+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10314 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
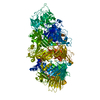
| Title | Tc holotoxin prepore TcdA1-TcdB2-TccC3-Cdc42 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | EM density map of ABC holotoxin formed by TcdA1 and TcdB2-TccC3-Cdc42 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationGBD domain binding / Golgi transport complex / positive regulation of pinocytosis / endothelin receptor signaling pathway involved in heart process / dendritic cell migration / cardiac neural crest cell migration involved in outflow tract morphogenesis / storage vacuole / apolipoprotein A-I receptor binding / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis / neuron fate determination ...GBD domain binding / Golgi transport complex / positive regulation of pinocytosis / endothelin receptor signaling pathway involved in heart process / dendritic cell migration / cardiac neural crest cell migration involved in outflow tract morphogenesis / storage vacuole / apolipoprotein A-I receptor binding / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis / neuron fate determination / regulation of attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore / organelle transport along microtubule / positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly / Inactivation of CDC42 and RAC1 / host-mediated perturbation of viral process / cardiac conduction system development / regulation of filopodium assembly / leading edge membrane / neuropilin signaling pathway / establishment of Golgi localization / GTP-dependent protein binding / adherens junction organization / filopodium assembly / cell junction assembly / establishment of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity / dendritic spine morphogenesis / thioesterase binding / regulation of lamellipodium assembly / regulation of stress fiber assembly / embryonic heart tube development / RHO GTPases activate KTN1 / DCC mediated attractive signaling / regulation of postsynapse organization / CD28 dependent Vav1 pathway / positive regulation of filopodium assembly / Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway / RHOV GTPase cycle / phagocytosis, engulfment / regulation of mitotic nuclear division / nuclear migration / small GTPase-mediated signal transduction / Myogenesis / heart contraction / positive regulation of cytokinesis / spindle midzone / RHOJ GTPase cycle / RHOQ GTPase cycle / establishment of cell polarity / Golgi organization / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / RHOU GTPase cycle / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / CDC42 GTPase cycle / macrophage differentiation / RHOG GTPase cycle / RAC2 GTPase cycle / RAC3 GTPase cycle / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / GPVI-mediated activation cascade / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / phagocytic vesicle / RAC1 GTPase cycle / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / substantia nigra development / Gene and protein expression by JAK-STAT signaling after Interleukin-12 stimulation / actin filament organization / small monomeric GTPase / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / filopodium / EGFR downregulation / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / cellular response to type II interferon / endocytosis / apical part of cell / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / cell-cell junction / mitotic spindle / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / intracellular protein localization / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / positive regulation of cell growth / actin cytoskeleton organization / G protein activity / midbody / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / neuron projection / postsynapse / positive regulation of cell migration / Golgi membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Photorhabdus luminescens (bacteria) Photorhabdus luminescens (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Roderer D / Raunser S / Schubert E / Sitsel O | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1 items Germany, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019Title: Towards the application of Tc toxins as a universal protein translocation system. Authors: Daniel Roderer / Evelyn Schubert / Oleg Sitsel / Stefan Raunser /  Abstract: Tc toxins are bacterial protein complexes that inject cytotoxic enzymes into target cells using a syringe-like mechanism. Tc toxins are composed of a membrane translocator and a cocoon that ...Tc toxins are bacterial protein complexes that inject cytotoxic enzymes into target cells using a syringe-like mechanism. Tc toxins are composed of a membrane translocator and a cocoon that encapsulates a toxic enzyme. The toxic enzyme varies between Tc toxins from different species and is not conserved. Here, we investigate whether the toxic enzyme can be replaced by other small proteins of different origin and properties, namely Cdc42, herpes simplex virus ICP47, Arabidopsis thaliana iLOV, Escherichia coli DHFR, Ras-binding domain of CRAF kinase, and TEV protease. Using a combination of electron microscopy, X-ray crystallography and in vitro translocation assays, we demonstrate that it is possible to turn Tc toxins into customizable molecular syringes for delivering proteins of interest across membranes. We also infer the guidelines that protein cargos must obey in terms of size, charge, and fold in order to apply Tc toxins as a universal protein translocation system. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10314.map.gz emd_10314.map.gz | 12.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10314-v30.xml emd-10314-v30.xml emd-10314.xml emd-10314.xml | 14.6 KB 14.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_10314.png emd_10314.png | 42.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10314 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10314 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10314 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10314 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10314.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10314.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
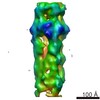
| Annotation | EM density map of ABC holotoxin formed by TcdA1 and TcdB2-TccC3-Cdc42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.14 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of TcdA1 pentamer and TcdB2-TccC3-Cdc42
| Entire | Name: Complex of TcdA1 pentamer and TcdB2-TccC3-Cdc42 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of TcdA1 pentamer and TcdB2-TccC3-Cdc42
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of TcdA1 pentamer and TcdB2-TccC3-Cdc42 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Photorhabdus luminescens (bacteria) Photorhabdus luminescens (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.7 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: TcdA1
| Macromolecule | Name: TcdA1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Photorhabdus luminescens (bacteria) Photorhabdus luminescens (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MNESVKEIPD VLKSQCGFNC LTDISHSSFN EFRQQVSEHL SWSETHDLYH DAQQAQKDNR LYEARILKRA NPQLQNAVHL AILAPNAELI GYNNQFSGRA SQYVAPGTVS SMFSPAAYLT ELYREARNLH ASDSVYYLDT RRPDLKSMAL SQQNMDIELS TLSLSNELLL ...String: MNESVKEIPD VLKSQCGFNC LTDISHSSFN EFRQQVSEHL SWSETHDLYH DAQQAQKDNR LYEARILKRA NPQLQNAVHL AILAPNAELI GYNNQFSGRA SQYVAPGTVS SMFSPAAYLT ELYREARNLH ASDSVYYLDT RRPDLKSMAL SQQNMDIELS TLSLSNELLL ESIKTESKLE NYTKVMEMLS TFRPSGATPY HDAYENVREV IQLQDPGLEQ LNASPAIAGL MHQASLLGIN ASISPELFNI LTEEITEGNA EELYKKNFGN IEPASLAMPE YLKRYYNLSD EELSQFIGKA SNFGQQEYSN NQLITPVVNS SDGTVKVYRI TREYTTNAYQ MDVELFPFGG ENYRLDYKFK NFYNASYLSI KLNDKRELVR TEGAPQVNIE YSANITLNTA DISQPFEIGL TRVLPSGSWA YAAAKFTVEE YNQYSFLLKL NKAIRLSRAT ELSPTILEGI VRSVNLQLDI NTDVLGKVFL TKYYMQRYAI HAETALILCN APISQRSYDN QPSQFDRLFN TPLLNGQYFS TGDEEIDLNS GSTGDWRKTI LKRAFNIDDV SLFRLLKITD HDNKDGKIKN NLKNLSNLYI GKLLADIHQL TIDELDLLLI AVGEGKTNLS AISDKQLATL IRKLNTITSW LHTQKWSVFQ LFIMTSTSYN KTLTPEIKNL LDTVYHGLQG FDKDKADLLH VMAPYIAATL QLSSENVAHS VLLWADKLQP GDGAMTAEKF WDWLNTKYTP GSSEAVETQE HIVQYCQALA QLEMVYHSTG INENAFRLFV TKPEMFGAAT GAAPAHDALS LIMLTRFADW VNALGEKASS VLAAFEANSL TAEQLADAMN LDANLLLQAS IQAQNHQHLP PVTPENAFSC WTSINTILQW VNVAQQLNVA PQGVSALVGL DYIQSMKETP TYAQWENAAG VLTAGLNSQQ ANTLHAFLDE SRSAALSTYY IRQVAKAAAA IKSRDDLYQY LLIDNQVSAA IKTTRIAEAI ASIQLYVNRA LENVEENANS GVISRQFFID WDKYNKRYST WAGVSQLVYY PENYIDPTMR IGQTKMMDAL LQSVSQSQLN ADTVEDAFMS YLTSFEQVAN LKVISAYHDN INNDQGLTYF IGLSETDAGE YYWRSVDHSK FNDGKFAANA WSEWHKIDCP INPYKSTIRP VIYKSRLYLL WLEQKEITKQ TGNSKDGYQT ETDYRYELKL AHIRYDGTWN TPITFDVNKK ISELKLEKNR APGLYCAGYQ GEDTLLVMFY NQQDTLDSYK NASMQGLYIF ADMASKDMTP EQSNVYRDNS YQQFDTNNVR RVNNRYAEDY EIPSSVSSRK DYGWGDYYLS MVYNGDIPTI NYKAASSDLK IYISPKLRII HNGYEGQKRN QCNLMNKYGK LGDKFIVYTS LGVNPNNSSN KLMFYPVYQY SGNTSGLNQG RLLFHRDTTY PSKVEAWIPG AKRSLTNQNA AIGDDYATDS LNKPDDLKQY IFMTDSKGTA TDVSGPVEIN TAISPAKVQI IVKAGGKEQT FTADKDVSIQ PSPSFDEMNY QFNALEIDGS GLNFINNSAS IDVTFTAFAE DGRKLGYESF SIPVTLKVST DNALTLHHNE NGAQYMQWQS YRTRLNTLFA RQLVARATTG IDTILSMETQ NIQEPQLGKG FYATFVIPPY NLSTHGDERW FKLYIKHVVD NNSHIIYSGQ LTDTNINITL FIPLDDVPLN QDYHAKVYMT FKKSPSDGTW WGPHFVRDDK GIVTINPKSI LTHFESVNVL NNISSEPMDF SGANSLYFWE LFYYTPMLVA QRLLHEQNFD EANRWLKYVW SPSGYIVHGQ IQNYQWNVRP LLEDTSWNSD PLDSVDPDAV AQHDPMHYKV STFMRTLDLL IARGDHAYRQ LERDTLNEAK MWYMQALHLL GDKPYLPLST TWSDPRLDRA ADITTQNAHD SAIVALRQNI PTPAPLSLRS ANTLTDLFLP QINEVMMNYW QTLAQRVYNL RHNLSIDGQP LYLPIYATPA DPKALLSAAV ATSQGGGKLP ESFMSLWRFP HMLENARGMV SQLTQFGSTL QNIIERQDAE ALNALLQNQA AELILTNLSI QDKTIEELDA EKTVLEKSKA GAQSRFDSYG KLYDENINAG ENQAMTLRAS AAGLTTAVQA SRLAGAAADL VPNIFGFAGG GSRWGAIAEA TGYVMEFSAN VMNTEADKIS QSETYRRRRQ EWEIQRNNAE AELKQIDAQL KSLAVRREAA VLQKTSLKTQ QEQTQSQLAF LQRKFSNQAL YNWLRGRLAA IYFQFYDLAV ARCLMAEQAY RWELNDDSAR FIKPGAWQGT YAGLLAGETL MLSLAQMEDA HLKRDKRALE VERTVSLAEV YAGLPKDNGP FSLAQEIDKL VSQGSGSAGS GNNNLAFGAG TDTKTSLQAS VSFADLKIRE DYPASLGKIR RIKQISVTLP ALLGPYQDVQ AILSYGDKAG LANGCEALAV SHGMNDSGQF QLDFNDGKFL PFEGIAIDQG TLTLSFPNAS MPEKGKQATM LKTLNDIILH IRYTIK |
-Macromolecule #2: chimeric protein TcdB2-TccC3-cdc42
| Macromolecule | Name: chimeric protein TcdB2-TccC3-cdc42 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Photorhabdus luminescens (bacteria) Photorhabdus luminescens (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MQNSQDFSIT ELSLPKGGGA ITGMGEALTP TGPDGMAALS LPLPISAGRG YAPAFTLNYN SGAGNSPFGL GWDCNVMTIR RRTHFGVPHY DETDTFLGPE GEVLVVADQP RDESTLQGIN LGATFTVTGY RSRLESHFSR LEYWQPKTTG KTDFWLIYSP DGQVHLLGKS ...String: MQNSQDFSIT ELSLPKGGGA ITGMGEALTP TGPDGMAALS LPLPISAGRG YAPAFTLNYN SGAGNSPFGL GWDCNVMTIR RRTHFGVPHY DETDTFLGPE GEVLVVADQP RDESTLQGIN LGATFTVTGY RSRLESHFSR LEYWQPKTTG KTDFWLIYSP DGQVHLLGKS PQARISNPSQ TTQTAQWLLE ASVSSRGEQI YYQYRAEDDT GCEADEITHH LQATAQRYLH IVYYGNRTAS ETLPGLDGSA PSQADWLFYL VFDYGERSNN LKTPPAFSTT GSWLCRQDRF SRYEYGFEIR TRRLCRQVLM YHHLQALDSK ITEHNGPTLV SRLILNYDES AIASTLVFVR RVGHEQDGNV VTLPPLELAY QDFSPRHHAH WQPMDVLANF NAIQRWQLVD LKGEGLPGLL YQDKGAWWYR SAQRLGEIGS DAVTWEKMQP LSVIPSLQSN ASLVDINGDG QLDWVITGPG LRGYHSQRPD GSWTRFTPLN ALPVEYTHPR AQLADLMGAG LSDLVLIGPK SVRLYANTRD GFAKGKDVVQ SGDITLPVPG TDPRKLVAFS DVLGSGQAHL VEVSATKVTC WPNLGRGRFG QPITLPGFSQ PATEFNPAQV YLADLDGSGP TDLIYVHTNR LDIFLNKSGN GFAEPVTLRF PEGLRFDHTC QLQMADVQGL GVASLILSVP HMSPHHWRCD LTNMKPWLLN EMNNNMGVHH TLRYRSSSQF WLDEKAAALT TGQTPVCYLP FPIHTLWQTE TEDEISGNKL VTTLRYARGA WDGREREFRG FGYVEQTDSH QLAQGNAPER TPPALTKNWY ATGLPVIDNA LSTEYWRDDQ AFAGFSPRFT TWQDNKDVPL TPEDDNSRYW FNRALKGQLL RSELYGLDDS TNKHVPYTVT EFRSQVRRLQ HTDSRYPVLW SSVVESRNYH YERIASDPQC SQNITLSSDR FGQPLKQLSV QYPRRQQPAI NLYPDTLPDK LLANSYDDQQ RQLRLTYQQS SWHHLTNNTV RVLGLPDSTR SDIFTYVAEN VPAGGLNLEL LSDKNSLIAD DKPREYLGQQ KTAYTDGQNT TPLQTPTRQA LIAFTETTVF NQSTLSAFNG SIPSDKLSTT LEQAGYQQTN YLFPRTGEDK VWVAHHGYTD YGTAAQFWRP QKQSNTQLTG KITLIWDANY CVVVQTRDAA GLTTSAKYDW RFLTPVQLTD INDNQHLITL DALGRPITLR FWGTENGKMT GYSSPEKASF SPPSDVNAAI ELKKPLPVAQ CQVYAPESWM PVLSQKTFNR LAEQDWQKLY NARIITEDGR ICTLAYRRWV QSQKAIPQLI SLLNNGPRLP PHSLTLTTDR YDHDPEQQIR QQVVFSDGFG RLLQAAARHE AGMARQRNED GSLIINVQHT ENRWAVTGRT EYDNKGQPIR TYQPYFLNDW RYVSNDSARQ EKEAYADTHV YDPIGREIKV ITAKGWFRRT LFTPWFTVNE DENDTAAEVK KVKMPGSRPM KNIDPKLYQK TPTVSVYDNR GLIIRNIDFH RTTANGDPDT RITRHQYDIH GHLNQSIDPR LYEAKQTNNT IKPNFLWQYD LTGNPLCTES IDAGRTVTLN DIEGRPLLTV TATGVIQTRQ YETSSLPGRL LSVAEQTPEE KTSRITERLI WAGNTEAEKD HNLAGQCVRH YDTAGVTRLE SLSLTGTVLS QSSQLLIDTQ EANWTGDNET VWQNMLADDI YTTLSTFDAT GALLTQTDAK GNIQRLAYDV AGQLNGSWLT LKGQTEQVII KSLTYSAAGQ KLREEHGNDV ITEYSYEPET QRLIGIKTRR PSDTKVLQDL RYEYDPVGNV ISIRNDAEAT RFWHNQKVMP ENTYTYDSLY QLISATGREM ANIGQQSHQF PSPALPSDNN TYTNYTRTYT YDRGGNLTKI QHSSPATQNN YTTNITVSNR SNRAVLSTLT EDPAQVDALF DAGGHQNTLI SGQNLNWNTR GELQQVTLVK RDKGANDDRE WYRYSGDGRR MLKINEQQAS NNAQTQRVTY LPNLELRLTQ NSTATTEDLQ VITVGEAGRA QVRVLHWESG KPEDIDNNQL RYSYDNLIGS SQLELDSEGQ IISEEEYYPY GGTALWAARN QTEASYKTIR YSGKERDATG LYYYGYRYYQ PWIGRWLSSD PAGTIDGLNL YRMVRNNPVT LLDPDGLEPM AMQTIKCVVV GDGAVGKTCL LISYTTNKFP SEYVPTVFDN YAVTVMIGGE PYTLGLFDTA GQEDYDRLRP LSYPQTDVFL VCFSVVSPSS FENVKEKWVP EITHHCPKTP FLLVGTQIDL RDDPSTIEKL AKNKQKPITP ETAEKLARDL KAVKYVECSA LTQRGLKNVF DEAILAALEP |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Average electron dose: 65.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: SPHIRE / Number images used: 56665 |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















