[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-10666: Influenza C virus polymerase in complex with chicken ANP32A - Sub... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10666 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
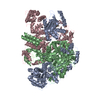
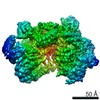
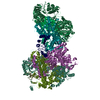
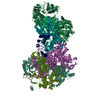
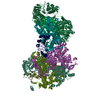
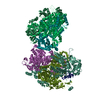
| Title | Influenza C virus polymerase in complex with chicken ANP32A - Subclass 1 | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | LocScale map | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Influenza Polymerase / ANP32 / replication / RNA-dependent RNA polymerase / VIRAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcap snatching / viral transcription / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA transcription via inhibition of RNA polymerase II activity / 7-methylguanosine mRNA capping / virion component / endonuclease activity / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / host cell cytoplasm / symbiont-mediated suppression of host gene expression / viral translational frameshifting ...cap snatching / viral transcription / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA transcription via inhibition of RNA polymerase II activity / 7-methylguanosine mRNA capping / virion component / endonuclease activity / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / host cell cytoplasm / symbiont-mediated suppression of host gene expression / viral translational frameshifting / RNA-directed RNA polymerase / viral RNA genome replication / nucleotide binding / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / DNA-templated transcription / host cell nucleus / RNA binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Influenza C virus (C/Johannesburg/1/66) / Influenza C virus (C/Johannesburg/1/66) /   Influenza C virus (strain C/Johannesburg/1/1966) Influenza C virus (strain C/Johannesburg/1/1966) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Carrique L / Keown JR | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3 items United Kingdom, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Host ANP32A mediates the assembly of the influenza virus replicase. Authors: Loïc Carrique / Haitian Fan / Alexander P Walker / Jeremy R Keown / Jane Sharps / Ecco Staller / Wendy S Barclay / Ervin Fodor / Jonathan M Grimes /  Abstract: Aquatic birds represent a vast reservoir from which new pandemic influenza A viruses can emerge. Influenza viruses contain a negative-sense segmented RNA genome that is transcribed and replicated by ...Aquatic birds represent a vast reservoir from which new pandemic influenza A viruses can emerge. Influenza viruses contain a negative-sense segmented RNA genome that is transcribed and replicated by the viral heterotrimeric RNA polymerase (FluPol) in the context of viral ribonucleoprotein complexes. RNA polymerases of avian influenza A viruses (FluPolA) replicate viral RNA inefficiently in human cells because of species-specific differences in acidic nuclear phosphoprotein 32 (ANP32), a family of essential host proteins for FluPol activity. Host-adaptive mutations, particularly a glutamic-acid-to-lysine mutation at amino acid residue 627 (E627K) in the 627 domain of the PB2 subunit, enable avian FluPolA to overcome this restriction and efficiently replicate viral RNA in the presence of human ANP32 proteins. However, the molecular mechanisms of genome replication and the interplay with ANP32 proteins remain largely unknown. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of influenza C virus polymerase (FluPolC) in complex with human and chicken ANP32A. In both structures, two FluPolC molecules form an asymmetric dimer bridged by the N-terminal leucine-rich repeat domain of ANP32A. The C-terminal low-complexity acidic region of ANP32A inserts between the two juxtaposed PB2 627 domains of the asymmetric FluPolA dimer, suggesting a mechanism for how the adaptive PB2(E627K) mutation enables the replication of viral RNA in mammalian hosts. We propose that this complex represents a replication platform for the viral RNA genome, in which one of the FluPol molecules acts as a replicase while the other initiates the assembly of the nascent replication product into a viral ribonucleoprotein complex. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10666.map.gz emd_10666.map.gz | 40.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10666-v30.xml emd-10666-v30.xml emd-10666.xml emd-10666.xml | 29.1 KB 29.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_10666_fsc.xml emd_10666_fsc.xml | 9.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_10666.png emd_10666.png | 140.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10666.cif.gz emd-10666.cif.gz | 8.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_10666_additional_1.map.gz emd_10666_additional_1.map.gz emd_10666_half_map_1.map.gz emd_10666_half_map_1.map.gz emd_10666_half_map_2.map.gz emd_10666_half_map_2.map.gz | 49.4 MB 77.7 MB 77.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10666 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10666 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10666 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10666 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6xzrMC  6xzdC  6xzgC  6xzpC  6xzqC  6y0cC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10666.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10666.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
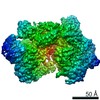
| Annotation | LocScale map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.37 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
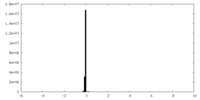
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: RELION 3.1 locally filtered map threshold
| File | emd_10666_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RELION 3.1 locally filtered map threshold | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
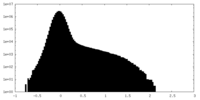
| Density Histograms |
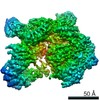
-Half map: None
| File | emd_10666_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | None | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
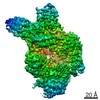
-Half map: None
| File | emd_10666_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | None | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Influenza C virus polymerase in complex with chicken ANP32A
| Entire | Name: Influenza C virus polymerase in complex with chicken ANP32A |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Influenza C virus polymerase in complex with chicken ANP32A
| Supramolecule | Name: Influenza C virus polymerase in complex with chicken ANP32A type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Influenza C virus (C/Johannesburg/1/66) Influenza C virus (C/Johannesburg/1/66) |
-Supramolecule #2: Influenza C virus polymerases
| Supramolecule | Name: Influenza C virus polymerases / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Influenza C virus (C/Johannesburg/1/66) Influenza C virus (C/Johannesburg/1/66) |
-Supramolecule #3: Chicken Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family memb...
| Supramolecule | Name: Chicken Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A (ANP32A) type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #4: Influenza viral RNA (vRNA) promoter 47mer
| Supramolecule | Name: Influenza viral RNA (vRNA) promoter 47mer / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 / Details: Synthetic RNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: Synthetic construct (others) |
-Macromolecule #1: RNA (5'-R(*AP*GP*UP*AP*GP*AP*AP*AP*CP*AP*AP*GP*GP*GP*CP*CP*CP*UP*...
| Macromolecule | Name: RNA (5'-R(*AP*GP*UP*AP*GP*AP*AP*AP*CP*AP*AP*GP*GP*GP*CP*CP*CP*UP*G)-3') type: rna / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: Synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.901737 KDa |
| Sequence | String: AGUAGAAACA AGGGUAUUUU UCUUUACUAG UCUACCCUGC UUUUGCU |
-Macromolecule #2: Polymerase acidic protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Polymerase acidic protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Influenza C virus (strain C/Johannesburg/1/1966) Influenza C virus (strain C/Johannesburg/1/1966) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 82.025531 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSKTFAEIAE AFLEPEAVRI AKEAVEEYGD HERKIIQIGI HFQVCCMFCD EYLSTNGSDR FVLIEGRKRG TAVSLQNELC KSYDLEPLP FLCDIFDREE KQFVEIGITR KADDSYFQSK FGKLGNSCKI FVFSYDGRLD KNCEGPMEEQ KLRIFSFLAT A ADFLRKEN ...String: MSKTFAEIAE AFLEPEAVRI AKEAVEEYGD HERKIIQIGI HFQVCCMFCD EYLSTNGSDR FVLIEGRKRG TAVSLQNELC KSYDLEPLP FLCDIFDREE KQFVEIGITR KADDSYFQSK FGKLGNSCKI FVFSYDGRLD KNCEGPMEEQ KLRIFSFLAT A ADFLRKEN MFNEIFLPDN EETIIEMKKG KTFLELRDES VPLPFQTYEQ MKDYCEKFKG NPRELASKVS QMQSNIKLPI KH YEQNKFR QIRLPKGPMA PYTHKFLMEE AWMFTKISDP ERSRAGEILI DFFKKGNLSA IRPKDKPLQG KYPIHYKNLW NQI KAAIAD RTMVINENDH SEFLGGIGRA SKKIPEISLT QDVITTEGLK QSENKLPEPR SFPRWFNAEW MWAIKDSDLT GWVP MAEYP PADNELEDYA EHLNKTMEGV LQGTNCAREM GKCILTVGAL MTECRLFPGK IKVVPIYARS KERKSMQEGL PVPSE MDCL FGICVKSKSH LNKDDGMYTI ITFEFSIREP NLEKHQKYTV FEAGHTTVRM KKGESVIGRE VPLYLYCRTT ALSKIK NDW LSKARRCFIT TMDTVETICL RESAKAEENL VEKTLNEKQM WIGKKNGELI AQPLREALRV QLVQQFYFCI YNDSQLE GF CNEQKKILMA LEGDKKNKSS FGFNPEGLLE KIEECLINNP MCLFMAQRLN ELVIEASKRG AKFFKTD UniProtKB: Polymerase acidic protein |
-Macromolecule #3: RNA-directed RNA polymerase catalytic subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: RNA-directed RNA polymerase catalytic subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Influenza C virus (strain C/Johannesburg/1/1966) Influenza C virus (strain C/Johannesburg/1/1966) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 86.145945 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MEINPYLMFL NNDVTSLIST TYPYTGPPPM SHGSSTKYTL ETIKRTYDYS RTSVEKTSKV FNIPRRKFCN CLEDKDELVK PTGNVDISS LLGLAEMMEK RMGEGFFKHC VMEAETEILK MHFSRLTEGR QTYDWTSERN MPAATALQLT VDAIKETEGP F KGTTMLEY ...String: MEINPYLMFL NNDVTSLIST TYPYTGPPPM SHGSSTKYTL ETIKRTYDYS RTSVEKTSKV FNIPRRKFCN CLEDKDELVK PTGNVDISS LLGLAEMMEK RMGEGFFKHC VMEAETEILK MHFSRLTEGR QTYDWTSERN MPAATALQLT VDAIKETEGP F KGTTMLEY CNKMIEMLDW KEIKFKKVKT VVRREKDKRS GKEIKTKVPV MGIDSIKHDE FLIRALTINT MAKDGERGKL QR RAIATPG MIVRPFSKIV ETVAQKICEK LKESGLPVGG NEKKAKLKTT VTSLNARMNS DQFAVNITGD NSKWNECQQP EAY LALLAY ITKDSSDLMK DLCSVAPVLF CNKFVKLGQG IRLSNKRKTK EVIIKAEKMG KYKNLMREEY KNLFEPLEKY IQKD VCFLP GGMLMGMFNM LSTVLGVSTL CYMDEELKAK GCFWTGLQSS DDFVLFAVAS NWSNIHWTIR RFNAVCKLIG INMSL EKSY GSLPELFEFT SMFFDGEFVS NLAMELPAFT TAGVNEGVDF TAAMSIIKTN MINNSLSPST ALMALRICLQ EFRATY RVH PWDSRVKGGR MKIINEFIKT IENKDGLLIA DGGKLMNNIS TLHIPEEVLK FEKMDEQYRN RVFNPKNPFT NFDKTID IF RAHGPIRVEE NEAVVSTHSF RTRANRTLLN TDMRAMMAEE KRYQMVCDMF KSVFESADIN PPIGAMSIGE AIEEKLLE R AKMKRDIGAI EDSEYEEIKD IIRDAKKARL ESR UniProtKB: RNA-directed RNA polymerase catalytic subunit |
-Macromolecule #4: Polymerase basic protein 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Polymerase basic protein 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Influenza C virus (strain C/Johannesburg/1/1966) Influenza C virus (strain C/Johannesburg/1/1966) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 104.272359 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSLLLTIAKE YKRLCQDAKA AQMMTVGTVS NYTTFKKWTT SRKEKNPSLR MRWAMSSKFP IIANKRMLEE AQIPKEHNNV ALWEDTEDV SKRDHVLASA SCINYWNFCG PCVNNSEVIK EVYKSRFGRL ERRKEIMWKE LRFTLVDRQR RRVDTQPVEQ R LRTGEIKD ...String: MSLLLTIAKE YKRLCQDAKA AQMMTVGTVS NYTTFKKWTT SRKEKNPSLR MRWAMSSKFP IIANKRMLEE AQIPKEHNNV ALWEDTEDV SKRDHVLASA SCINYWNFCG PCVNNSEVIK EVYKSRFGRL ERRKEIMWKE LRFTLVDRQR RRVDTQPVEQ R LRTGEIKD LQMWTLFEDE APLASKFILD NYGLVKEMRS KFANKPLNKE VVAHMLEKQF NPESRFLPVF GAIRPERMEL IH ALGGETW IQEANTAGIS NVDQRKNDIR AVCRKVCLAA NASIMNAKSK LVEYIKSTSM RIGETERKLE ELILETDDVS PEV TLCKSA LGGQLGKTLS FGPMLLKKIS GSGVKVKDTV YIQGVRAVQF EYWSEQEEFY GEYKSATALF SRKERSLEWI TIGG GINED RKRLLAMCMI FCRDGDYFKD APATITMADL STKLGREIPY QYVMMNWIQK SEDNLEALLY SRGIVETNPG KMGSS MGID GSKRAIKSLR AVTIQSGKID MPESKEKIHL ELSDNLEAFD SSGRIVATIL DLPSDKKVTF QDVSFQHPDL AVLRDE KTA ITKGYEALIK RLGTGDNDIP SLIAKKDYLS LYNLPEVKLM APLIRPNRKG VYSRVARKLV STQVTTGHYS LHELIKV LP FTYFAPKQGM FEGRLFFSND SFVEPGVNNN VFSWSKADSS KIYCHGIAIR VPLVVGDEHM DTSLALLEGF SVCENDPR A PMVTRQDLID VGFGQKVRLF VGQGSVRTFK RTASQRAASS DVNKNVKKIK MSNENLYFQG ELKTAALAQH DEAVDNKFN KEQQNAFYEI LHLPNLNEEQ RNAFIQSLKD DPSQSANLLA EAKKLNDAQA PKVDNKFNKE QQNAFYEILH LPNLNEEQRN AFIQSLKAD PSQSANLLAE AKKLNGAQAP KVDANSAGKS T UniProtKB: Polymerase basic protein 2 |
-Macromolecule #5: LRRcap domain-containing protein
| Macromolecule | Name: LRRcap domain-containing protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.91591 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: HHHHHHLEVL FQGPMDMKKR IHLELRNRTP SDVKELVLDN CRSYEGKIEG LTDEFEELEF LSTINVGLAS VANLPKLNKL KKLELSDNR VSGGLEVLAE KCPNLTHLNL SGNKIKDLGT IEPLKKLENL KSLDLFNCEV TNLNDYRENV FKLLPQLTYL D GYDRDDKE ...String: HHHHHHLEVL FQGPMDMKKR IHLELRNRTP SDVKELVLDN CRSYEGKIEG LTDEFEELEF LSTINVGLAS VANLPKLNKL KKLELSDNR VSGGLEVLAE KCPNLTHLNL SGNKIKDLGT IEPLKKLENL KSLDLFNCEV TNLNDYRENV FKLLPQLTYL D GYDRDDKE APDSDAEGYV EGLDDEEEDE DVLSLVKDRD DKEAPDSDAE GYVEGLDDEE EDEDEEEYDD DAQVVEDEED EE EEEEGEE EDVSGEEEED EEGYNDGDVD DDEDEEEPDE ERGQKRKREP EDEGDEDD UniProtKB: Acidic nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.28 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 294 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-44 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 3678 / Average exposure time: 11.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 38.8 e/Å2 Details: Single specimen tilt of 30 degrees for around two third of the images |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



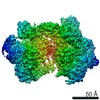






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)