[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8sxf: The C-terminal protease CtpA-LbcA complex of pseudomonas aerugino... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8sxf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The C-terminal protease CtpA-LbcA complex of pseudomonas aeruginosa with the TPR at the high position | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / CtpA / LbcA / C-terminal protease / Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcell envelope organization / cell wall biogenesis / protein secretion by the type III secretion system / cell envelope / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / endopeptidase activity / periplasmic space / serine-type endopeptidase activity / signal transduction / proteolysis / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.92 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Hsu, H.-C. / Li, H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2024 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2024Title: P. aeruginosa CtpA protease adopts a novel activation mechanism to initiate the proteolytic process. Authors: Hao-Chi Hsu / Michelle Wang / Amanda Kovach / Andrew J Darwin / Huilin Li /  Abstract: During bacterial cell growth, hydrolases cleave peptide cross-links between strands of the peptidoglycan sacculus to allow new strand insertion. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa carboxyl-terminal ...During bacterial cell growth, hydrolases cleave peptide cross-links between strands of the peptidoglycan sacculus to allow new strand insertion. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa carboxyl-terminal processing protease (CTP) CtpA regulates some of these hydrolases by degrading them. CtpA assembles as an inactive hexamer composed of a trimer-of-dimers, but its lipoprotein binding partner LbcA activates CtpA by an unknown mechanism. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of the CtpA-LbcA complex. LbcA has an N-terminal adaptor domain that binds to CtpA, and a C-terminal superhelical tetratricopeptide repeat domain. One LbcA molecule attaches to each of the three vertices of a CtpA hexamer. LbcA triggers relocation of the CtpA PDZ domain, remodeling of the substrate binding pocket, and realignment of the catalytic residues. Surprisingly, only one CtpA molecule in a CtpA dimer is activated upon LbcA binding. Also, a long loop from one CtpA dimer inserts into a neighboring dimer to facilitate the proteolytic activity. This work has revealed an activation mechanism for a bacterial CTP that is strikingly different from other CTPs that have been characterized structurally. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8sxf.cif.gz 8sxf.cif.gz | 262.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8sxf.ent.gz pdb8sxf.ent.gz | 206.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8sxf.json.gz 8sxf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sx/8sxf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sx/8sxf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sx/8sxf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sx/8sxf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  40850MC  8sxeC  8sxgC  8sxhC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 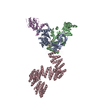
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42920.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | | Mass: 61742.066 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Protein/peptide | | Mass: 528.644 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: conforamtion A of CtpA-LbcA complex of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.42 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.8 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 279 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1300 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.5 sec. / Electron dose: 66 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 26257 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 11520 / Height: 8184 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2090314 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.92 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 623456 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 2 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 135.5 / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj




