[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- SASDBR3: Wild type RNF8 complexed with Ubc13 (C87K, K92A mutant): conjugat... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDBR3 |
|---|---|
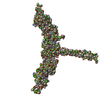
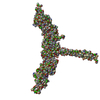
 Sample Sample | Wild type RNF8 complexed with Ubc13 (C87K, K92A mutant): conjugated to Ubiquitin
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationUBC13-MMS2 complex / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme complex / ubiquitin-protein transferase activator activity / sperm DNA condensation / positive regulation of protein K63-linked ubiquitination / DNA double-strand break processing / protein K6-linked ubiquitination / isotype switching / DNA damage tolerance / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme ...UBC13-MMS2 complex / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme complex / ubiquitin-protein transferase activator activity / sperm DNA condensation / positive regulation of protein K63-linked ubiquitination / DNA double-strand break processing / protein K6-linked ubiquitination / isotype switching / DNA damage tolerance / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / response to ionizing radiation / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / protein monoubiquitination / ubiquitin ligase complex / interstrand cross-link repair / regulation of DNA repair / protein autoubiquitination / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / signal transduction in response to DNA damage / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / antiviral innate immune response / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 upon TLR3 ligation / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Regulation of PTEN localization / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / ubiquitin binding / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / positive regulation of DNA repair / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / Degradation of CDH1 / Translesion synthesis by POLK / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Josephin domain DUBs / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / Degradation of CRY and PER proteins / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Regulation of signaling by CBL Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2016 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2016Title: RNF8 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Stimulates Ubc13 E2 Conjugating Activity That Is Essential for DNA Double Strand Break Signaling and BRCA1 Tumor Suppressor Recruitment. Authors: Curtis D Hodge / Ismail H Ismail / Ross A Edwards / Greg L Hura / Andrew T Xiao / John A Tainer / Michael J Hendzel / J N Mark Glover /    Abstract: DNA double strand break (DSB) responses depend on the sequential actions of the E3 ubiquitin ligases RNF8 and RNF168 plus E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 to specifically generate histone Lys-63- ...DNA double strand break (DSB) responses depend on the sequential actions of the E3 ubiquitin ligases RNF8 and RNF168 plus E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 to specifically generate histone Lys-63-linked ubiquitin chains in DSB signaling. Here, we defined the activated RNF8-Ubc13∼ubiquitin complex by x-ray crystallography and its functional solution conformations by x-ray scattering, as tested by separation-of-function mutations imaged in cells by immunofluorescence. The collective results show that the RING E3 RNF8 targets E2 Ubc13 to DSB sites and plays a critical role in damage signaling by stimulating polyubiquitination through modulating conformations of ubiquitin covalently linked to the Ubc13 active site. Structure-guided separation-of-function mutations show that the RNF8 E2 stimulating activity is essential for DSB signaling in mammalian cells and is necessary for downstream recruitment of 53BP1 and BRCA1. Chromatin-targeted RNF168 rescues 53BP1 recruitment involved in non-homologous end joining but not BRCA1 recruitment for homologous recombination. These findings suggest an allosteric approach to targeting the ubiquitin-docking cleft at the E2-E3 interface for possible interventions in cancer and chronic inflammation, and moreover, they establish an independent RNF8 role in BRCA1 recruitment. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDBR3 SASDBR3 |
|---|
-Related structure data
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
| Model #461 |  Type: mix / Software: MES-FoXS / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|---|
| Model #462 |  Type: mix / Software: MES-FoXS / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
| Model #463 |  Type: mix / Software: MES-FoXS / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
| Model #464 |  Type: mix / Software: MES-FoXS / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
| Model #465 |  Type: mix / Software: MES-FoXS / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Wild type RNF8 complexed with Ubc13 (C87K, K92A mutant): conjugated to Ubiquitin Entity id: 304 / 305 / 306 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: HEPES / Concentration: 20.00 mM / pH: 6.8 / Composition: 200 mM NaCl, 0.01 mM, ZnSO4, and 1 mM DTT |
| Entity #304 | Name: RNF8 / Type: protein / Description: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF8 / Formula weight: 17.618 / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: O76064 Sequence: GPLGSPEFQE HWALMEELNR SKKDFEAIIQ AKNKELEQTK EEKEKMQAQK EEVLSHMNDV LENELQCIIC SEYFIEAVTL NCAHSFCSYC INEWMKRKIE CPICRKDIKS KTYSLVLDNC INKMVNNLSS EVKERRIVLI RERKAKRLF |
| Entity #305 | Name: Ubc13 - C87K, K92A / Type: protein Description: Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 N double mutant (C87K, K92A) Formula weight: 17.89 / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: P61088 Sequence: GPLGSPEFMA GLPRRIIKET QRLLAEPVPG IKAEPDESNA RYFHVVIAGP QDSPFEGGTF KLELFLPEEY PMAAPKVRFM TKIYHPNVDK LGRIKLDILA DKWSPALQIR TVLLSIQALL SAPNPDDPLA NDVAEQWKTN EAQAIETARA WTRLYAMNNI |
| Entity #306 | Name: UBC / Type: protein / Description: Polyubiquitin-C / Formula weight: 8.565 / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: P0CG48 Sequence: MQIFVKTLTG KTITLEVEPS DTIENVKAKI QDKEGIPPDQ QRLIFAGKQL EDGRTLSDYN IQKESTLHLV LRLRGG |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: Advanced Light Source (ALS) 12.3.1 (SIBYLS) City: Berkeley, CA / 国: USA  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.103 Å / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.103 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 2M | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller