+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural analysis of the NifL-NifA complex reveals the molecular basis of anti-activation of nitrogen fixation gene expression in Azotobacter vinelandii. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | FEBS J, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Sep 7, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Marcelo Bueno Batista / Jake Richardson / Michael W Webster / Dmitry Ghilarov / John W Peters / David M Lawson / Ray Dixon /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Understanding the molecular basis of regulated nitrogen (N) fixation is essential for engineering N-fixing bacteria that fulfill the demand of crop plants for fixed nitrogen, reducing our reliance on ...Understanding the molecular basis of regulated nitrogen (N) fixation is essential for engineering N-fixing bacteria that fulfill the demand of crop plants for fixed nitrogen, reducing our reliance on synthetic nitrogen fertilizers. In Azotobacter vinelandii and many other members of Proteobacteria, the two-component system comprising the anti-activator protein (NifL) and the Nif-specific transcriptional activator (NifA)controls the expression of nif genes, encoding the nitrogen fixation machinery. The NifL-NifA system evolved the ability to integrate several environmental cues, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon availability. The nitrogen fixation machinery is thereby only activated under strictly favorable conditions, enabling diazotrophs to thrive in competitive environments. While genetic and biochemical studies have enlightened our understanding of how NifL represses NifA, the molecular basis of NifA sequestration by NifL depends on structural information on their interaction. Here, we present mechanistic insights into how nitrogen fixation is regulated by combining biochemical and genetic approaches with a low-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) map of the oxidized NifL-NifA complex. Our findings define the interaction surface between NifL and NifA and reveal how this interaction can be manipulated to generate bacterial strains with increased nitrogen fixation rates able to secrete surplus nitrogen outside the cell, a crucial step in engineering improved nitrogen delivery to crop plants. |
 External links External links |  FEBS J / FEBS J /  PubMed:40915976 PubMed:40915976 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 6.45 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-53294, PDB-9qq6: |
| Chemicals | 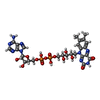 ChemComp-FAD:  ChemComp-ADP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / biological nitrogen fixation / transcriptional regulation / sustainable agriculture |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 azotobacter vinelandii dj (bacteria)
azotobacter vinelandii dj (bacteria)