
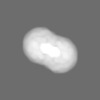
| Title | OsBOR3 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology | Bicarbonate transporter, eukaryotic / Bicarbonate transporter-like, transmembrane domain / HCO3- transporter integral membrane domain / solute:inorganic anion antiporter activity / monoatomic anion transport / membrane / Boron transporter Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
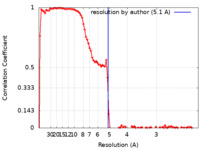
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Byrne B / Barritt JD | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
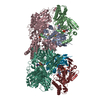
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2021 Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2021Title: Structural and functional insights into the mechanism of action of plant borate transporters. Authors: Savvas Saouros / Thotegowdanapalya C Mohan / Cristina Cecchetti / Silke Lehmann / Joseph D Barrit / Nicola J Scull / Paul Simpson / Yilmaz Alguel / Alexander D Cameron / Alexandra M E Jones ...Authors: Savvas Saouros / Thotegowdanapalya C Mohan / Cristina Cecchetti / Silke Lehmann / Joseph D Barrit / Nicola J Scull / Paul Simpson / Yilmaz Alguel / Alexander D Cameron / Alexandra M E Jones / Bernadette Byrne /   Abstract: Boron has essential roles in plant growth and development. BOR proteins are key in the active uptake and distribution of boron, and regulation of intracellular boron concentrations. However, their ...Boron has essential roles in plant growth and development. BOR proteins are key in the active uptake and distribution of boron, and regulation of intracellular boron concentrations. However, their mechanism of action remains poorly studied. BOR proteins are homologues of the human SLC4 family of transporters, which includes well studied mammalian transporters such as the human Anion Exchanger 1 (hAE1). Here we generated Arabidopsis thaliana BOR1 (AtBOR1) variants based (i) on known disease causing mutations of hAE1 (S466R, A500R) and (ii) a loss of function mutation (D311A) identified in the yeast BOR protein, ScBOR1p. The AtBOR1 variants express in yeast and localise to the plasma membrane, although both S466R and A500R exhibit lower expression than the WT AtBOR1 and D311A. The D311A, S466R and A500R mutations result in a loss of borate efflux activity in a yeast bor1p knockout strain. A. thaliana plants containing these three individual mutations exhibit substantially decreased growth phenotypes in soil under conditions of low boron. These data confirm an important role for D311 in the function of the protein and show that mutations equivalent to disease-causing mutations in hAE1 have major effects in AtBOR1. We also obtained a low resolution cryo-EM structure of a BOR protein from Oryza sativa, OsBOR3, lacking the 30 C-terminal amino acid residues. This structure confirms the gate and core domain organisation previously observed for related proteins, and is strongly suggestive of an inward facing conformation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_11996.map.gz emd_11996.map.gz | 3.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-11996-v30.xml emd-11996-v30.xml emd-11996.xml emd-11996.xml | 13.8 KB 13.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_11996_fsc.xml emd_11996_fsc.xml | 11.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_11996.png emd_11996.png | 100.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_11996_msk_1.map emd_11996_msk_1.map | 59.6 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11996 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11996 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11996 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11996 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_11996.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 59.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_11996.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 59.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_11996_msk_1.map emd_11996_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Borate transporter 3 from Oryza sativa (osBOR3)
| Entire | Name: Borate transporter 3 from Oryza sativa (osBOR3) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Borate transporter 3 from Oryza sativa (osBOR3)
| Supramolecule | Name: Borate transporter 3 from Oryza sativa (osBOR3) / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Homodimer of the osBOR3 integral membrane protein in LMNG detergent belt. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Oryza sativa borate transporter 3
| Macromolecule | Name: Oryza sativa borate transporter 3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MEESFVPLRG IKNDLHGRL Q CYKQDWTG GF RAGIRIL APT TYIFFA SAIP VISFG EQLER NTDG VLTAVQ TLA STALCGI IH SFLGGQPL L ILGVAEPTV LMYTFMFNFA KDRPDLGRR L FLAWTGWV CV WTAILLF LLA ILGACS IINR FTRIA ...String: MEESFVPLRG IKNDLHGRL Q CYKQDWTG GF RAGIRIL APT TYIFFA SAIP VISFG EQLER NTDG VLTAVQ TLA STALCGI IH SFLGGQPL L ILGVAEPTV LMYTFMFNFA KDRPDLGRR L FLAWTGWV CV WTAILLF LLA ILGACS IINR FTRIA GELFG LLIA MLFMQQ AIK GLVDEFR IP ERENRKAL E FVSSWRFAN GMFAIVLSFG LLLTALRSR K ARSWRYGT GW LRGFIAD YGV PLMVLV WTGV SYIPY GSVPK GIPR RLFSPN PWS PGAYDNW TV IRDMPNVP L LYIIGAFIP ATMIAVLYYF DHSVASQLA Q QKEFNLRK PP SFHYDLL LLG FLTLLC GLIG IPPAN GVIPQ SPMH TKSLAT LKH QLLRNRL VA TARQSMSQ N ASLSQLYGS MQEAYQQMQT PLIYQQPSV K GLNELKDS TV QMASSMG NID APVDET VFDI EKEID DLLPI EVKE QRLSNL LQA SMVGGCV AA MPLLKKIP T SVLWGYFAF MAIESLPGNQ FWERILLLF T APSRRYKV LE EYHTTFV ETV PFKTIA MFTL FQTMY LLVCF GITW IPIAGV LFP LMIMLLV PV RQYILPKL F KGAHLTDLD AAEYEESPAI PFIAAQDID V ALARTQSA EI LDDIVTR SRG EI |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 20.265 kPa |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: 3 second blot time -2 blot force. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 6285 / Average exposure time: 4.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)