[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8u02: CryoEM structure of D2 dopamine receptor in complex with GoA KE m... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8u02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure of D2 dopamine receptor in complex with GoA KE mutant and dopamine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / GPCR / Dopamine / DRD2 / Dominant Negative | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / negative regulation of dephosphorylation / positive regulation of glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor production / acid secretion / dopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity, coupled via Gi/Go / nervous system process involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure / response to histamine / negative regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep / regulation of synapse structural plasticity ...negative regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / negative regulation of dephosphorylation / positive regulation of glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor production / acid secretion / dopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity, coupled via Gi/Go / nervous system process involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure / response to histamine / negative regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep / regulation of synapse structural plasticity / regulation of locomotion involved in locomotory behavior / neuron-neuron synaptic transmission / adenohypophysis development / negative regulation of dopamine secretion / negative regulation of cellular response to hypoxia / hyaloid vascular plexus regression / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting dopamine receptor signaling pathway / cerebral cortex GABAergic interneuron migration / positive regulation of renal sodium excretion / response to inactivity / orbitofrontal cortex development / regulation of potassium ion transport / Dopamine receptors / negative regulation of neuron migration / dopamine binding / branching morphogenesis of a nerve / regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / positive regulation of growth hormone secretion / phospholipase C-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / peristalsis / heterotrimeric G-protein binding / drinking behavior / G protein-coupled receptor complex / grooming behavior / behavioral response to ethanol / auditory behavior / striatum development / positive regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / dopaminergic synapse / mu-type opioid receptor binding / positive regulation of urine volume / corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 binding / positive regulation of multicellular organism growth / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / non-motile cilium / heterocyclic compound binding / negative regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / response to iron ion / vesicle docking involved in exocytosis / adult walking behavior / arachidonate secretion / ciliary membrane / response to morphine / G protein-coupled dopamine receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / temperature homeostasis / positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation / regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / positive regulation of cytokinesis / regulation of heart contraction / pigmentation / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse / dopamine metabolic process / dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / regulation of dopamine secretion / response to light stimulus / cellular response to ethanol / positive regulation of receptor internalization / associative learning / lateral plasma membrane / neuroblast proliferation / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / endocytic vesicle / negative regulation of protein secretion / potassium channel regulator activity / long-term memory / prepulse inhibition / response to axon injury / sperm flagellum / postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / synapse assembly / negative regulation of blood pressure / regulation of sodium ion transport / behavioral response to cocaine / cellular response to retinoic acid / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / axon terminus / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / G protein-coupled serotonin receptor binding / adenylate cyclase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting serotonin receptor signaling pathway / presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / acrosomal vesicle / axonogenesis / negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / regulation of heart rate / negative regulation of innate immune response / negative regulation of cell migration / muscle contraction / response to amphetamine Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.28 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Krumm, B.E. / Kapolka, N.J. / Fay, J.F. / Roth, B.L. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: A neurodevelopmental disorder mutation locks G proteins in the transitory pre-activated state. Authors: Kevin M Knight / Brian E Krumm / Nicholas J Kapolka / W Grant Ludlam / Meng Cui / Sepehr Mani / Iya Prytkova / Elizabeth G Obarow / Tyler J Lefevre / Wenyuan Wei / Ning Ma / Xi-Ping Huang / ...Authors: Kevin M Knight / Brian E Krumm / Nicholas J Kapolka / W Grant Ludlam / Meng Cui / Sepehr Mani / Iya Prytkova / Elizabeth G Obarow / Tyler J Lefevre / Wenyuan Wei / Ning Ma / Xi-Ping Huang / Jonathan F Fay / Nagarajan Vaidehi / Alan V Smrcka / Paul A Slesinger / Diomedes E Logothetis / Kirill A Martemyanov / Bryan L Roth / Henrik G Dohlman /  Abstract: Many neurotransmitter receptors activate G proteins through exchange of GDP for GTP. The intermediate nucleotide-free state has eluded characterization, due largely to its inherent instability. Here ...Many neurotransmitter receptors activate G proteins through exchange of GDP for GTP. The intermediate nucleotide-free state has eluded characterization, due largely to its inherent instability. Here we characterize a G protein variant associated with a rare neurological disorder in humans. Gα has a charge reversal that clashes with the phosphate groups of GDP and GTP. As anticipated, the purified protein binds poorly to guanine nucleotides yet retains wild-type affinity for G protein βγ subunits. In cells with physiological concentrations of nucleotide, Gα forms a stable complex with receptors and Gβγ, impeding effector activation. Further, we demonstrate that the mutant can be easily purified in complex with dopamine-bound D2 receptors, and use cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure, including both domains of Gα, without nucleotide or stabilizing nanobodies. These findings reveal the molecular basis for the first committed step of G protein activation, establish a mechanistic basis for a neurological disorder, provide a simplified strategy to determine receptor-G protein structures, and a method to detect high affinity agonist binding in cells. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8u02.cif.gz 8u02.cif.gz | 210.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8u02.ent.gz pdb8u02.ent.gz | 161 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8u02.json.gz 8u02.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u0/8u02 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u0/8u02 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u0/8u02 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u0/8u02 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41776MC 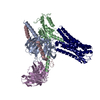 8tzqC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 50685.355 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DRD2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DRD2 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 40100.434 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNAO1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNAO1 / Production host:  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 39418.086 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host:  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 7861.143 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host:  |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-LDP / |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human DRD2 in complex with heterotrimeric G protein GoA (K46E) and dopamine Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.12 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 3.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.28 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 153270 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj























