[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
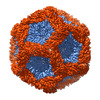
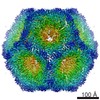
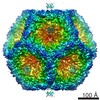
Yorodumi- EMDB-0245: Structure of the in vitro assembled bacteriophage phi6 P1P4 complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-0245 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the in vitro assembled bacteriophage phi6 P1P4 complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Bacteriophage phi6 in vitro assembled P1P4 particle | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Pseudomonas phage phi6 (virus) Pseudomonas phage phi6 (virus) | |||||||||
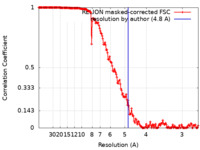
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Huiskonen JT / Ilca SL | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2018 Journal: mBio / Year: 2018Title: Dual Role of a Viral Polymerase in Viral Genome Replication and Particle Self-Assembly. Authors: Xiaoyu Sun / Serban L Ilca / Juha T Huiskonen / Minna M Poranen /   Abstract: Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) viruses package several RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRp) together with their dsRNA genome into an icosahedral protein capsid known as the polymerase complex. This ...Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) viruses package several RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRp) together with their dsRNA genome into an icosahedral protein capsid known as the polymerase complex. This structure is highly conserved among dsRNA viruses but is not found in any other virus group. RdRp subunits typically interact directly with the main capsid proteins, close to the 5-fold symmetric axes, and perform viral genome replication and transcription within the icosahedral protein shell. In this study, we utilized phage Φ6, a well-established virus self-assembly model, to probe the potential roles of the RdRp in dsRNA virus assembly. We demonstrated that Φ6 RdRp accelerates the polymerase complex self-assembly process and contributes to its conformational stability and integrity. We highlight the role of specific amino acid residues on the surface of the RdRp in its incorporation during the self-assembly reaction. Substitutions of these residues reduce RdRp incorporation into the polymerase complex during the self-assembly reaction. Furthermore, we determined that the overall transcription efficiency of the Φ6 polymerase complex increased when the number of RdRp subunits exceeded the number of genome segments. These results suggest a mechanism for RdRp recruitment in the polymerase complex and highlight its novel role in virion assembly, in addition to the canonical RNA transcription and replication functions. Double-stranded RNA viruses infect a wide spectrum of hosts, including animals, plants, fungi, and bacteria. Yet genome replication mechanisms of these viruses are conserved. During the infection cycle, a proteinaceous capsid, the polymerase complex, is formed. An essential component of this capsid is the viral RNA polymerase that replicates and transcribes the enclosed viral genome. The polymerase complex structure is well characterized for many double-stranded RNA viruses. However, much less is known about the hierarchical molecular interactions that take place in building up such complexes. Using the bacteriophage Φ6 self-assembly system, we obtained novel insights into the processes that mediate polymerase subunit incorporation into the polymerase complex for generation of functional structures. The results presented pave the way for the exploitation and engineering of viral self-assembly processes for biomedical and synthetic biology applications. An understanding of viral assembly processes at the molecular level may also facilitate the development of antivirals that target viral capsid assembly. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_0245.map.gz emd_0245.map.gz | 395.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-0245-v30.xml emd-0245-v30.xml emd-0245.xml emd-0245.xml | 12.6 KB 12.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_0245_fsc.xml emd_0245_fsc.xml | 16.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_0245.png emd_0245.png | 221.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_0245_msk_1.map emd_0245_msk_1.map | 421.9 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0245 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0245 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0245 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0245 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_0245.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_0245.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Bacteriophage phi6 in vitro assembled P1P4 particle | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.35 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
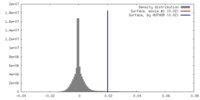
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_0245_msk_1.map emd_0245_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
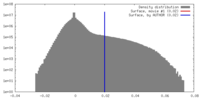
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Pseudomonas phage phi6
| Entire | Name:  Pseudomonas phage phi6 (virus) Pseudomonas phage phi6 (virus) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Pseudomonas phage phi6
| Supramolecule | Name: Pseudomonas phage phi6 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / NCBI-ID: 10879 / Sci species name: Pseudomonas phage phi6 / Virus type: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE / Virus isolate: OTHER / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: Yes |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:  Pseudomonas syringae (bacteria) Pseudomonas syringae (bacteria) |
| Host system | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: P1 protein from bacteriophage phi6
| Macromolecule | Name: P1 protein from bacteriophage phi6 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: DEXTRO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Pseudomonas phage phi6 (virus) Pseudomonas phage phi6 (virus) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MFNLKVKDL NGSARGLTQA FAIGELKNQL SVGALQLPLQ FTRTFSASMT S ELLWEVGK GNIDPVMYAR LFFQYAQAGG ALSVDELVNQ FTEYHQSTAC NP EIWRKLT AYITGSSNRA IKADAVGKVP PTAILEQLRT LAPSEHELFH HIT TDFVCH VLSPLGFILP ...String: MFNLKVKDL NGSARGLTQA FAIGELKNQL SVGALQLPLQ FTRTFSASMT S ELLWEVGK GNIDPVMYAR LFFQYAQAGG ALSVDELVNQ FTEYHQSTAC NP EIWRKLT AYITGSSNRA IKADAVGKVP PTAILEQLRT LAPSEHELFH HIT TDFVCH VLSPLGFILP DAAYVYRVGR TATYPNFYAL VDCVRASDLR RMLT ALSSV DSKMLQATFK AKGALAPALI SQHLANAATT AFERSRGNFD ANAVV SSVL TILGRLWSPS TPKELDPSAR LRNTNGIDQL RSNLALFIAY QDMVKQ RGR AEVIFSDEEL SSTIIPWFIE AMSEVSPFKL RPINETTSYI GQTSAID HM GQPSHVVVYE DWQFAKEITA FTPVKLANNS NQRFLDVEPG ISDRMSAT L APIGNTFAVS AFVKNRTAVY EAVSQRGTVN SNGAEMTLGF PSVVERDYA LDRDPMVAIA ALRTGIVDES LEARASNDLK RSMFNYYAAV MHYAVAHNPE VVVSEHQGV AAEQGSLYLV WNVRTELRIP VGYNAIEGGS IRTPEPLEAI A YNKPIQPS EVLQAKVLDL ANHTTSIHIW PWHEASTEFA YEDAYSVTIR NK RYTAEVK EFELLGLGQR RERVRILKPT VAHAIIQMWY SWFVEDDRTL AAA RRTSRD DAEKLAIDGR RMQNAVTLLR KIEMIGTTGI GASAVHLAQS RIVD QMAGR GLIDDSSDLH VGINRHRIRI WAGLAVLQMM GLLSRSEAEA LTKVL GDSN ALGMVVATTD IDPSL |
-Macromolecule #2: P4 protein from bacteriophage phi6
| Macromolecule | Name: P4 protein from bacteriophage phi6 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: DEXTRO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Pseudomonas phage phi6 (virus) Pseudomonas phage phi6 (virus) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPIVVTQAH IDRVGIAADL LDASPVSLQV LGRPTAINTV VIKTYIAAVM E LASKQGGS LAGVDIRPSV LLKDTAIFTK PKAKSADVES DVDVLDTGIY SV PGLARKP VTHRWPSEGI YSGVTALMGA TGSGKSITLN EKLRPDVLIR WGE VAEAYD ELDTAVHIST ...String: MPIVVTQAH IDRVGIAADL LDASPVSLQV LGRPTAINTV VIKTYIAAVM E LASKQGGS LAGVDIRPSV LLKDTAIFTK PKAKSADVES DVDVLDTGIY SV PGLARKP VTHRWPSEGI YSGVTALMGA TGSGKSITLN EKLRPDVLIR WGE VAEAYD ELDTAVHIST LDEMLIVCIG LGALGFNVAV DSVRPLLFRL KGAA SAGGI VAVFYSLLTD ISNLFTQYDC SVVMVVNPMV DAEKIEYVFG QVMAS TVGA ILCADGNVSR TMFRTNKGRI FNGAAPLAAD THMPSMDRPT SMKALD HTS IASVAPLERG SVDTDDRNSA PRRGANFSL |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 1.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: OTHER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)