+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9qq6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
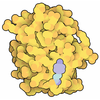
| Title | Structure of the Azotobacter vinelandii NifL-NifA complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / biological nitrogen fixation / transcriptional regulation / sustainable agriculture | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprotein histidine kinase activity / nitrogen fixation / histidine kinase / phosphorelay signal transduction system / sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.45 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bueno Batista, M. / Richardson, J. / Webster, M.W. / Ghilarov, D. / Peters, J.W. / Lawson, D.M. / Dixon, R. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  United States, 9items United States, 9items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: FEBS J / Year: 2025 Journal: FEBS J / Year: 2025Title: Structural analysis of the NifL-NifA complex reveals the molecular basis of anti-activation of nitrogen fixation gene expression in Azotobacter vinelandii. Authors: Marcelo Bueno Batista / Jake Richardson / Michael W Webster / Dmitry Ghilarov / John W Peters / David M Lawson / Ray Dixon /   Abstract: Understanding the molecular basis of regulated nitrogen (N) fixation is essential for engineering N-fixing bacteria that fulfill the demand of crop plants for fixed nitrogen, reducing our reliance on ...Understanding the molecular basis of regulated nitrogen (N) fixation is essential for engineering N-fixing bacteria that fulfill the demand of crop plants for fixed nitrogen, reducing our reliance on synthetic nitrogen fertilizers. In Azotobacter vinelandii and many other members of Proteobacteria, the two-component system comprising the anti-activator protein (NifL) and the Nif-specific transcriptional activator (NifA)controls the expression of nif genes, encoding the nitrogen fixation machinery. The NifL-NifA system evolved the ability to integrate several environmental cues, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon availability. The nitrogen fixation machinery is thereby only activated under strictly favorable conditions, enabling diazotrophs to thrive in competitive environments. While genetic and biochemical studies have enlightened our understanding of how NifL represses NifA, the molecular basis of NifA sequestration by NifL depends on structural information on their interaction. Here, we present mechanistic insights into how nitrogen fixation is regulated by combining biochemical and genetic approaches with a low-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) map of the oxidized NifL-NifA complex. Our findings define the interaction surface between NifL and NifA and reveal how this interaction can be manipulated to generate bacterial strains with increased nitrogen fixation rates able to secrete surplus nitrogen outside the cell, a crucial step in engineering improved nitrogen delivery to crop plants. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9qq6.cif.gz 9qq6.cif.gz | 427.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9qq6.ent.gz pdb9qq6.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9qq6.json.gz 9qq6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/9qq6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/9qq6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/9qq6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/9qq6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  53294MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 59897.203 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: The wild-type sequence was pre-pended by a Strep-Tag II in place of the N-terminal methionine with sequence MASWSHPQFEKGADDDDKV Source: (gene. exp.)  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: nifL, Avin_50990 / Production host: Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: nifL, Avin_50990 / Production host:  #2: Protein | | Mass: 58979.191 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: A hexahistidine tag was appended directly to the C-terminus of the wild-type sequence Source: (gene. exp.)  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: nifA, Avin_51000 / Production host: Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: nifA, Avin_51000 / Production host:  #3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: NifL-NifA complex from Azotobacter vinelandii / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.24 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: 20 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 300 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM ADP, 1 mM TCEP |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: The particles had a tendency to aggregate, were prone to orientational bias and because they were long and thin, they were difficult to distinguish from the background. |
| Specimen support | Details: glow discharged for 60 seconds at 8 mA using an ACE 200 (Leica Microsystems) Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 80 K / Temperature (min): 80 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.27 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 14218 Details: mode: counting; super resolution, x2 binning, magnified pixel size 0.83 Angstrom |
| Image scans | Width: 5760 / Height: 4092 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2186245 Details: Used template-based picking with 2D-classes from blob picker | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.45 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 209009 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 456 / Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL / Target criteria: cross-correlation coefficient / Details: Real space refinement in COOT and PHENIX | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Source name: AlphaFold / Type: in silico model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj