+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9leg | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | AMO complex | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / AMO complex | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.36 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li, Z.Q. / Yang, X.Y. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 2items China, 2items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of ammonia monooxygenase. Authors: Xiaoyun Yang / Zongqiang Li / Tie-Qiang Mao / Chaofu Ma / Guo-Hao Chen / Hong-Po Dong / Sen-Fang Sui /  Abstract: Ammonia monooxygenase (AMO) oxidizes ammonia to hydroxylamine. Limited knowledge of the structural information of AMO hinders our understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying ammonia ...Ammonia monooxygenase (AMO) oxidizes ammonia to hydroxylamine. Limited knowledge of the structural information of AMO hinders our understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying ammonia oxidation, impacting the mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing agricultural productivity using ammonium as a nitrogen source. Herein, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the AMO complex from an isolated strain of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB). AMO is a cylinder-shaped homotrimeric assembly composed of five subunits. A single-transmembrane protein and a soluble protein are potentially crucial in signal transduction during ammonia oxidation and mediating interactions with the outer membrane protein assembly machinery. Three modeled coppers, along with an adjacent water-mediated hydrogen-bond network, may facilitate an efficient proton transfer pathway from the periplasmic Cu to the active site Cu within the inner membrane, where Cu and Cu will act in concert to catalyze substrate reaction. The distinctive surface charge characteristics of AMO provide valuable insights into the structural features that govern ammonium assimilation and material transport during ammonia oxidation. These findings shed light on the molecular complexities of AMO and provides a structural foundation for elucidating the catalytic mechanism of ammonia oxidation. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9leg.cif.gz 9leg.cif.gz | 700.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9leg.ent.gz pdb9leg.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9leg.json.gz 9leg.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/le/9leg https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/le/9leg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/le/9leg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/le/9leg | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  63025MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Ammonia monooxygenase subunit ... , 3 types, 9 molecules ALUBMVCNW
| #1: Protein | Mass: 31736.248 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_11133 / Production host: Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_11133 / Production host:  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3PUN8 Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3PUN8#2: Protein | Mass: 46935.816 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_11134 / Production host: Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_11134 / Production host:  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3PUR7 Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3PUR7#3: Protein | Mass: 31698.678 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_11132 / Production host: Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_11132 / Production host:  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3PUB4 Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3PUB4 |
|---|
-Protein / Protein/peptide , 2 types, 6 molecules DOXEPY
| #4: Protein | Mass: 7051.081 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_103624 / Production host: Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_103624 / Production host:  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3JYQ0 Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3JYQ0#5: Protein/peptide | Mass: 5046.772 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_104318 / Production host: Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / Gene: SAMN05421881_104318 / Production host:  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3KVX9 Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1H3KVX9 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 8 types, 642 molecules 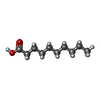
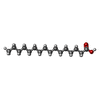









| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-A1EZJ / ( Mass: 721.942 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C37H72NO10P / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION #7: Chemical | ChemComp-DKA / #8: Chemical | ChemComp-PLM / #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ZP7 / ( #10: Chemical | ChemComp-CU / #11: Chemical | ChemComp-A1EZI / [( Mass: 662.918 Da / Num. of mol.: 9 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C36H71O8P / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION #12: Chemical | #13: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Bacterial AMO complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#5 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) Nitrosomonas halophila (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F30 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.36 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 94482 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj