+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8r3y | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
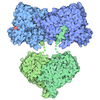
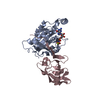
| Title | Cryo EM structure of a stable LGL/aPKC Iota/Par-6 complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN / Kinase / Polarity / Kinase substrate complex. | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationGolgi cis cisterna / regulation of cellular localization / establishment of spindle orientation / diacylglycerol-dependent, calcium-independent serine/threonine kinase activity / Golgi vesicle budding / PAR polarity complex / Tight junction interactions / regulation of establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cell-cell junction maintenance / protein kinase C ...Golgi cis cisterna / regulation of cellular localization / establishment of spindle orientation / diacylglycerol-dependent, calcium-independent serine/threonine kinase activity / Golgi vesicle budding / PAR polarity complex / Tight junction interactions / regulation of establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cell-cell junction maintenance / protein kinase C / establishment of apical/basal cell polarity / diacylglycerol-dependent serine/threonine kinase activity / myosin II binding / regulation of Notch signaling pathway / negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process / eye photoreceptor cell development / positive regulation of protein localization to centrosome / Schmidt-Lanterman incisure / GTP-dependent protein binding / establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity / Golgi to plasma membrane transport / membrane organization / cellular response to chemical stress / cell-cell junction organization / cortical actin cytoskeleton organization / centrosome cycle / protein targeting to membrane / tight junction / RHOV GTPase cycle / cortical actin cytoskeleton / positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway / establishment of cell polarity / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / exocytosis / cell leading edge / RHOU GTPase cycle / brush border / CDC42 GTPase cycle / viral process / positive regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of glial cell proliferation / bicellular tight junction / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / intercellular bridge / vesicle-mediated transport / ruffle / RAC1 GTPase cycle / cytoskeleton organization / secretion / axonogenesis / response to interleukin-1 / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / GTPase activator activity / actin filament organization / trans-Golgi network membrane / positive regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / protein localization to plasma membrane / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / adherens junction / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / positive regulation of neuron projection development / : / phospholipid binding / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / small GTPase binding / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / centriolar satellite / cellular response to insulin stimulus / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / cell migration / microtubule cytoskeleton / protein-containing complex assembly / early endosome membrane / cell cortex / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / cytoskeleton / protein phosphorylation / protein kinase activity / endosome / intracellular signal transduction / cilium / apical plasma membrane / Golgi membrane / axon / cell division / protein serine kinase activity / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / centrosome / protein kinase binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / glutamatergic synapse / structural molecule activity / extracellular exosome / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.68 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Earl, C.P. / Briggs, D.C. / McDonald, N.Q. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3items United Kingdom, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Capture, mutual inhibition and release mechanism for aPKC-Par6 and its multisite polarity substrate Lgl. Authors: Christopher P Earl / Mathias Cobbaut / André Barros-Carvalho / Marina E Ivanova / David C Briggs / Eurico Morais-de-Sá / Peter J Parker / Neil Q McDonald /   Abstract: The mutually antagonistic relationship of atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) and partitioning-defective protein 6 (Par6) with the substrate lethal (2) giant larvae (Lgl) is essential for regulating ...The mutually antagonistic relationship of atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) and partitioning-defective protein 6 (Par6) with the substrate lethal (2) giant larvae (Lgl) is essential for regulating polarity across many cell types. Although aPKC-Par6 phosphorylates Lgl at three serine sites to exclude it from the apical domain, aPKC-Par6 and Lgl paradoxically form a stable kinase-substrate complex, with conflicting roles proposed for Par6. We report the structure of human aPKCι-Par6α bound to full-length Llgl1, captured through an aPKCι docking site and a Par6 contact. This complex traps a phospho-S663 Llgl1 intermediate bridging between aPKC and Par6, impeding phosphorylation progression. Thus, aPKCι is effectively inhibited by Llgl1 while Llgl1 is captured by aPKCι-Par6. Mutational disruption of the Lgl-aPKC interaction impedes complex assembly and Lgl phosphorylation, whereas disrupting the Lgl-Par6 contact promotes complex dissociation and Lgl phosphorylation. We demonstrate a Par6-regulated substrate capture-and-release model requiring binding by active Cdc42 and the apical partner Crumbs to drive complex disassembly. Our results suggest a mechanism for mutual regulation and spatial control of aPKC-Par6 and Lgl activities. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8r3y.cif.gz 8r3y.cif.gz | 453.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8r3y.ent.gz pdb8r3y.ent.gz | 364.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8r3y.json.gz 8r3y.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r3/8r3y https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r3/8r3y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r3/8r3y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r3/8r3y | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  18877MC  8r3xC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 39146.004 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PRKCI, DXS1179E / Cell line (production host): HEK293 FreeStyle / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PRKCI, DXS1179E / Cell line (production host): HEK293 FreeStyle / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P41743, protein kinase C Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P41743, protein kinase C |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 101889.805 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LLGL1, DLG4, HUGL, HUGL1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293 Freestyle / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LLGL1, DLG4, HUGL, HUGL1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293 Freestyle / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15334 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15334 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 10856.517 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PARD6A, PAR6A / Cell line (production host): HEK293 Freestyle / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PARD6A, PAR6A / Cell line (production host): HEK293 Freestyle / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NPB6 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NPB6 |
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ANP / |
| Has ligand of interest | N |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: aPKCiota-Par6-Llgl1 complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.22 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293 Freestyle Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293 Freestyle | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Sample was double affinity purified and gel filtered. Sample was monodisperse. | ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 45mA / Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K Details: 4 ul of aPKCiota-Par6-Llgl1 complex at a concentration of 0.4 mg/ml was applied to R1.2/1.3 Quantifoil 300 mesh copper grids which had been glow-discharged for 45 s at 45 mA . Grids were ...Details: 4 ul of aPKCiota-Par6-Llgl1 complex at a concentration of 0.4 mg/ml was applied to R1.2/1.3 Quantifoil 300 mesh copper grids which had been glow-discharged for 45 s at 45 mA . Grids were blotted for 2.5 s at 100% humidity using an FEI Vitrobot MK IV. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 8 sec. / Electron dose: 48.1 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 4002 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum ER |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1069057 Details: Semi-automated picking with Xmipp3 and particle extraction in Relion-3 yielded 47,516 particles from 1000 micrographs 38. After reference-free 2D classification in Relion-3, eight 2D classes ...Details: Semi-automated picking with Xmipp3 and particle extraction in Relion-3 yielded 47,516 particles from 1000 micrographs 38. After reference-free 2D classification in Relion-3, eight 2D classes were selected and used as templates for reference-based particle picking in Gautomatch. A total of particles were extracted with 2-fold binning and submitted to 8 rounds of 2D classification in Relion-3. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.68 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 121194 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL Details: Initial fitting was done in Chimera. Interactive Model building was done in COOT & Isolde Refinement was done using Phenix. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj