+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 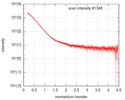 |
|---|---|
 Sample Sample | RXRΔH12/RAR Heterodimer : N-CoRNID Complex (1:1)
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTranscriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / Carnitine shuttle / Transcriptional regulation of white adipocyte differentiation / Signaling by Retinoic Acid / NR1H2 & NR1H3 regulate gene expression to control bile acid homeostasis / NR1H3 & NR1H2 regulate gene expression linked to cholesterol transport and efflux / definitive erythrocyte differentiation / SUMOylation of intracellular receptors / Recycling of bile acids and salts / Downregulation of SMAD2/3:SMAD4 transcriptional activity ...Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / Carnitine shuttle / Transcriptional regulation of white adipocyte differentiation / Signaling by Retinoic Acid / NR1H2 & NR1H3 regulate gene expression to control bile acid homeostasis / NR1H3 & NR1H2 regulate gene expression linked to cholesterol transport and efflux / definitive erythrocyte differentiation / SUMOylation of intracellular receptors / Recycling of bile acids and salts / Downregulation of SMAD2/3:SMAD4 transcriptional activity / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts / CD4-positive, CD25-positive, alpha-beta regulatory T cell differentiation / Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway / visceral serous pericardium development / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 27-hydroxycholesterol / ventricular cardiac muscle cell differentiation / mesenchyme development / HDACs deacetylate histones / Endogenous sterols / Notch-HLH transcription pathway / positive regulation of translational initiation by iron / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / maternal placenta development / angiogenesis involved in coronary vascular morphogenesis / Regulation of lipid metabolism by PPARalpha / Cytoprotection by HMOX1 / secretory columnal luminar epithelial cell differentiation involved in prostate glandular acinus development / positive regulation of thyroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / cardiac muscle cell differentiation / nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding / thalamus development / camera-type eye development / regulation of thyroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway / nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding / histone deacetylase regulator activity / RNA polymerase II intronic transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / regulation of branching involved in prostate gland morphogenesis / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / locomotor rhythm / nuclear steroid receptor activity / cellular response to Thyroglobulin triiodothyronine / regulation of multicellular organism growth / epidermis development / establishment of skin barrier / cardiac muscle cell proliferation / positive regulation of bone mineralization / nuclear retinoid X receptor binding / heart morphogenesis / retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / hormone-mediated signaling pathway / transcription repressor complex / embryo implantation / negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / cholesterol homeostasis / placenta development / RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / circadian regulation of gene expression / mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin DNA binding / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / transcription coactivator binding / nuclear receptor activity / transcription corepressor activity / T cell differentiation in thymus / heart development / gene expression / chromatin organization / transcription regulator complex / sequence-specific DNA binding / in utero embryonic development / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / protein stabilization / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / protein domain specific binding / negative regulation of gene expression / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / chromatin binding / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / mitochondrion / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species | Mouse (Mus musculus) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2019 Journal: Structure / Year: 2019Title: Interplay of Protein Disorder in Retinoic Acid Receptor Heterodimer and Its Corepressor Regulates Gene Expression. Authors: Tiago N Cordeiro / Nathalie Sibille / Pierre Germain / Philippe Barthe / Abdelhay Boulahtouf / Fréderic Allemand / Rémy Bailly / Valérie Vivat / Christine Ebel / Alessandro Barducci / ...Authors: Tiago N Cordeiro / Nathalie Sibille / Pierre Germain / Philippe Barthe / Abdelhay Boulahtouf / Fréderic Allemand / Rémy Bailly / Valérie Vivat / Christine Ebel / Alessandro Barducci / William Bourguet / Albane le Maire / Pau Bernadó /    Abstract: In its unliganded form, the retinoic acid receptor (RAR) in heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) exerts a strong repressive activity facilitated by the recruitment of transcriptional ...In its unliganded form, the retinoic acid receptor (RAR) in heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) exerts a strong repressive activity facilitated by the recruitment of transcriptional corepressors in the promoter region of target genes. By integrating complementary structural, biophysical, and computational information, we demonstrate that intrinsic disorder is a required feature for the precise regulation of RAR activity. We show that structural dynamics of RAR and RXR H12 regions is an essential mechanism for RAR regulation. Unexpectedly we found that, while mainly disordered, the corepressor N-CoR presents evolutionary conserved structured regions involved in transient intramolecular contacts. In the presence of RXR/RAR, N-CoR exploits its multivalency to form a cooperative multisite complex that displays equilibrium between different conformational states that can be tuned by cognate ligands and receptor mutations. This equilibrium is key to preserving the repressive basal state while allowing the conversion to a transcriptionally active form. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDF54 SASDF54 |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: RXRΔH12/RAR Heterodimer : N-CoRNID Complex (1:1) / Specimen concentration: 0.80-11.20 / Entity id: 1515 / 1536 / 1538 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 50mM Tris HCl, 150mM NaCl, 2mM TCEP. / pH: 7.5 |
| Entity #1515 | Name: N-CoR-NID / Type: protein Description: Nuclear receptor CoRepressor 1; Nuclear Receptor Interaction Domain (NID) Formula weight: 29.139 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Mouse (Mus musculus) / References: UniProt: Q60974 Sequence: GPHMQVPRTH RLITLADHIC QIITQDFARN QVPSQASTST FQTSPSALSS TPVRTKTSSR YSPESQSQTV LHPRPGPRVS PENLVDKSRG SRPGKSPERS HIPSEPYEPI SPPQGPAVHE KQDSMLLLSQ RGVDPAEQRS DSRSPGSISY LPSFFTKLES TSPMVKSKKQ ...Sequence: GPHMQVPRTH RLITLADHIC QIITQDFARN QVPSQASTST FQTSPSALSS TPVRTKTSSR YSPESQSQTV LHPRPGPRVS PENLVDKSRG SRPGKSPERS HIPSEPYEPI SPPQGPAVHE KQDSMLLLSQ RGVDPAEQRS DSRSPGSISY LPSFFTKLES TSPMVKSKKQ EIFRKLNSSG GGDSDMAAAQ PGTEIFNLPA VTTSGAVSSR SHSFADPASN LGLEDIIRKA LMGSFDDKVE DHGVVMSHPV GIMPGSASTS VVTSSEARRD E |
| Entity #1536 | Name: RXR / Type: protein Description: Retinoid-X receptor alpha (RXR-alpha) Ligand Binding Domain (LBD) Formula weight: 26.47 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Mouse (Mus musculus) / References: UniProt: P28700 Sequence: SANEDMPVEK ILEAELAVEP KTETYVEANM GLNPSSPNDP VTNICQAADK QLFTLVEWAK RIPHFSELPL DDQVILLRAG WNELLIASAS HRSIAVKDGI LLATGLHVHR NSAHSAGVGA IFDRVLTELV SKMRDMQMDK TELGCLRAIV LFNPDSKGLS NPAEVEALRE ...Sequence: SANEDMPVEK ILEAELAVEP KTETYVEANM GLNPSSPNDP VTNICQAADK QLFTLVEWAK RIPHFSELPL DDQVILLRAG WNELLIASAS HRSIAVKDGI LLATGLHVHR NSAHSAGVGA IFDRVLTELV SKMRDMQMDK TELGCLRAIV LFNPDSKGLS NPAEVEALRE KVYASLEAYC KHKYPEQPGR FAKLLLRLPA LRSIGLKCLE HLFFFKLIGD TPIDTFLMEM LEAPHQAT |
| Entity #1538 | Name: RXRΔH12 / Type: protein Description: Retinoid-X receptor alpha (RXR-alpha) Δ helix12 Formula weight: 23.5 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Mouse (Mus musculus) / References: UniProt: P28700 Sequence: STSSANEDMP VEKILEAELA VEPKTETYVE ANMGLNPSSP NDPVTNICQA ADKQLFTLVE WAKRIPHFSE LPLDDQVILL RAGWNELLIA SASHRSIAVK DGILLATGLH VHRNSAHSAG VGAIFDRVLT ELVSKMRDMQ MDKTELGCLR AIVLFNPDSK GLSNPAEVEA ...Sequence: STSSANEDMP VEKILEAELA VEPKTETYVE ANMGLNPSSP NDPVTNICQA ADKQLFTLVE WAKRIPHFSE LPLDDQVILL RAGWNELLIA SASHRSIAVK DGILLATGLH VHRNSAHSAG VGAIFDRVLT ELVSKMRDMQ MDKTELGCLR AIVLFNPDSK GLSNPAEVEA LREKVYASLE AYCKHKYPEQ PGRFAKLLLR LPALRSIGLK CLE |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: ESRF BM29 / City: Grenoble / 国: France  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.099 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.9 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.099 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 2.9 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 1M / Type: Dectris / Pixsize x: 172 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
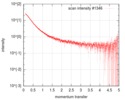
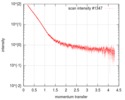
| Scan |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller